Showing posts from category development.
-
IRP Editors Cover Rwanda’s Population, Health, and Environment Challenges
›The original version of this article appeared on the International Reporting Project website.
The International Reporting Project (IRP) and 12 senior editors and producers from across the United States traveled to Rwanda this year to learn about issues affecting Rwanda and other countries in Africa and to help them improve their news organizations’ international coverage. Some of the editors focused on Rwanda’s extensive population, health, and environmental challenges:
Nicholas Aster, founder and publisher of San Francisco’s Triple Pundit, covered sustainable development in Kigali, coffee’s empowerment potential, and eco-tourism sites like Volcanoes National Park. Aster also became interested in Rwanda’s efforts to avert disaster by corralling Lake Kivu’s CO2 reserves into a power supply. At the close of his trip, Aster reflected on Rwanda’s sustainability goals in a photo essay.
Tom Paulson, host and reporter for KPLU’s Humanosphere, discovered the positive side of aid and development in Rwanda, including girls’ education initiatives and coffee farming improvements. Moreoever, Paulson documented the Gatekeepers’ trip to Volcanoes National Park, including a visit from a mountain gorilla who became a little too friendly. Paulson has also posted several questions the Gatekeepers asked President Paul Kagame when they met with him, including his policies on restricting free speech, curbing population growth, and preventing another genocide. At the close of the trip, Paulson composed a photo slideshow that shows a growing, vibrant Rwanda, and he also outlined 10 reasons why the complex and sometimes contradictory country can’t be described in a sound-bite.
Sue Horton, op-ed and Sunday Opinion editor of the Los Angeles Times, began chronicling her trip with a survey of Rwanda’s history on genocide, governance, and gorillas. On the road to meet Rwanda’s famed gorillas, Horton noted Rwanda’s strengths and challenges: its ambitious vision for the future encourages a growth in infrastructure and the country has showed impressive gains in healthcare provision and access, but Kigali is relocating residents who don’t fit the image.
The deputy managing editor of Global Post, Andrew Meldrum, also found a note of optimism in witnessing how far Rwanda has come since the genocide, particularly after hearing the testimonies of the genocide’s youngest victims: children born of sexual violence during the genocide. And his Global Post colleague Jon Rosen delves into the country’s population growth and the government’s approach to family planning.
In addition to the Gatekeeper Editor Trips, the IRP offers individual Fellowships to U.S. reporters to travel overseas on five-week reporting trips. In 2009, IRP Fellow Perry Beeman discovered a Rwanda similar to that which the Gatekeepers encountered: a country that has made much progress, but still has many challenges ahead. Beeman, who also was a public policy scholar at the Woodrow Wilson Center, created a multimedia series, “Renewal in Rwanda”, for The Des Moines Register; his reporting garnered him an Overseas Press Club citation for Best Reporting in 2010.
Rwandans, Beeman found, are dedicated to conservation. President Kagame is committed to the environment and is driven to develop clean, sustainable power and to convert from subsistence agriculture to a stronger, more diversified economy. But everyone has a hand in this effort, including schoolchildren who report on conservation in song, dance, and dramatic arts. Beeman also examined efforts to preserve the Gishwati Forest, including gorilla and chimpanzee preservation efforts from villagers to businessmen to researchers. Beeman emphasized the importance of immersing oneself in an environment in order to report on it, and he did so by, among other things, tracking wild chimpanzees in the forest.
For more information about IRP’s Fellowships and Gatekeeper Editor trips, visit their website at InternationalReportingProject.org.
Photo Credit: “The Broadsheet in Kyovu, Kigali,” courtesy of flickr user noodlepie (Graham Holliday). -
Ambassador Melanne Verveer, U.S. Department of State
Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues on Durban and the Role of Women in Combating Climate Change
›December 23, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Ambassador Melanne Verveer, appeared on the White House Council on Environmental Quality blog.
Last week I traveled to Durban, South Africa to participate in the Conference of the Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change to highlight the critical and largely untapped potential of women to combat climate change. Studies have shown that it is often women who are on the frontlines of, and suffer disproportionately from, the impacts of climate change. This is certainly important. But we must remember that women are also a powerful force for finding solutions to climate change across the board, including in areas such as agriculture, sustainable forest management, and energy access.
Agriculture, which accounts for approximately 14 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions and is a sector that can be particularly sensitive to climate variability and change, is one key area where women can play a major role. A recent FAO report shows that women, in many places, are the main producers of the world’s staple crops, particularly in developing countries and regions likely to be adversely affected by climate change impacts. However, globally, only a small minority of women farmers have access to land tenure. This is a problem for many reasons – including that it limits women’s potential to combat climate change. Studies have shown that women with the right to property are significantly more capable of investing in climate-smart agricultural productivity; we have a lot of work to do to unlock women’s potential in this area.
Women also have untapped potential for increasing energy access, which directly relates to climate change. For example, nearly three billion people globally still rely on traditional cookstoves and open fires to prepare food for their families. In most instances, women are responsible for cooking – not to mention also spending many hours per week collecting fuel, which often puts women at risk of gender based violence. The resulting smoke exposure causes an estimated two million premature deaths annually, with women and young children the most affected. Cookstoves also impact the climate through emissions of greenhouse gases and short-lived particles such as black carbon. Engaging women is critical to tackling this problem. As we work to build a global market for clean cookstoves, integrating women into the cookstoves supply chain will help increase clean cookstove adoption rates while also creating new economic development opportunities. And as Secretary Clinton has noted, women create a multiplier effect in local communities because they disproportionately spend more of their earned income on food, healthcare, home improvement, and schooling.
The United States recognizes the power of women’s potential in these areas and many others, and is investing in major initiatives including Feed the Future and the Global Alliance for Clean Cookstoves, where women’s role in generating transformative change is front and center.
I went to Durban to highlight the critical role of women in combating climate change. While there, I worked with U.S. negotiators on the Durban texts and participated in public engagement events. Our efforts to build on the gender equality and women’s empowerment language in the Cancun agreements are reflected in several crucial institutional developments, including language on gender balance related to the composition of the board of the new Green Climate Fund, the Standing Committee, and the Adaptation Committee. We also worked to reflect gender considerations in the mission of the Climate Technology Center and Network. USAID Assistant Administrator Eric Postel and I solicited input during a meeting with leading non-governmental organizations working on gender and climate issues, and I hosted a high-level side event at the U.S. Center focused on unlocking women’s potential to combat climate change. The level of enthusiasm among my fellow panelists and the audience at the event was inspirational.
We made progress in Durban, but we can’t stop here. To achieve the future we all seek, we must do more. As the late Wangari Maathai, founder of the Green Belt Movement and ground-breaking advocate on women and the environment said, “We must not tire, we must not give up, we must persist.” The future of not only women, but our planet, depends on it.
Ambassador Melanne Verveer is U.S. Ambassador-at-Large for Global Women’s Issues.
Sources: Food and Agriculture Organization, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, The White House.
Photo Credit: “Melanne S. Verveer,” courtesy of the U.S. Embassy, Kabul. -
In Somalia, Beyond the Immediate Crises, Demography Reveals a Long-Term Challenge
›December 21, 2011 // By Elizabeth Leahy MadsenIn the nearly 20 years since the infamous intervention that resulted in the deaths of dozens of American and UN peacekeeping soldiers on the streets of Mogadishu, Somalia has become the epitome of a “failed state.” Neighboring countries, global bodies, and aid agencies are rushing to respond to the country’s rapidly evolving political, security and humanitarian crises.
Diplomatic attention has focused on decentralized, weak governance that is divided among the Al Shabab insurgency, clan warlords, and a hamstrung and largely ineffective Transitional Federal Government, whose control does not extend beyond the capital. Foreign militaries have had to devote naval resources to curtailing daring and far-reaching acts of piracy against civilian and military vessels from networks based in Somalia. Aid groups have been stymied in their efforts to stem famine as access to populations in the hardest-hit areas has been cut off by Al Shabab and food aid has been stolen. Most recently, Kenyan and, reportedly, Ethiopian forces have crossed the border, extending the reach of the country’s political crisis. Hundreds of thousands of have fled conditions of hunger, illness, and violence into neighboring countries.
Perhaps the deepest woe of a “failed state” is that its problems are deep-seated and cannot be solved during the brief span of a UN meeting or the news cycle following the latest terrorist attack. Amid the extraordinary efforts to battle the country’s crises, one of the most important underlying structural factors is often overlooked: the country’s unusual demographic picture.
A Demographic Outlier
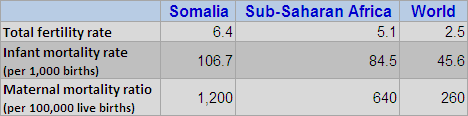
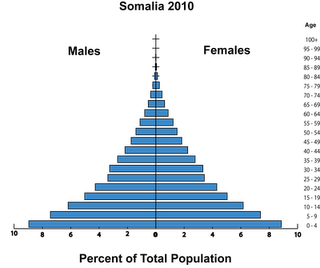
Somalia is a global outlier in demographic terms, with rates of fertility (6.4 children per woman), infant mortality (107 deaths per 1,000 births), and maternal mortality (1,200 deaths per 100,000 live births) all above the already-high averages for sub-Saharan Africa. These demographic indicators are both a reflection of the abysmal state of health care in the country and a warning that its economic and security challenges are unlikely to be easily resolved.Research shows that where at least 60 percent of the population is younger than 30 years old, countries are more prone to outbreaks of civil conflict, and the risk increases as the proportional size of the “youth bulge” grows. In Somalia, 70 percent of the population is younger than 30, a level comparable to Iraq and the Palestinian Territories. With little to no improvements in health care, Somalia’s age structure has remained unchanged over the past 40 years. Unlike dozens of other countries where fertility has declined significantly in recent decades, Somali women have nearly as many children on average today as they did in the 1970s. The current total fertility rate of 6.4 children per woman is only a 12 percent decline from the 1970 rate.
Despite high infant mortality – more than 10 percent of children die before turning one – this sustained high fertility rate has generated rapid population growth, with each successive generation larger than the next. Somalia’s population has almost tripled since 1970, from 3.6 to 9.3 million, although population density remains low (one-third the world average). If the fertility rate remains constant at the current level – not an unreasonable projection considering how stagnant it has been over past decades – Somalia would be home to 33 million people by 2050. Even if the fertility rate drops to near four children per woman, as projected in the UN’s medium variant, the population would still triple to 28 million by mid-century given the demographic momentum of decades of high fertility.
The fertility decline built into the UN’s medium variant projection – which would still place Somalia among the highest total fertility rates in the world by 2050 – is unlikely without steady and major improvements in the country’s health system, particularly women’s health. But with decades of conflict, weak governance and little investment, the environment for reproductive health services is dire.
A recent World Health Organization assessment described “unacceptable levels of unmet need, extreme inequities in access…slow progress…[and] underinvestment and poorly coordinated actions.” Pregnancy and childbirth are major risks to women’s well-being. Somali women have a one in 14 chance of dying from maternal causes over their lifetimes, the second-highest risk in the world. Funding to improve reproductive and maternal health care remains too low to meet demand. The United Nations Population Fund reports that donors spent about $6 million on population and reproductive health programs in 2008, about one-third as much as was spent in Benin and Burundi, which have smaller populations.
The Future for Youth
Instability and violence have become entrenched in Somalia; according to the Armed Conflict Dataset, civil conflict occurred in 12 of the past 20 years. The direct causes of the conflict are typically recorded as struggles for power and resources among competing clans. But in considering the underlying causes of conflict, demographic security scholars have suggested that very young age structures such as Somalia’s can create both motive and opportunity for recruitment into a violent uprising. As ever-growing numbers of young people face adulthood with few prospects for employment, hopelessness or desperation can make them vulnerable to the promise of well-being and identity offered by a political faction or rebel group.
There are 1.7 million people between the ages of 15 and 24 in Somalia today, with another 2.5 million following in the next ten-year age cohort. With opportunities for education, jobs, and equitable participation in society, these youth would represent a promising future for their country. Unfortunately, such opportunities are not afforded to most of them. A United Nations survey found that the secondary school enrollment rate is just six percent, with poverty and early marriage keeping many young people out of school. World Bank data from 2002 show that two-thirds of urban working-age adults and 41 percent of those in rural areas were unemployed. Nearly half of the population lives on less than $1 per day.
Youth Education, Economic Opportunities Could Increase Stability
While global attention centers on the government’s commitment to a new roadmap for peace and the efforts of the African Union’s peacekeeping forces to drive Al Shabab out of Mogadishu, development agencies have recognized demographic security as an important component of Somalia’s future.
The United Nations Children’s Fund is supporting schools for displaced children in Mogadishu, saying in a press release that “providing them with learning opportunities in a safe environment is critical for the country’s long-term stability and growth.”
The U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID) has announced plans for a new program called the Somali Youth Leaders Initiative, which aims to improve young people’s access to secondary education and economic opportunities and to increase their civic participation. In designing the program, USAID noted “the recruitment of boys and men by extremist organizations and piracy networks” and “the common perception that an increasing youth population is a potentially destabilizing force.”
As the October 4 bombing at the Education Ministry in Mogadishu showed, young people are often the victims of the country’s instability. Programs such as those of UNICEF and USAID that empower young people to capitalize on their potential should be a greater focus among initiatives to address Somalia’s long-term future as well as its immediate crises.
Elizabeth Leahy Madsen is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and former senior research associate at Population Action International.
Sources: BBC, Population Action International, The New York Times, UCDP/PRIO, UNICEF, UNESCO, UN Population Division, UN Population Fund, Urdal (2006), USAID, World Bank, World Health Organization.
Image Credit: “Somalia Suffers from Worst Drought in Century,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo/Stuart Price; charts arranged by Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, data from the UN Population Division and World Health Organization. -
Watch: Dr. Vik Mohan on Integrating Family Planning and Conservation in Madagascar
›The integration of population, health, and environment programming “enables us to create synergies that mean we are more effective at achieving both health and conservation goals,” said Dr. Vik Mohan, director of sexual and reproductive health programming for Blue Ventures, in an interview with ECSP at the 2011 International Conference on Family Planning.
After Blue Ventures established their first clinic in 2007 in the village of Andavadoaka, on Madagascar’s southwest coast, “we felt immense pressure to scale up our intervention,” said Mohan. “We started with one clinic in one village, and now we have a multi-site service covering all 40 villages that we partner with for our community-based conservation work,” he said.
According to data compiled by Blue Ventures, the average total fertility rate in the region is 6.7 children per woman. The London-based eco-tourism-turned health and environment NGO offers a variety of family planning services to meet local demand, including mobile outreach clinics and community-based distribution of contraceptives. They also partner with Marie Stopes International to offer long-acting and permanent methods of contraception for those that want it.
“This Model Can Be Taken to Scale”
By integrating conservation and reproductive health messaging and service delivery, “we are getting greater buy-in from the community because they all see the added value of the breadth of things that we offer them,” Mohan said. “Men who came to hear about fisheries management get to hear about family planning technologies, practically for the first time in their lives.”
The fishermen are able to see the links between food security and population growth through their own experience, he added. “We believe very passionately this model can be taken to scale,” Mohan said. “This is something that could be easily replicated in other regions. Definitely in other coastal regions, but almost certainly in other remote areas – perhaps areas of high biodiversity where there are existing projects, perhaps conservation projects – but where there is an unmet need for healthcare and family planning in particular.”
“My advice to other organizations, whether you are doing healthcare or whether you are doing conservation, is just think holistically,” said Mohan. “If you are a conservation organization that recognizes that there is an unmet healthcare need for the communities that you work with, then…don’t be afraid to ask those questions, and don’t be afraid to build capacity to meet the need, if you find one. Or, don’t be afraid to partner with health NGOs to enable that need to be met.”
For more on Blue Ventures’ integrated efforts, see also ECSP FOCUS Issue 23, “To Live With the Sea: Reproductive Health Care and Marine Conservation in Madagascar,” co-authored by Vik Mohan. -
Can “Climate-Smart Agriculture” Help Feed Africa’s Growing Population?
›December 13, 2011 // By Brenda ZuluFood production needs to increase 70 percent by 2050 to meet the demands of a growing world population, said former UN Secretary-General Kofi Annan in a keynote address on “climate-smart agriculture” at a COP-17 event hosted by the World Bank and African Union. Annan, who is now chairman of the Alliance for a Green Revolution in Africa (AGRA), said this was a particular concern in Africa, where four out of five citizens are dependent on agriculture for their livelihoods.
One in seven people in the world do not have enough food to eat, Annan said, and climate change is expected to make this challenge more difficult to overcome. Climate-smart agriculture includes a wide variety of techniques that help increase the resilience of communities and protect them from extreme weather events, such as terracing to prevent soil erosion, improving weather forecasting, managing water runoff, and developing irrigation systems.
“Climate change affects us by undermining our resource base through water and soil degradation,” said Prime Minister of Ethiopia Meles Zenawi at the event. “There is need to protect the resources and to rehabilitate green areas of our land.” He said that since 70 percent of Africans are small-scale farmers and that most of the poor in Africa were farmers, there is no better way to fight poverty on the continent than through agriculture.
South African President Jacob Zuma said at the event that given that the UN projects a population of more than nine billion people in the world by 2050, agriculture should be a priority as it is more vulnerable to climate change than any other sector.
“Climate-smart agriculture includes proven practical techniques such as mulching, intercropping, conservation agriculture, integrated crop management and agro forestry, improved grazing, and innovative better weather management,” he said, all of which have the potential to help increase crop yields.
Mary Robinson, chair of the Global Leaders Council for Reproductive Health, said there could be no smart agriculture without integrating women’s issues, because climate change affects women disproportionately. “Women make the connection between climate-smart agriculture, food security, and gender,” she said.
“Our ability to feed the growing population under climate variability and change will require new expertise and harmonized efforts,” said Robinson.
Annan agreed, saying African women should be fully involved in early action that can support technical assistance, such as screening agriculture plans to ensure they are “climate smart” as well as integrating climate resilience and mitigation into ongoing poverty-reduction programs and testing new approaches.
But according to Brylyne Chitsunge, a farmer from Pretoria speaking on the panel, things will need to change considerably from the status quo. “The small-scale farmer remains very much marginalized in institutions,” she said. “They exist on paper but they really don’t exist.”
Brenda Zulu is a member of Women’s Edition for Population Reference Bureau and a freelance writer based in Zambia. Her reporting from the COP-17 meeting in Durban (see the “From Durban” series on New Security Beat) is part of a joint effort by the Aspen Institute, Population Action International, and the Wilson Center.
Sources: World Bank, World Food Programme.
Photo Credit: “Cultivated hillsides,” courtesy of flickr user coda (Damien du Toit). -
Michael Kugelman, Ahmad Rafay Alam, and Gitanjali Bakshi for Foreign Policy
Why South Asia Needs a Kabul Water Treaty
›December 12, 2011 // By Wilson Center Staff
Pakistan is once again accusing India of water hegemony. This time, however, the accusation refers not to Indian damming of the Western Rivers in the disputed regions of Jammu and Kashmir, but to Indian support for Afghan development projects along the Kabul River. This accusation indulges in conspiratorial thinking, and distracts from a factual understanding of the water issues between the two countries.
-
The Legacy of Little America: Aid and Reconstruction in Afghanistan
›In 2007, the United States built a $305 million diesel power plant in Afghanistan – the world’s most expensive power plant of its kind. Yet the facility is rarely used, because the impoverished country cannot afford to operate it.
This ill-fated power plant does not represent the only time America has lavished tremendous amounts of money on development projects in Afghanistan that have failed to meet objectives. At a December 7 presentation organized by the Wilson Center’s Asia Program and co-sponsored with the Middle East Program and International Security Studies, Rajiv Chandrasekaran discussed Washington’s expensive attempts to modernize southern Afghanistan’s Helmand River Valley from the 1940s to 1970s – and the troubling implications for U.S. development projects in that country today.
From Morrison Knudsen to USAID
According to Chandrasekaran, a Wilson Center Public Policy Scholar and Washington Post journalist, the story begins after World War II, when Afghanistan’s development-minded king, Zahir Shah, vowed to modernize his country. He hired Morrison Knudsen – an American firm that had built the Hoover Dam and the San Francisco Bay Bridge – to construct irrigation canals and a large dam on the Helmand River. Shah’s view was that by making use of the Hindu Kush’s great waters, prosperity would emerge and turn a dry valley into fertile ground.
Unfortunately, problems arose from the start. The region’s soil was not only shallow, but also situated on a thick layer of subsoil that prevented sufficient drainage. When the soil was irrigated, water pooled at the surface and salt accumulated heavily. Yet despite these challenges, King Shah was determined to continue the massive enterprise. And so, increasingly, was the U.S. government – particularly when Washington began to fear that if it did not support this project, the Soviets would.
In 1949, the United States provided the first installment of what would amount to more than $80 million over a 15-year period. With this aid in hand, Morrison Knudsen not only completed the canals and dam but also constructed a new modern community. Americans called the town Lashkar Gah, but Afghans christened it “Little America.” It boasted a movie theater, a co-ed swimming pool, and a tennis court. Children listened to Elvis Presley records, drank lemonade, and learned English at Afghanistan’s only co-ed school.
However, problems continued to proliferate. Afghans in Lashkar Gah – many of whom had been lured away from their ancestral homelands on the promises of better harvests – did not experience greater farm yields. In the 1960s, the Afghans severed their contract with Morrison Knudsen, and began working directly with U.S. government agencies, including the new U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID). The result was some fairly productive farms, but, due in great part to waterlogging and soil salinity, the objective of transforming the region into Afghanistan’s breadbasket was not attained. U.S. funding slowed in the 1970s, and the grand experiment officially ended in 1978, when all Americans pulled out of Lashkar Gah following a coup staged by Afghanistan’s Communist Party.
“We Need To Find a Middle Ground”
What implications does all this have for U.S. reconstruction efforts in Afghanistan today? Chandrasekaran offered several lessons for American policymakers. One is “beware the suit-wearing modern Afghan” who claims to speak for his less-development-inclined countrymen. Another is to be aware that “there is only so much money that the land can absorb.” Finally, it is unrealistic to expect patterns of behavior to change quickly; he noted how Afghans in Lashkar Gah continued to flood their fields even when advised not to do so.
These lessons are not being heeded today, according to Chandrasekaran. He cited a USAID agricultural project, launched in late 2009, that allocated a whopping $300 million to just two provinces annually, with $30 million spent over only a few months. He said that while this effort may have generated some employment, the immense amounts of money at play fueled tensions among Afghans. Furthermore, contended Chandrasekaran, the program “focused too much on instant gratification and not on building an agricultural economy.”
In conclusion, Chandrasekaran insisted that foreign aid is essential in Afghanistan (and at the recently concluded Bonn Conference, Afghan President Hamid Karzai agreed, calling for financial assistance to continue until 2030). He described past aid efforts as either “starving the patient” or “pumping food into him.” We need to find a middle ground, he argued, and said that working on more modest projects with small Afghan nongovernment organizations is one possibility. The problem, he acknowledged, is that Washington is under pressure to spend ample quantities of money, and therefore depends on large implementing partners – no matter the unsatisfactory results.
Michael Kugelman is program associate with the Asia Program at the Wilson Center. -
Youth Need More Information on Climate, Population Links
›December 9, 2011 // By Brenda ZuluYouth need more information about climate change, but also on its links to reproductive health and gender, said Esther Agbarakwe, technical advisor for the Africa Youth Initiative on Climate Change. Speaking at the joint Aspen Institute, Population Action International, and Wilson Center side event, “Healthy Women, Healthy Planet,” at the COP-17 climate conference, Agbarakwe pointed out that “there are critical issues, like demography, the number of young people, and young women in this population, that should be discussed.” But, she said, they would likely not be brought up in any official manner at the conference because of fears about “population control.”
In Nigeria, young people, and particularly young girls, are frequently excluded from formal discussions about climate change and sustainable development. Growing up, Agbarakwe said she was aware of environmental change due to pollution in the Niger Delta, but her parents did not talk to her about reproductive health. In her community, many young girls had unplanned pregnancies and boys dropped out of school. It was only through a child rights activists’ club that she learned about how she could protect herself.
“That is why there is need to have young women in this discussion,” she said.
Giving a Voice to the Most Affected
Wendy Mnyandu, a student from Durban’s Zwelibanzi High School attending the side event, noted in an interview that climate changes have affected mothers more because they are dependent on the forest for energy.
“It is important for villagers to adapt to new technologies [such as] cook stoves, where they can use less fuelwood that will not take away the forest,” she said.
At the Wilson Center earlier this year, Agbarakwe explained how insufficient rain has led to longer trips to collect water, increasing women’s vulnerability. A friend of hers was raped while walking to the next village to fetch water after her own community’s well dried up – an ordeal that was not only emotionally and physically traumatizing, but also isolated her from her community and jeopardized her future plans and dreams.
“It is important for more men to talk about this topic,” said Roger-Mark De Souza, vice president of research at Population Action international, who also spoke at the side event. “I am talking on behalf of my mother, my daughters, my wife, and my granddaughters, for their voices are not often heard. I am a father of two young teenage boys and they know how to talk about this. By talking about it, we can see how family planning is very effective,” he said.
Talking About Population to Climate Experts, and Vice Versa
“Just last week I was in Dakar, Senegal, at the International Conference on Family Planning,” said De Souza. “I was talking to specialists and I was getting them interested in climate change.” Similarly, “more and more we find that climate change activists and specialists are appreciating that climate change is important to women and their wellbeing,” he said.
Population Action International (PAI) has mapped agricultural production, water stress, and increased vulnerability to climate change. “We see that there are 26 global hotspots where these issues are critical. What we have also done is look at these hotspots to determine where there is a very high unmet need for family planning,” said De Souza. PAI is using these maps to show the climate change community that a cost-effective investment in family planning could increase resilience in these areas.
De Souza said that in order to build support for programs that address these issues, it is important to look at national adaptation programs of action and their funding needs. “Funding is critical, and these types of interventions produce results – we need to understand where those missed opportunities are and tell that story to our policymakers and our delegations that are here in Durban and to keep with that message when we go back home,” he said.
Empowering Young African Women
Agbarakwe became interested in these issues after meeting former president of Ireland Mary Robinson, who also spoke at the side event. “I had met a Nigerian young man who challenged me that it was difficult for a woman to realize her career dreams because one day she will have to be married and bear children,” said Agbarakwe:When I saw my passion, I was confused and asked questions of Robinson on what she would do if she found herself at the crossroads like me. She told me as a young woman, I will find myself at a crossroad. That is why I am very determined about this issue, and that is what is needed, because when young women are empowered they actually can make decisions.
Robinson, the chair of the Global Leaders Council for Reproductive Health, said in an interview that she was heartened to see the number of youth at the side event. In Durban, she spoke with a group of young women who were part of Oxfam’s Project Empower:We met young women and several of them had come from the Eastern Cape [of South Africa]. They had come to Durban to look for work. Instead they found themselves in rural poverty. They had dreams of a better life for themselves, but their daily reality they talked to us about was nobody’s dream. They talked to us about negative impacts of their communities – the violence against women that is very prevalent, the unplanned pregnancies, and the reality of women who even have to use their bodies to gain money.
African women are looking for contraceptives, such as the female condom, where they can be in control, said Robinson; there are about 215 million women in the world who do not want to get pregnant but are not using modern contraception. “If we were to solve that problem, women [would not only] be better mothers, but also be better leaders in their communities,” she said.
The good thing was that they were ready to talk about the problems and did not consider themselves to be victims. They were strong women. They had learned to say ‘no’ and to say ‘respect me.’ They talked about going into some of the clinics and facing encounters with the police and that the police did not respect them. ‘We do not accept that anymore. We know now that we are members of the community who wish to be respected,’ they explained.
Brenda Zulu is a member of Women’s Edition for Population Reference Bureau and a freelance writer based in Zambia. Her reporting from the COP-17 meeting in Durban (see the “From Durban” series on New Security Beat) is part of a joint effort by the Aspen Institute, Population Action International, and the Wilson Center.
Sources: Population Action International, World Health Organization.
Photo Credit: “Viet Nam and Primary Education,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo; video courtesy of Population Action International.