-
Emily Puckart, MHTF blog
Maternal Health in Kenya: New Research Unnecessary, Time to Address Existing Gaps
›The original version of this article, by Emily Puckart, appeared on the Maternal Health Task Force blog.
During the recent Wilson Center/African Population and Health Research Center meeting in Nairobi on improving health systems through a maternal health framework, participants focused on knowledge gaps in the Kenyan health system that can negatively affect maternal healthcare. This focus on gaps sparked discussion around research needed (or not needed) in the maternal health field, supply gaps, and gaps between addressing technical, medical issues of maternal health (like preeclampsia or postpartum hemorrhage), and larger society-wide gaps like gender equity. The gaps highlighted by participants at the Nairobi dialogue included:- Gaps in knowledge: During the dialogue, members of the Kenyan maternal health community discussed the possibility of strengthening community health workers as an information delivery platform. Participants wondered about the possibility of using community health workers to distribute information both downward to the end user (patients), and then again to gather information from end users and distribute it upwards through the system to reflect the opinions of the direct users of the healthcare system.
- Supply gaps: Participants argued that while there is a large body of information in terms of maternal health supplies at the national level in Kenya, there is not as much data on supplies at the actual health facility level, where it is much needed and would be very helpful to successfully treat patients.
- Gaps in healthcare delivery: There is a strong need to address inequality in the distribution of health services as there are unequal services in rural and urban areas. Within those broad areas there may be further inequalities, as even in urban areas, slum areas or neighborhoods on the edges of cities may have less access to quality healthcare than populations that live in wealthier areas of the city or closer to the city center. Further there are broader questions of gender and access to care. Where women are not able to control household finances, they may be unable to access and pay for lifesaving care. Participants framed the question in a rights framework, “Do we value the lives of women less than men?”
- Health workforce gaps: There is a mismatch between the supply of health workers and the absorption of those trained health workers in Kenya. Many of them are not incentivized professionally or financially to stay in the system where they are trained. These health workers may leave for other countries or prefer to stay in urban areas depriving rural areas of a surplus of trained health workers.
- Gaps between words and actions: Several of the small working groups pointed to accountability as a serious issue, as there are gaps between the words of politicians on health issues and actual actions. The gap between the government promised funding for health and the actual lower amount of spending was consistently highlighted during the Nairobi dialogue as a serious gap in holding governments accountable for their promises.
The lively conversation provoked by a broad discussion of gaps in the Kenyan health system provided fertile ground to develop action points on maternal healthcare that participants then presented on the second day of the meeting to several Kenyan members of parliament. Ideally, this will be the first discussion of many as maternal health advocates, field workers, and researchers coalesce around ways to address the gaps in maternal healthcare in Nairobi and elsewhere.
Emily Puckart is a senior program assistant at the Maternal Health Task Force (MHTF).
Photo Credit: Jonathan Odhong, African Population and Health Research Center. -
Twin Challenges: Population and Climate Change in 2050
›

 With global population reaching 7 billion, a lot of attention has been paid to the question of how to sustainably support so many people, much less the 9 billion expected by 2050, or the 10 billion possible by 2100. Add in the environmental variability projected from climate change and the outlook for supporting bigger and bigger populations gets even more problematic. Two new maps – one by the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), the other by McGill University PhD candidate Jason Samson – show how the world might change over the next 40 years in the face of these twin challenges.
With global population reaching 7 billion, a lot of attention has been paid to the question of how to sustainably support so many people, much less the 9 billion expected by 2050, or the 10 billion possible by 2100. Add in the environmental variability projected from climate change and the outlook for supporting bigger and bigger populations gets even more problematic. Two new maps – one by the Population Reference Bureau (PRB), the other by McGill University PhD candidate Jason Samson – show how the world might change over the next 40 years in the face of these twin challenges.
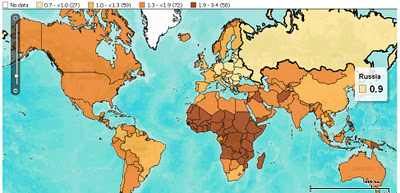
Nine Billion in 2050
PRB’s map, built using their DataFinder tool, shows the world in 2050 in terms individual country growth rates between now and then. Japan, Russia, and countries in Eastern Europe are set to grow more slowly than anywhere else, and some of that group will actually shrink by 10 to 20 percent of their current size. Western, Central, and Eastern Africa will be home to the highest increases. Niger’s 2050 population is expected to be 340 percent its 2011 size – the largest growth of any country.
The map is based on country-level data pulled from a number of sources: the UN Population Division’s latest “World Population Prospects,” the UN Statistics Division’s “Demographic Yearbook 2008,” the U.S. Census Bureau’s International Database, and PRB’s own estimates. It’s unclear what numbers come from which sources, though it is clear that PRB’s 2050 estimates span the UN’s range of medium, high, and constant-fertility variants. In spite of these variations, none of PRB’s estimates come anywhere near the UN Population Division’s low variant estimates.
PRB’s map, echoing its 2011 World Population Data Sheet, shows a world where sub-Saharan Africa will bear the brunt of population growth. The average country in Africa in 2050 is projected to be slightly more than twice its 2011 size; the average European country is expected to barely break even. Africa is home to more countries whose populations are estimated to least double (34) or triple (4) than any other continent. Europe, meanwhile, is home to more countries whose populations will stagnate (8), or even shrink (19), than anywhere else. Interestingly, the Caribbean is a close second in terms of countries whose populations are projected to stay the same (seven to Europe’s eight), and Asia is second to Europe in terms of countries whose populations are projected to shrink (Georgia, Japan, Armenia, South Korea, and Taiwan).
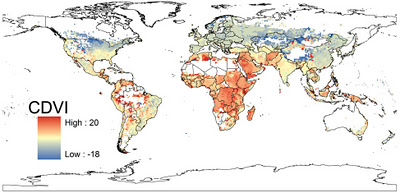
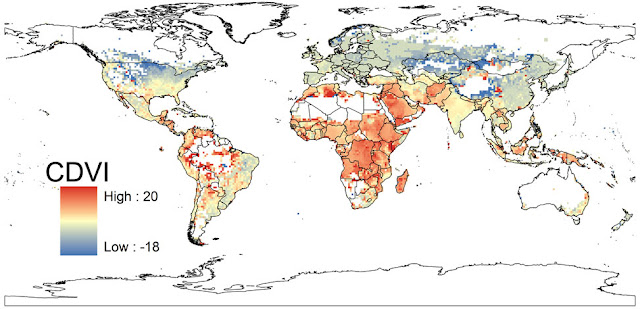
More People, More Climate Change, More Vulnerability
Samson’s map takes on the same time period but projects where people will be most vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Since his map takes into account population growth (measuring where people are most vulnerable, remember), unsurprisingly, Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and central South America are covered in bright red dots, indicating high vulnerability. Conversely, North America, Europe, and much of Central Asia are in shades of blue.
Samson built his index using four environmental predictors – annual mean temperature, mean temperature diurnal range, total annual precipitation, and precipitation seasonality – taken from WorldClim’s 2050 forecasts, and 2005 sub-national population data from Columbia’s Center for International Earth Science Information Network. In spite of the sub-national population data, Samson makes a point to justify his use of supranational climate data in order to best reflect “the scale at which climate conditions vary.” He writes that localized issues like urbanization and coastal flooding “are probably best investigated with targeted regional models rather than by attempting to modify global models to include all factors of potential regional importance.”
Samson’s research shows that, generally, people living in places that are already hot will be more vulnerable to climate change over time, while people in more temperate climates will feel a negligible impact. Though he projects the largest real temperature changes will happen in temperate climates like North America and Europe, the comparatively smaller changes in Africa, the Middle East, Southeast Asia, and central South America are expected to have a greater impact because those regions are already very hot, their natural resources are stressed, and they are expected to bear the brunt of population growth over the next few decades.
These findings reflect a disparity between those responsible for climate change and those bearing the brunt of it, which, although not surprising, “has important implications for climate adaptation and mitigation policies,” said Sampson, discussing the map in a McGill press release.
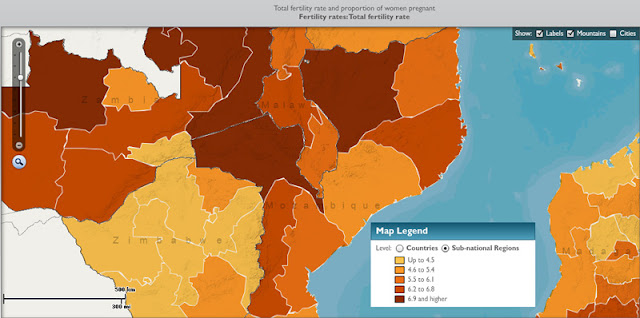
Sub-National Data “Present a Very Different Picture”
Though they offer a useful approximate glimpse at what the world might look at in 2050, both of these maps fall prey to over-aggregation. By looking at national rather than sub-national data, we miss how nuanced population growth rates can be within a country. Stimson Center Demographer-in-Residence Richard Cincotta wrote in a recent New Security Beat post that “national level comparisons of total fertility rates tend to communicate the false impression of a world with demographically homogeneous states.” Sub-national data, including differences between urban and rural areas and minority-majority fertility rates, “present a very different picture.”
And that difference matters. When it comes to looking at how population interacts with other issues, like the environment, poverty, and conflict, the importance of a sub-national approach becomes evident. In its 2011 data sheet, PRB writes that “poverty has emerged as a serious global issue, particularly because the most rapid population growth is occurring in the world’s poorest countries and, within many countries, in the poorest states and provinces.”
Edward Carr, an assistant geography professor at the University of South Carolina currently serving as a AAAS science fellow with USAID, argues that national-level data obscures our ability to understand food insecurity as well. The factors that drive insecurity “tend to be determined locally,” writes Carr in a post on his blog, and “you cannot aggregate [those factors] at the national level and get a meaningful understanding of food insecurity – and certainly not actionable information.”
The same is true when it comes to climate vulnerability. In a report from The Robert S. Strauss Center’s Climate Change and African Political Stability Program, authors Joshua Busby, Todd Smith, and Kaiba White write that “research announcing that ‘Africa is vulnerable to climate change,’ or even ‘Ethiopia is vulnerable,’ without explaining which parts of Ethiopia are particularly vulnerable and why, is of limited value to the international policy community.”
“It is of even less use to Africans themselves, in helping them prioritize scarce resources,” add Busby et al.
Understanding the joint problems of climate change and population growth on a global level helps frame the challenges facing the world as it moves toward 8, 9, and possibly 10 billion. But knowing the ins and outs of how these issues interact on a local level will be a necessary step before policymakers and others can hope to craft meaningful responses that minimize our vulnerability to these challenges over the coming decades.
Sources: Center for International Earth Science Information Network at Columbia University, Climate Change and African Political Stability Program at the Robert S. Strauss Center, McGill University, Population Reference Bureau, UN Population Division, UN Statistics Division, U.S. Census Bureau, University of South Carolina, WorldClim.
Image Credit: “2050 Population As a Multiple of 2011,” courtesy of PRB; CDVI map used with permission, courtesy of McGill University; Sub-national total fertility rates in Southern Africa, courtesy of MEASURE DHS, arranged by Schuyler Null. -
Rwanda: Dramatic Uptake in Contraceptive Use Spurs Unprecedented Fertility Decline
›November 8, 2011 // By Elizabeth Leahy Madsen
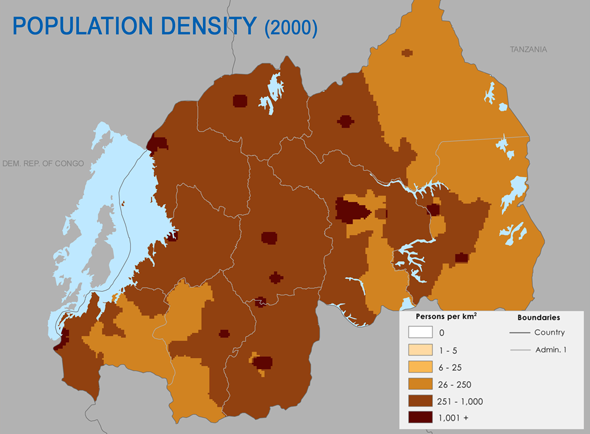
With over 400 people per square kilometer, the highest rate on the African mainland, population density is perhaps the most widely-discussed factor of Rwanda’s demography. Some scholars, notably Jared Diamond, have argued that it played a primary role in sparking the 1994 genocide through competition for land (although others present a more complex theory based in policies and governance).
-
Improving Maternal Health: A Conversation With Kenyan Field Workers and Policymakers
›“The traditional strategies for improving the health system include the horizontal approach, which prioritizes non-communicable diseases, and the vertical approach which prioritizes communicable diseases such as HIV/AIDS,” said John Townsend, vice president of reproductive health programs at Population Council, during a webcast discussion – the second in a series – between the Woodrow Wilson Center in Washington, DC, and maternal health experts in Nairobi, Kenya. [Video Below]
Recently, a third strategy, called the “diagonal approach,” was developed to more clearly define health system priorities and guide general system-wide improvements. Participants in both locations discussed this new approach and other structural improvements that can be made to better integrate maternal health indicators into developing country health systems on October 17.
The meeting was part of the 2011 Advancing Dialogue on Maternal Health series, with the Wilson Center’s Global Health Initiative and the African Population and Health Research Center. Participants in Nairobi were assigned to three topical groups and asked to identify challenges and opportunities related to their themes.
The Role of Policymakers and Funders
“We must engage [policymakers and donors] in forums like this one to share findings and share lessons learned,” said participant Sylvia Bushuru of Kenya as she reported back from the policymakers and funders working group. The group focused on steps required to hold politicians accountable to commitments made to maternal health, such as the Abuja Declaration, which requires the Ministry of Finance to dedicate 15 percent of the budget to health. Currently, only 5.5 percent of the Kenya budget is dedicated to the health sector.
Identifying strategic partners will help in reaching ambitious goals, the group agreed; however, they noted that it’s important to ensure that these partnerships and policies extend to an operational level. Besides the overall budget pledge, important steps like ensuring 24-hour emergency health facilities in rural areas and implementing a results-based financing plan based on maternal health indicators have yet to be completed.
A Definition of Priorities through a Diagonal Approach
James Wariero, a regional health advisor with the MDG Centre for East and South Africa, served as the representative for the group discussing the “diagonal approach,” which focused on how maternal health indicators can best set priorities to improve the overall health system. They identified antenatal care visits as a priority because they also serve as an entry point to other health services, including HIV/AIDS treatment.
Discussing gender, he said that “male involvement in maternal health will have benefits for child health and other issues…it is an area with little headway here in Kenya and other similar countries in Africa.” Additionally, Wariero discussed how the diagonal approach could be used to link maternal health indicators with other sectors such as technology and information systems.
The group said that improving the health system should start at the district level to ensure the most vulnerable populations at the community level have proper access. However, they said that ideally district-level programming should be evaluated and funded through results-based financing and structured on clear maternal health indicators.
Knowledge Gaps and Research Needed
“We initially began our discussion surrounding the [World Health Organization’s] six health system blocks,” reported Dr. Kristine Kisaka, a program officer with Deutsche Stiftung Weltbevoelkerung and representative from the “knowledge gaps and research needed” group. This group identified access to mobile phones for maternal health data collection as a major resource gap. Instead of calling for additional research they said they would prefer better implementation of existing, evidence-based programming.
Utilizing the World Health Organization’s health system framework, the group identified existing knowledge gaps to improve maternal health in Kenya and six recommendations:- Strengthen community strategies through a national synchronization of information
- Harmonize planning and implementation of the provisioning of supplies and commodities at the community level
- Address inequalities in the distribution and delivery of health services, ensuring distribution to urban and rural centers, including slums
- Centralize health financing in order to reach both national and community levels
- Empower households in financing, including both women and men, so they plan and save for maternal health
- Address the imbalance in supply and demand of healthcare workers
Linkages: Key To Improving Maternal Health Systems
“It’s really about linkages,” said John Townsend, giving closing remarks after the presentations from Nairobi. Maternal health indicators can be a catalyst for change, due to their strong cross-cutting links to other development systems, such as transportation, the economy, and education. “I think the call to action that the Kenyan working groups made is quite valuable,” he said, but the question is, “How do we get intelligent decision alternatives in front of our leaders to figure out what are the best investments given the critical resources?”
“The private sector [presents] an opportunity,” said Townsend. “I think we need to be more explicit about how we want to engage with them and what we would like to see from them.” He pointed out that the national maternal health strategy in Kenya is explicit and promising, but there needs to be stronger links between the national strategy and the operational aspects of actually implementing it.
Event Resources:- Photo gallery
- Presentation: “Improving Health Systems Through a Maternal Health Framework,” African Population and Health Research Center
- Video
Photo Credit: #1 and #3, courtesy of Jonathan Odhong, African Population and Health Research Center; #2 courtesy of David Hawxhurst/Wilson Center. -
Pascal Gakwaya Kalisa, PHE Champion
Coffee Farmer and Extension Manager Promotes Improved Health and Livelihoods in Rwandan Coffee Communities
›
This PHE Champion profile was produced by the BALANCED Project.
Mr. Pascal Gakwaya Kalisa has produced coffee in the densely populated country of Rwanda for the past nine years. A proud member of the 1,200 member Maraba Coffee Cooperative in Huye District in the Southern Province of Rwanda, Kalisa knows that a larger income alone does not ensure a better quality of life for his fellow coffee farmers and their families. He also knows that a successful coffee growing/exporting enterprise depends on preserving the fragile Rwandan soils, as well as on the health and well-being of farming families and communities. Therefore, Kalisa and other cooperative members treat the land and trees with a level of personal care that is necessary for optimum organic production and soil preservation.
Kalisa and the community have set up small, garden-sized coffee farms that are more productive than usual. Cooperative washing stations have enabled the small-scale farmers to improve product quality, and the cooperatives themselves are learning to negotiate better coffee prices with international buyers. Through such efforts and the support of many international donors and industry partners, Rwanda has become a producer of high quality specialty coffee since 2005, and its coffees are being marketed through renowned coffee roasters and importers in the United States, Europe, and Japan. In just six short years, Rwandan farmers have doubled their incomes and created 2,000 jobs, and the first renowned specialty coffee competition Cup of Excellence in Africa was held in Rwanda in 2008.
SPREAD: A Community Partnership
Recognizing the broad-based health, social, and economic needs of coffee farmers and their families in this part of East Africa, the U.S Agency for International Development initiated the Sustaining Partnerships to Enhance Rural Enterprise and Agribusiness Development project (SPREAD) to provide rural cooperatives and enterprises involved in high-value commodity chains with both appropriate technical assistance and access to health-related services and information. It is this combination of technical assistance and health-related outreach and services that has resulted in increased and sustained incomes and improved livelihoods.
Kalisa and other members of various cooperatives that SPREAD supports recognize that not only should farmers and their families preserve the land, but they must also preserve their own health in order to perform the labor needed to farm the crop that will produce the steady stream of high quality coffee upon which their livelihoods depend. Initiating community dialogues around issues such as protected sex, gender roles, and how coffee revenue is spent within households has also been crucial to project success among both youth and adults.
In his role as coffee zone coordinator for the SPREAD project, Kalisa works with coffee cooperatives to implement improved agricultural practices that improve the quality of their crop. This includes using cleaner environmental practices during coffee processing, such as introducing composting of coffee cherry pulp. Kalisa also helps disseminate integrated health and coffee messages through a weekly coffee talk-show produced by the National University of Rwanda’s Radio Salus, called Imbere Heza (“Bright Future”). In one show, for example, a man explained to a fellow farmer that to get good coffee cherries, he should thin his trees to renew his plantation.
Integrating Healthy Lives
Kalisa has also helped the SPREAD project’s health team deliver integrated messages on family planning, maternal and child health, alcohol, nutrition, gender issues, and the linkages between these. He uses examples such as the one about tree thinning to explain that families that space their children tend to be healthier, as they can plan the number of children to better fit with the financial and natural resources at hand.
Kalisa sees the benefits of using community agents to deliver integrated health, environment, and livelihood messages. This includes training extension agents to discuss environmental and human health issues in the context of coffee growing. Also, having coordinators from the coffee program and the health program go hand-in-hand to the field saves time, fuel, and other project costs. Kalisa believes that this campaign to educate coffee farmers and their families on the linkages between human health, a healthy environment, and strong livelihoods will lead to long-term change in their behavior, attitudes, and knowledge – change that will help them live better lives today and into the future.
This PHE Champion profile was produced by the BALANCED Project. A PDF version can be downloaded from the PHE Toolkit. PHE Champion profiles highlight people working on the ground to improve health and conservation in areas where biodiversity is critically endangered.
Photo Credit: “Rwanda photos 060,” courtesy of David Dewitt/counterculturecoffee. -
How Did We Arrive at 7 Billion – and Where Do We Go From Here? [Part Two]
›October 26, 2011 // By Elizabeth Leahy MadsenThe world’s women will determine whether the global population in 2050 is as low as 8 billion or as high as 11 billion through their choices (or lack thereof) about the number and timing of their children. Women in developing regions of the world will have the greatest effect on these potential population trajectories. Even if fertility rates remain constant at current levels (which is unlikely), developing regions would grow from 5.7 billion in 2010 to 9.7 billion in 2050, but the total population of developed countries would remain essentially unchanged. The UN estimates that the seven billionth person alive today will be born on October 31. Demographer Elizabeth Leahy Madsen explains how we got to that number, its significance, and where our demographic path might take us from here. Read part one here.
The UN estimates that the seven billionth person alive today will be born on October 31. Demographer Elizabeth Leahy Madsen explains how we got to that number, its significance, and where our demographic path might take us from here. Read part one here.
The world’s women will determine whether the global population in 2050 is as low as 8 billion or as high as 11 billion through their choices (or lack thereof) about the number and timing of their children. Women in developing regions of the world will have the greatest effect on these potential population trajectories. Even if fertility rates remain constant at current levels (which is unlikely), developing regions would grow from 5.7 billion in 2010 to 9.7 billion in 2050, but the total population of developed countries would remain essentially unchanged.
The way that people decide the timing and number of their children is not easily distilled into a simple formula with a single solution. Still, some basic and important facts are known. In the developing world, where more than 80 percent of the world’s population lives, women in rural areas, those who have little or no education, and those who are poor, have larger families. As demographers have shown in modeling the determinants of fertility, women tend to seek contraception once they are confident that their children will survive to adulthood and when socioeconomic development increases the “costs” of having children, for example by motivating parents to send them to school rather than to work.
One of the most direct reasons for past declines in fertility rates was the rapid expansion of family planning and reproductive health programs, supported by country governments and international donors, that enabled women and men to more effectively choose the size of their families. But today, about 215 million women across the developing world would like to delay or avoid pregnancy but are using ineffective contraception or none at all. Funding programs to meet the family planning needs of these women, which would cost about $3.6 billion annually, would both empower them and help fertility rates continue to decline.
Beyond Access: Gender Inequality Inhibits Contraceptive Use
While increasing support for family planning programs tops the list of demographers’ recommended policies, ensuring that contraceptives are available and accessible will not alone achieve the fertility declines projected in most of the UN’s range of possibilities. Many women who are having or planning to have large families know about family planning and where to find it, but are choosing not to use contraception for cultural reasons that are often deeply engrained.
In sub-Saharan Africa, the region with the highest global fertility rate, only 16 percent of married/partnered women of reproductive age are using effective contraception. In comparison, between 62 and 75 percent of their peers in Ireland, the United States, and Uruguay – countries whose fertility rates are almost exactly at replacement level – are using it.
Logically, sub-Saharan Africa needs similar levels of contraceptive use to bring its average fertility rate towards replacement level as the UN projects, so the region’s average prevalence rate for modern contraception would need to rise by at least 10 percentage points in each of the next four decades. However, contraceptive use in the region has grown by only 0.5 percentage points or less over the past 30 years.
What is inhibiting the use of contraception? Demographic and health surveys find in Nigeria, for example, that 10 percent of married women are using an effective contraceptive method, while twice as many have an unmet need for family planning. This low use of family planning demonstrates high potential for change in the country’s demographic future, which, as the most populous in Africa, will greatly influence global and regional trends. Yet among women who do not intend to use contraception, 39 percent report that they or their family members are opposed to family planning, and another 16 percent fear side effects or have other health-related concerns. If Nigeria’s fertility rate remains unchanged, the country will be home to 500 million people by 2050.
In Pakistan, where 24 percent of births are unintended, surveys show similar barriers. Ninety-six percent of married women know about effective contraceptive methods, but only 22 percent are using one. More than one-quarter of women who do not plan to use contraceptives report that their fertility is “up to God” and 23 percent report that they or their family members are opposed to family planning. Pakistan’s population would more than double from 174 million to 379 million by 2050 if current fertility trends hold constant.
Peak Planet? Population Growth and Consumption Strain Environmental Resources
Because Nigeria, Pakistan, and other countries’ demographic trajectories may not follow the path laid out in population projections, we can’t take a world of nine billion for granted. While human ingenuity and technological advancements have improved standards of living in many countries, scientists caution that the combination of rising human numbers and growing consumption has serious environmental implications. Already, the quantity and quality of fresh water supplies are under strain, and forests in many developing countries are being rapidly depleted.
Population projections are much more than wonkish speculation – they foreshadow the serious problems that lie ahead if health, environment, and development policies aren’t strengthened. If the UN projections of our demographic future are to bear any semblance of reality, we must move beyond the status quo. While improving physical access to family planning should remain a top priority, meeting unmet need will also require addressing the deep-seated challenges of women’s education and empowerment.
Elizabeth Leahy Madsen is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and former senior research associate at Population Action International.
Sources: Bongaarts and Sinding (2009), Bongaarts (2006), Futures Institute, Guttmacher Institute and UN Population Fund, Measure DHS, O’Neill, Dalton, Fuchs, Jiang, Shonali Pachauri, and Katarina Zigova (2010), UN Population Division, Washington Post.
Photo Credit: “Afghan Internally Displaced Persons,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. -
Robert Draper, National Geographic
People and Wildlife Compete in East Africa’s Albertine Rift
›The original version of this article, by Robert Draper, appeared on National Geographic.
The mwami remembers when he was a king of sorts. His judgment was sovereign, his power unassailable. Since 1954 he, like his father and grandfather before him, has been the head of the Bashali chiefdom in the Masisi District, an undulating pastoral region in eastern Democratic Republic of the Congo (DRC). Though his name is Sylvestre Bashali Mokoto, the other chiefs address him as simply doyen – seniormost. For much of his adult life, the mwami received newcomers to his district. They brought him livestock or other gifts. He in turn parceled out land as he saw fit.
Today the chief sits on a dirty couch in a squalid hovel in Goma, a Congolese city several hours south of Masisi. His domain is now the epicenter of a humanitarian crisis that has lasted for more than a decade yet has largely eluded the world’s attention. Eastern Congo has been overtaken by thousands of Tutsi and Hutu and Hunde fighting over what they claim is their lawful property, by militias aiming to acquire land by force, by cattlemen searching for less cluttered pastures, by hordes of refugees from all over this fertile and dangerously overpopulated region of East Africa seeking somewhere, anywhere, to eke out a living. Some years ago a member of a rebel army seized the mwami’s 200-acre estate, forcing him, humiliated and fearing for his safety, to retreat to this shack in Goma.
The city is a hornet’s nest. As recently as two decades ago Goma’s population was perhaps 50,000. Now it is at least 20 times that number. Armed males in uniform stalk its raggedy, unlit streets with no one to answer to. Streaming out of the outlying forests and into the city market is a 24/7 procession of people ferrying immense sacks of charcoal on bicycles or wooden, scooter-like chukudus. North of the city limits seethes Nyiragongo volcano, which last erupted in 2002, when its lava roared through town and wiped out Goma’s commercial district. At the city’s southern edge lies the silver cauldron of Lake Kivu – so choked with carbon dioxide and methane that some scientists predict a gas eruption in the lake could one day kill everyone in and around Goma.
The mwami, like so many far less privileged people, has run out of options. His stare is one of regal aloofness. Yet despite his cuff links and trimmed gray beard, he is not a chief here in Goma. He is only Sylvestre Mokoto, a man swept into the hornet’s nest, with no land left for him to parcel out. As his guest, a journalist from the West, I have brought no gifts, only demeaning questions. “Yes, of course my power has been affected greatly,” the mwami snaps at me. “When others back up their claims with guns, there is nothing I can do.”
Continue reading on National Geographic.
Photo Credit: “Aerial View of Goma,” courtesy of UN Photo/Marie Frechon. -
Water and Poverty in a World of 9 Billion, Vulnerable Agriculture in the Niger Basin
› In a two–part Water International special report on water, food, and poverty, examining 10 of the world’s major river basins, a team of researchers say that instead of worrying about having enough water to sustain the world’s growing demand, policymakers should be concerned with understanding how to manage what they already have.
In a two–part Water International special report on water, food, and poverty, examining 10 of the world’s major river basins, a team of researchers say that instead of worrying about having enough water to sustain the world’s growing demand, policymakers should be concerned with understanding how to manage what they already have.
Introducing the special report, Simon Cook, Myles Fisher, Tassilo Tiemann, and Alain Vidal note in “Water, Food and Poverty: Global- and Basin-Scale Analysis” that the vast majority of population growth over the next few decades is expected to happen in developing countries, “where the disjunct between poverty, water and food is particularly acute.” Gaining a better understanding of water – how much we have, who uses it, and how best to use it – is essential to improving development results in the face of this demographic explosion. Water is linked with poverty and development through issues like scarcity, access, and water-related hazards (like drought, flood, and disease). But the authors conclude that water productivity – the ease or difficulty in getting water from its source to agriculture – “is by far the most important water-related constraint to improved food, income and environmental security.”
In “Water, Agriculture and Poverty in the Niger River Basin,” Andrew Ogilvie et al., paint a bleak picture of life in one of West Africa’s most important basins, writing that “[m]uch of the population in the basin suffers from extreme, chronic poverty and remains vulnerable to droughts and malnutrition.” Many of the Niger basin’s 94 million residents rely on subsistence agriculture, and most of that agriculture relies on rainwater rather than groundwater irrigation systems. Over time, the authors write, “there is little doubt that climate change will increase the strain on already-vulnerable agriculture.” Population growth will exacerbate this strain; the basin’s population is expected to increase as much as fourfold by 2050. In spite of this bleak picture, the authors conclude that “[i]mprovements in rainfed agriculture can have an important impact on poverty reduction and food security due to the large population dependent on it.”
Showing posts from category Africa.