-
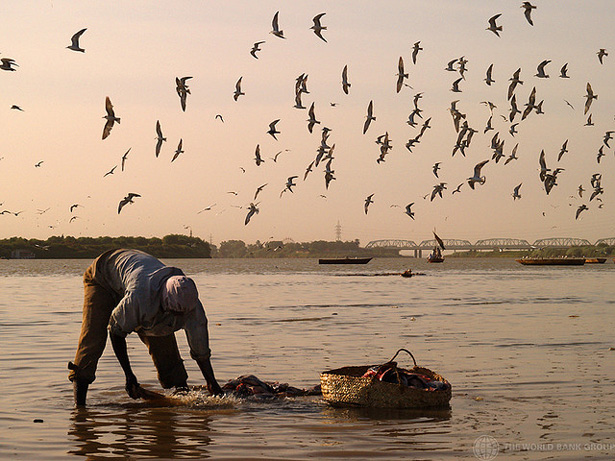
‘National Geographic’ Reports on “Water Grabbers” From Mali to India
›
Much ink has been spilled on the growing trend of global land grabs – land purchased en masse in developing countries like Ethiopia by foreigners mainly for agricultural export. But along with land, investors often also gain the right to use local water, and sometimes with little consideration for local livelihoods. Fred Pearce recently looked into these “water grabs” in a series for National Geographic.
-
Demographic and Environmental Dynamics Shape ‘Global Trends 2030’ Scenarios
›
“However rapid change has been over the past couple decades, the rate of change will accelerate in the future,” states the newest quadrennial report from the National Intelligence Council (NIC), Global Trends 2030: Alternative Worlds. Released late last year, the report identifies the “game-changers, megatrends, and black swans” that may determine the trajectory of world affairs over the next 15 years, including demographic dynamics and natural resource scarcity. [Video Below]
-
World Water Day Focuses on Cooperation in the Face of Growing Stress
›March 22, 2013 // By Schuyler Null
Cooperation, not conflict; that’s the theme of this year’s World Water Day. Collaboration over water has been the rule rather than the exception over the past 70 years, UNESCO explained in the launch of their International Year for Water Cooperation initiative earlier this year (which the rest of the UN is thoughtfully supporting).
But the fact that there’s need for such an initiative shows that water conflict and other water issues are not far from the minds of global policymakers. Scarcity, drought, climate change, food security, disease – water impacts people and their governments in so many ways. Here’s a rundown of some of our best related posts.
-
UNEP Highlights Environmental Impacts on Health in Africa
›March 20, 2013 // By Carolyn Lamere
While it can be convenient to think of human health and the environment as unrelated silos, they are in fact closely related. The United Nations Environment Program (UNEP) recently released a report underscoring this point especially for Africa, where large numbers of people are directly reliant on natural resources for their livelihoods.
-
Urban Health and Demography Trends: More Cities, More Problems?
›
Some 52 percent of the world’s population lives in cities, a proportion that will only grow throughout the next few decades. Understanding the health challenges facing urban residents is crucial for those who seek to improve human health, especially since many of these challenges differ from those facing inhabitants of rural areas, where global health resources have traditionally been concentrated. At a private meeting on March 4 at the Wilson Center, experts described how factors ranging from climate change and greenhouse gas emissions to reproductive health and rights impact urban health.
-
Africa Can Help Feed Africa: Removing Regional Barriers to Trade in Food Staples
›We need to understand why barriers to trade exist in order to alleviate the food insecurity that confronts Africa, said Makhtar Diop, World Bank vice president for Africa, at the Wilson Center in January.
The World Bank released a new report in October 2012 that is part of a series that concentrates on intraregional trade. Africa Can Help Feed Africa: Removing Regional Barriers to Trade in Food Staples, however, is unique, Diop said, because it “moves the focus from general barriers to trade in Africa to focus on food,” so that policymakers can move away from crisis response and address food insecurity at a base level. [Video Below]
-
In Uganda, Integrating Population, Health, and Environment to Meet Development Goals
›
Fifty years after independence, Uganda has one of the highest population growth rates in the world at 3.3 percent – a rate which puts the country on track to nearly double in population over the next two decades. More than 50 percent of the population is under the age of 18. This large youth cohort will ensure that the country continues to grow for decades to come, even if couples choose – and are able – to have smaller families. And according to the State of Uganda Population Report 2011, “with more than one million people added to the population every year, the quality of [health] service delivery will suffer.”
-
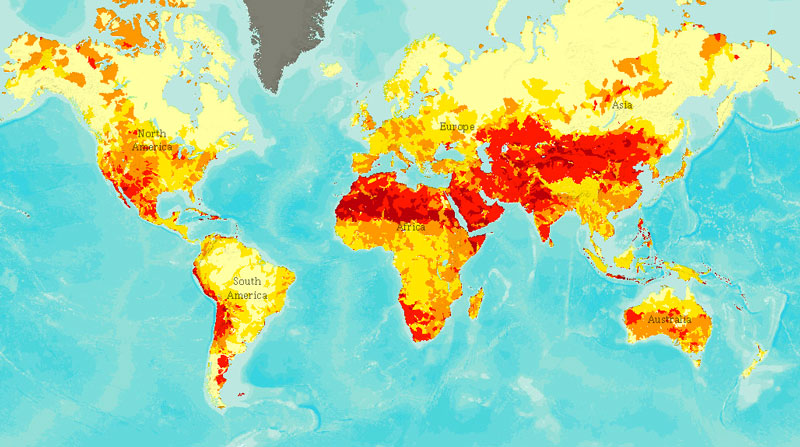
Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas Shows Detailed View of Global Water Vulnerability
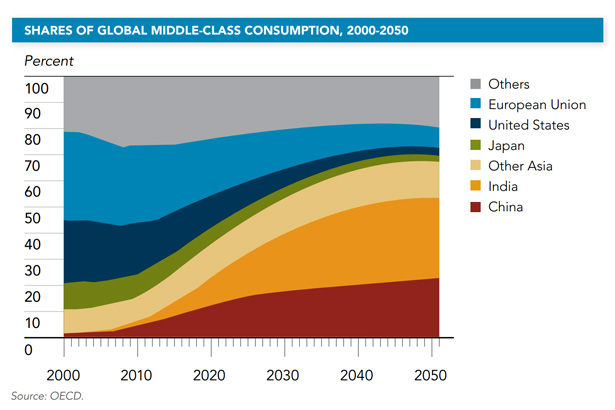
›As world population pushes towards nine billion by mid-century and millions are elevated to the global middle class every year, demand for water continues to grow as well. More people need more water for drinking and household use, but also for agriculture, mining, energy, and industry. With water often cited as a limit to growth and potential crisis point, the World Resources Institute has released the Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas, which details various types of water stress around the world in impressively detailed fashion.
Showing posts from category Africa.