-
The Feed for Fresh News on Population
›May 21, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffRT @popact: World Bank launches action plan to help poor countries reduce fertility rates and prevent maternal deaths http://paidc.org/ …
#Climate change & #demography 2of 10 factors “magnifying uncertainty” in 10 yr horizon of #NATO 2020 report @NATO_news http://ow.ly/1MqWi
Nick Kristof has people, poverty, conservation post with his Gabon column. Challenge is integrated response @NickKristof http://ow.ly/1LQUL
Rich Cincotta on where’s the home for political demography? ISA, AAG, PAA, APSA? All come up wanting @newsecuritybeat http://ow.ly/1LnBn
Population & environmental links in #Rwanda are grist for Reading Radar on @newsecuritybeat including @enviroscribe http://ow.ly/1KzZg
Stanford’s Paul Ehrlich weighs in on population and sustainability in the latest issue of PLoS Biology on the #MAHB. http://ow.ly/1HcC6
-
USAID’s Shah Focuses on Women, Innovation, Integration
›May 20, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffWomen in developing countries are “core to success and failure” of USAID’s plan to fight hunger and poverty, and “we will be focusing on women in everything we do,” said USAID Administrator Rajiv Shah at today’s launch of the “Feed the Future” guide.
But to solve the “tough problem” of how to best serve women farmers, USAID needs to “take risks and be more entrepreneurial,” said Shah, as it implements the Global Hunger and Food Security Initiative.
“A lot of this is going to fail and that’s OK,” Shah said, calling for a “culture of experimentation” at the agency. He welcomed input from the private sector, which was represented at the launch by Des Moines-based Pioneer Hi-Bred.
In one “huge change in our assistance model,” Feed the Future will be “country-led and country-owned,” said Shah, who asked NGOs and USAID implementing partners to “align that expertise behind country priorities” and redirect money away from Washington towards “building real local capacity.” USAID will “work in partnership, not patronage,” with its 20 target countries, he said.
To insure that the administration’s agricultural development efforts are aligned to the same goals, Shah said USAID will collect baseline data from the start on three metrics: women’s incomes, child malnutrition, and agricultural production.
“Whether it is finance, land tenure, public extension, or training efforts, it does not matter whether it is an ‘agricultural development’ category of program,” said Shah. All programs will “provide targeted services to women farmers.”
While Shah briefly mentioned integrating these efforts with the administration’s Global Health Initiative, he only gave one example. Nutrition programs would be tied to health “platforms that already exist at scale” in country, such as HIV, malaria, vaccination, and breastfeeding promotion programs, he said.
Targeting Food Security: The Wilson Center’s Africa Program Takes Aim
If “food supplies in Africa cannot be assured, then Africa’s future remains dismal, no matter how efforts of conflict resolution pan out or how sustained international humanitarian assistance becomes,” says Steve McDonald, director of the Wilson Center’s Africa Program, in the current issue of the Wilson Center’s newsletter, Centerpoint. “It sounds sophomoric, but food is essential to population health and happiness—its very survival—but also to productivity and creativity.”
The May 2010 edition of Centerpoint highlights regional integration, a key focus of U.S. policy, as a mechanism for assuring greater continuity and availability of food supplies. Drawing on proceedings from the Africa Program’s “Promoting Regional Integration and Food Security in Africa” event held in March, Centerpoint accentuates key conclusions on building infrastructure and facilitating trade.
Photo Credit: “USAID Administrator Shah visits a hospital in Haiti” courtesy Flickr user USAID_Images. -
Interplays Between Demographic and Climatic Changes
›“Impacts of Population Change on Vulnerability and the Capacity to Adapt to Climate Change and Variability: A Typology Based on Lessons from ‘a Hard Country,’” appearing in the journal Population and Environment, is a study of societal resilience by Robert McLeman from the University of Ottawa. Beginning with a literature review of the connections between population growth and greenhouse gas emissions, McLeman then details how demographic changes can negatively affect resilience–the ability of societies to cope and adapt to climate changes. Based on empirical studies of small communities undergoing local climate and demographic changes in eastern Ontario, McLeman finds that simultaneous demographic and climatic change “increased stress on local social networks…critical to climate adaptation.” “Climate Change and Population Migration in Brazil’s Northeast: Scenarios for 2025–2050,” also appearing in the journal Population and Environment, examines “demographic dynamics–particularly migration–driven by changes in the performance of the economy due to climate changes.” The region of study was chosen for its high levels of both population and poverty and its dry climate, “which will be severely impacted by growing temperatures.” The study concludes that predicted climate change impacts on agriculture are potential push migration factors and offers policy and planning recommendations to reduce migrant vulnerabilities.
“Climate Change and Population Migration in Brazil’s Northeast: Scenarios for 2025–2050,” also appearing in the journal Population and Environment, examines “demographic dynamics–particularly migration–driven by changes in the performance of the economy due to climate changes.” The region of study was chosen for its high levels of both population and poverty and its dry climate, “which will be severely impacted by growing temperatures.” The study concludes that predicted climate change impacts on agriculture are potential push migration factors and offers policy and planning recommendations to reduce migrant vulnerabilities.
Both articles are part of Population and Environment‘s special issue on “Climate Change: Understanding Anthropogenic Contributions and Responses.” -
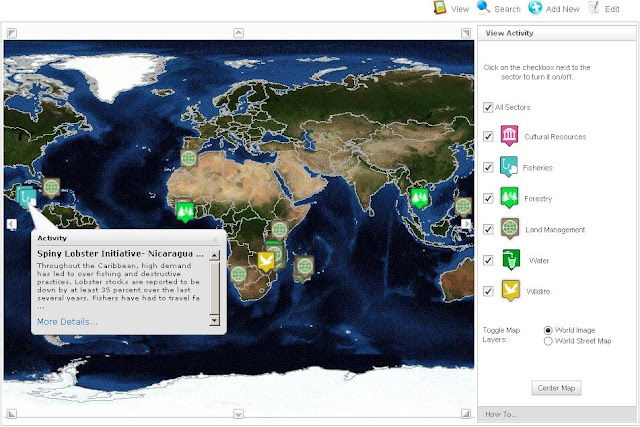
USAID Launches GeoExplorer: Connecting Natural Resource Management Activities, Practitioners, and Communities
›Part of USAID’s FRAMEweb community, GeoExplorer is a visual aggregator of natural resource management (NRM) activities, best practices, success stories, and lessons learned. As of launch, GeoExplorer is home to 43 activities, each searchable by scale (e.g. local, national, or regional), sub-sector (e.g. forestry, water, wildlife), and topic (e.g. governance, livelihoods, and health).
GeoExplorer was designed to foster knowledge sharing among and between practitioners, program managers, and researchers. USAID expects the tool to help avoid cases both of repeating past mistakes and reinventing the wheel, serve as a guide for study trips to the field, build community exchanges, and foster networking. It is built on ArcGIS architecture that USAID hopes will allow for continual expansion, particularly through the addition of GIS layers that can empower users with greater search options and tools for cross-project analytic analyses.
All activities on GeoExplorer are directly uploaded by users and USAID funding is not a requirement for inclusion. A FRAMEweb account (free) is all that is needed to sign-up and start adding your own projects. USAID hopes to make GeoExplorer available to host other NRM sub-sectors and even non-NRM activities in the future. -
Coffee and Contraception: Combining Agribusiness and Community Health Projects in Rwanda
›“Population pressures and diminishing land holdings – due to high fertility rates, war and genocide, and subsequent migration – have caused a rapid decrease in the forested and protected areas and increased soil infertility and food insecurity” in Rwanda, USAID’s Irene Kitzantides told a Wilson Center audience.
Kitzantides, a population, health, and environment advisor and global health fellow, said “the population is projected to reach over 14 million by 2025” – nearly one-third more than today, due to the country’s high fertility rate of nearly 5.5 children per women–which could continue to negatively impact forests and food supplies.
In response to these challenges, USAID supported the Sustaining Partnerships to Enhance Rural Enterprise and Agribusiness Development (SPREAD) Project. SPREAD uses an integrated population-health-environment (PHE) approach to develop the coffee agribusiness and bring family planning, HIV/AIDS, and reproductive health services to coffee workers.
Combining income generation with health services was thought an effective way to “fulfill the overall SPREAD goal of improving lives and livelihoods,” said Kitzantides.
A SPREADing Mandate: Integrating Health and Agribusiness
SPREAD follows USAID’s PEARL I and II Projects, which focused exclusively on agricultural development. Coffee is still at the center of SPREAD’s activities, with $5 million of the project’s $6 million USAID budget earmarked for agricultural development.
However, a broader mandate to include health services emerged after recognition that greater income alone does not ensure greater quality of life. The additional health funding leverages SPREAD’s already established relationships with farming cooperatives to bring health services to traditionally underserved rural communities.
“We really tried to build on the existing assets of the cooperative,” said Kitzantides. “We also really tried to complement local and national public health policy and partners.”
The integration of health with agricultural goals, and the use of already established in-country health programs, has made SPREAD extremely cost-effective, with HIV/AIDS prevention education costing less than $2 per person.
Examples of SPREAD’s integrated work include:Combined health and agricultural lessons: Kitzantides and her colleagues trained nearly 400 animateurs de café, cooperative employees running the agricultural education programs, to incorporate public health objectives into their activities. Combining health and agricultural education into one session takes advantage of workers already trained during previous USAID programs. The combination also attracts more male participants, who traditionally shunned HIV/AIDS, family planning, and reproductive health campaigns and services.
Radio programming: SPREAD worked with the agricultural radio program Imbere Heza (“Bright Future”) to incorporate health messaging at the end of each program.
 Mobile clinics: SPREAD works with cooperatives and local health centers to bring convenient services to farmers when they gather at sales or processing stations during harvests.
Mobile clinics: SPREAD works with cooperatives and local health centers to bring convenient services to farmers when they gather at sales or processing stations during harvests.Community theater: SPREAD hires local theater groups to perform skits on health. The farming communities “really love community theater and always ask for it,” said Kitzantides.

In its relatively short existence, SPREAD’s health activities have reached over 120,000 people with HIV/AIDS prevention messages; nearly 90,000 with messages discussing family planning/reproductive health; and almost 40,000 about maternal and child health. The project counts 347 women as new users of family planning services.
Lessons learned – which will be examined in more detail in an upcoming issue of Focus – include the importance of using community-based approaches to overcome perceived social barriers; the advantages of integrating cross-cutting activities at the outset of a program; and the need for strong monitoring and evaluation systems to measure the effort’s outcomes. Jason Bremner of the Population Research Bureau said PHE projects such as SPREAD go “beyond what the health sector itself can do and find new ways of reaching underserved remote populations.” He presented a soon-to-be-released PRB map plotting the location of more than 40 PHE projects in Africa.
Jason Bremner of the Population Research Bureau said PHE projects such as SPREAD go “beyond what the health sector itself can do and find new ways of reaching underserved remote populations.” He presented a soon-to-be-released PRB map plotting the location of more than 40 PHE projects in Africa.
The success of SPREAD and similar projects demonstrates the potential for PHE approaches to bring reproductive health and family planning services to rural areas, Bremner noted, but there is still much work to be done to scale up this integrated approach – and to document its successes.
Sustaining SPREAD
Kitzantides said it took several years to integrate health activities with the already established agricultural programs. Since USAID funding for the program is scheduled to end in 2011, she is uncertain that the time remaining will be enough for SPREAD’s health partners to develop the logistical and financial capacities to become self-sustaining. But SPREAD has changed attitudes and beliefs, two key objectives that do not require sustained funding.
“We used to talk about growing coffee, making money, buying material things like bikes – not about problems like malaria, HIV/AIDS, etc.,” said one SPREAD agricultural business manager during the program’s evaluation. “Someone could have 5 million Rwandan francs in the house but could suffer from malaria where medicine costs 500 Rwandan francs, due to ignorance. You have to teach people about production, you have to also think of their health to improve their lives.”
Photo Credits: Irene Kitzantides, courtesy David Hawxhurst; condom demonstration, courtesy Nick Fraser; community theater group, courtesy SPREAD Health Program; Jason Bremner, courtesy David Hawxhurst. -
Challenges Found in ‘The Places We Live’
›May 18, 2010 // By Julien KatchinoffThe work of photographer Jonas Bendicksen provided the inspiration for a research paper competition organized by the Woodrow Wilson Center’s Comparative Urban Studies Project, the Cities Alliance, the International Housing Coalition, USAID, and the World Bank. At “The Places We Live: Slums and Urban Poverty in the Developing World,” four of the winning papers (out of 200 entries) were critiqued by urbanization policy experts. The authors focused on critical issues facing the world’s rapidly urbanizing centers, including service delivery, the challenge of political cleavages, redevelopment mechanisms, sanitation, and citizen participation in urban development.
The competition was established to “tap into the academic community and encourage … a younger generation of academics…to think about the challenges of rapid urbanization and the needs of slum dwellers and what we can do about it,” said USAID’s Jessica Tulodo. “It is the central issue that we are going to be grappling with for the coming decades and beyond. How do we not just address the challenges, but harness the opportunities of urban growth and how do we ensure that the larger population of urban poor can benefit and participate?”
“This is an effort to rekindle a stronger debate between the academic community and policymakers. I think that’s desperately absent, particularly in this field,” said Christopher Williams, the U.S. Representative of UN-HABITAT.
All Politics Are Local: Urban Services in Zambia
In her case study of the shanty compounds on the periphery of Lusaka, Zambia, Danielle Resnick investigates how the ruling government — through “development initiatives” — suppresses political opposition and controls weaker economic and political factions. The difficult relationship between local service delivery and inter-party politics is endemic in many African countries, where local municipalities are often run by opposition parties.
Christopher Williams, in his review, praised Resnick’s work for capturing the intricacies and complexity of rapid urbanization in Zambia and beyond, noting that it offered a “scathing” critique of direct budget assistance by foreign donors.
“Land Sharing”: A New Approach for Slums in Southeast Asia
Paul Rabe’s “Land Sharing in Phnom Penh and Bangkok: Lessons From Four Decades of Innovative Slum Redevelopment Projects in Two Southeast Asian ‘Boom Towns'” examines the emerging issue of land conflict in redeveloping urban areas and innovative solutions such as land sharing. Sometimes called a “win-win-win,” land sharing through multi-use agreements based on maximized utility can help to mediate the needs of slum dwellers, private developers, and municipal governments.
Rabe found that land sharing has several limitations, including programmatic delays, muted benefits for stakeholders, and limited deployments. “In retrospect,” he said, “the institutional setting [for land sharing] is not mature enough to accommodate a fairly complex redevelopment procedure.”
If donors and civil society groups are willing to brave a complex and highly politicized environment, land sharing may be an innovative option for those looking to quell redevelopment conflict. Robin Rajack of the World Bank said it was critical for the future sustainability of growing urbanization, as improving the ability of the urban poor to navigate difficult land tenure changes may foster urban economic growth.
Maintaining Sanitation, Building Community in India
In “Desired Outcomes, Unexpected Processes: Two Stories of Sanitation Maintenance in Erode Tenements, India,” Sai Balakrishnan asks why, “within the same municipality, are residents of some tenements more willing to contribute towards septic tank maintenance than others?” Her analysis of two communities in the state of Tamil Nadu in Southern India finds that asset ownership, embedded and accessible politicians, and political patronage did not improve maintenance of sanitation infrastructure. Instead, the critical factors were the spatial proximity of infrastructure, bundling of water and sanitation services, and “street-level bureaucrats.”
Reviewer Bob Buckley of the Rockefeller Foundation asked if future research could incorporate empirical data on the costs of sanitation problems for communities, “beyond the visuals,” which could provide a deeper understanding of the difficulty of delivering services in urban slums.
Gaming Community Participation in Argentina
Josh Lerner’s “What Games Can Teach Us about Community Participation: Participatory Urban Development in Rosario’s Villas” reveals the results of his six months of fieldwork in the slums of Rosario, Argentina. Although urban redevelopment can produce conflict–especially when combined with vast inequities in economic and political power–Lerner found that taking a game theory approach to difficult land-use decisions helped to “enhance the quality of community participation, by making it more attractive, active, and effective, and making decisions fairer and more transparent.”
William Corbett of Cities Alliance warned that if developing countries cannot effectively deal with the chaotic informality of land tenure and urban development, “gangs with guns will do it for you”– particularly when urban change and resource or land scarcity provokes competition for limited resources.
Photo Credits: “Christopher Williams, Danielle Resnick; Moynahan Boardroom” courtesy of David Hawxhurst.
-
New Maternal Mortality Statistics: A Catalyst for Increased Investment
›Maternal mortality rates in many low income countries, such as India, are declining, according to a recent study by researchers at the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington. According to the report, maternal deaths have fallen from 526,000 a year in 1980 to 342,900 in 2008. This news, while welcoming, has caused dissent among some global health activists who fear donors and policymakers will dismiss the issue and call into question the higher maternal mortality rates last reported by the United Nations. While concerns over monitoring and evaluation raise important methodology questions, this news must also serve as catalyst for world leaders and donors to take action and recognize that investing in women pays.
The data reported by IHME only concludes what maternal health advocates already know. “We know how to save women’s lives, we don’t need a cure…this is a political problem and political will is essential,” said Theresa Shaver, director of White Ribbon Alliance, at a Wilson Center event in December 2008. Greater funding for family planning and access to emergency obstetric care and HIV/AIDS services should all be included in a scaling up resources for improved maternal health programs. “Without HIV, annual maternal deaths would have been 281,500 in 2008,” said Richard Horton, editor of The Lancet, in last week’s Lancet comments.
Investing in contraception and family planning services through vertical funding mechanisms can reduce maternal mortality rates by addressing all of a woman’s health needs at the time of service. To widen the platform of comprehensive services for women and their families, efforts to link public health services and offer more at one location should be expanded. “Many women have expressed a need for contraception and family planning services…when you offer family planning services on-site with HIV services, you have a huge uptake in family planning use,” shared Michelle Moloney-Kitts, assistant coordinator at the Office of the U.S. Global AIDS Coordinator at a the Wilson Center in December 2009.
Yet political will remains in short supply. “Despite strong advocacy efforts, political leaders have either ignored the call or failed to make the health of women in pregnancy a priority,” stated Horton. Six countries–Afghanistan, Democratic Republic of Congo, Ethiopia, India, Nigeria, and Pakistan–account for over half of all maternal deaths worldwide, and increased investment in these countries will improve maternal health targets, such as Millennium Development Goal (MDG) 5 seeking to reduce maternal deaths by 75 percent.
Progress is possible and “policymakers are more likely to act on issues that they think they can do something about,” said Jeremy Shiffman, associate professor of public administration at Syracuse University, at the Wilson Center in March 2009. The maternal health community must rally around these positive findings and galvanize support for greater financial contributions. “Two decades of concerted campaigning by those dedicated to maternal health is working,” said Horton.” “[G]reater investment in that work is likely to deliver even greater benefits.”
Calyn Ostrowski is the program associate for the Wilson Center’s Global Health Initiative.
Photo Credits: A woman in India safely delivers her baby in the hospital through the Madhya Pradesh Health Sector Reform program. Courtesy Flickr user Department for International Development -
As Somalia Sinks, Neighbors Face a Fight to Stay Afloat
›May 14, 2010 // By Schuyler NullThe week before the international Istanbul conference on aid to Somalia, the UN’s embattled envoy to the country, Ahmedou Ould-Abdallah, warned the Security Council that if the global community “did not take the right action in Somalia now, the situation will, sooner or later, force us to act and at a much higher price.”
The UN High Commission for Refugees (UNHCR) also issued strong warnings this week. Deputy High Commissioner Alexander Aleinikoff said in Geneva, “The displacement crisis is worsening with the deterioration of the situation inside Somalia and we need to prepare fast for new and possibly large-scale displacement.”
But the danger is not limited to Somalia. The war-torn country’s cascading set of problems – criminal, health, humanitarian, food, and environmental – threaten to spill over into neighboring countries.
A Horrendous Humanitarian Crisis
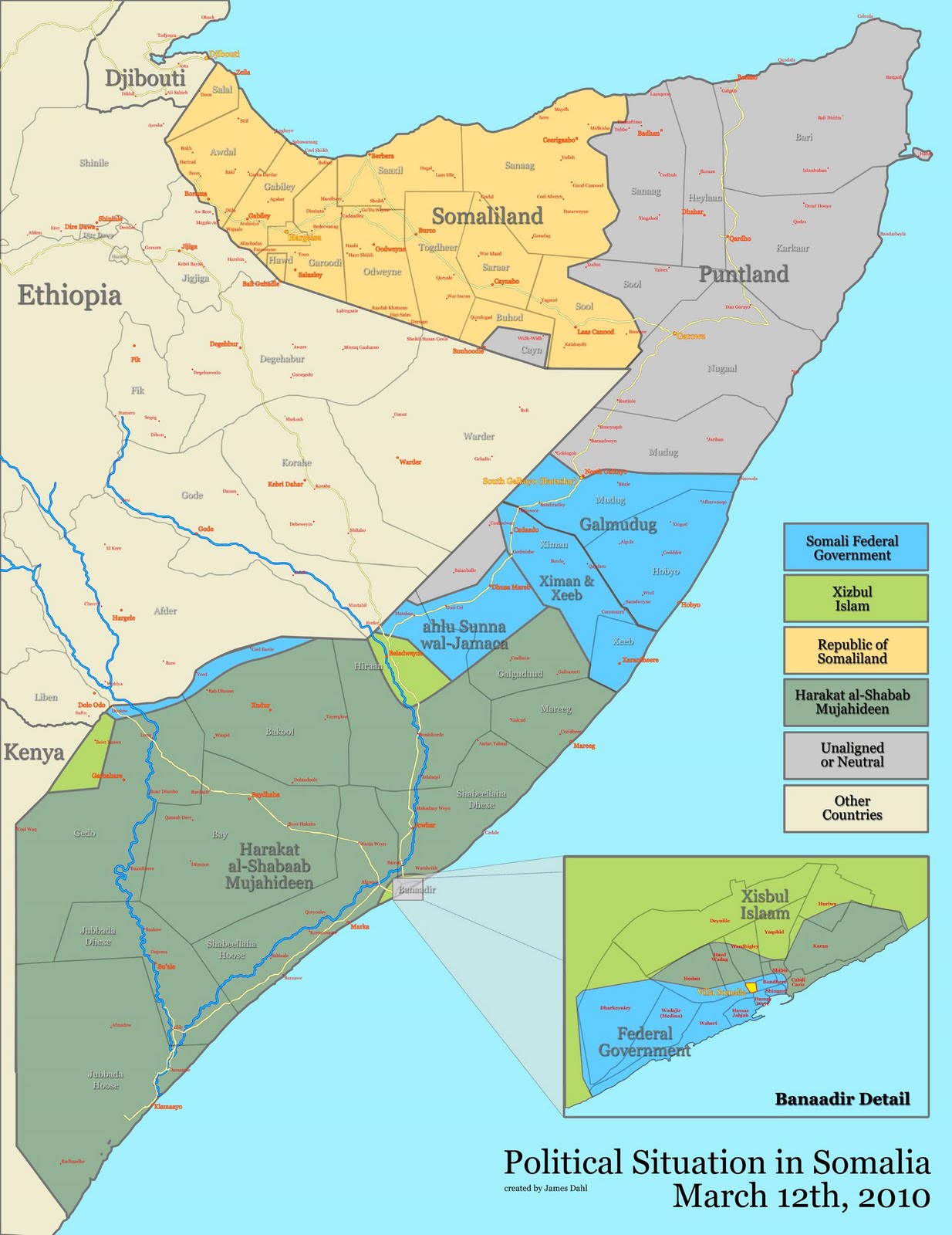
The UN- and U.S.-backed Transitional Federal Government (TFG) controls only parts of Mogadishu and small portions of central Somalia, while insurgent group Al Shabab controls nearly the entire south. The northern area is divided into semi-autonomous Somaliland and Puntland, which also fall outside of the transitional government’s control.
But the civil war is only one part of what Ould-Abdallah called a “horrendous” humanitarian crisis.
According to the UN, 3.2 million Somalis rely on foreign assistance for food – 43 percent of the population – and 1.4 million have been internally displaced by war. Another UN-backed study finds that approximately 50 percent of women and 60 percent of children under five are anemic. Most distressing, the UN Security Council reported in March that up to half of all food aid sent to Somalia is diverted from people in need by militants and corrupt officials, including UN and government employees.
Because of the country’s large youth bulge – 45 percent of Somalia’s population is under the age of 15 – food and health conditions are expected to get much worse before they get better. In the 2009 Failed States Index, Somalia ranks as the least stable state in the world and, along with Zimbabwe, has the highest demographic pressures.
Islamic Militants and the Battle for the High Seas
Yet the West continues to focus on the sensational pirate attacks on Somalia’s coast. The root cause of these attacks is not simply lawlessness say Somali officials, instead, they began partly as desperate attempts to stop foreign commercial fleets from depleting Somalia’s tuna-rich, lawless shores. A 2006 High Seas Task Force reported that at any given time, “some 700 foreign-owned vessels are engaged in unlicensed and unregulated fishing in Somali waters, exploiting high value species such as tuna, shark, lobster and deep-water shrimp.”
The transitional government opposes the fishermen-turned-pirates, but can do little to stop them. Al Shabab has thus far allowed pirates to operate freely in their territory. Their tacit approval may be tied to reports that the group has received portions of ransoms in the past.
Another hardline Islamist group, Hizbul Islam, recently took over the pirate safe haven of Haradhere, allegedly in response to local pleas for better security, but the move may simply have been part of an ongoing struggle with Al Shabab for control of pirate ransoms and port taxes – one of the few sectors of the economy that has remained lucrative.
“I can say to you, they are not different from pirates — they also want money,” Yusuf Mohamed Siad, defense minister with Somalia’s TFG, told Time Magazine.
A Toxic ThreatInitially the pirates claimed one of their goals was to ward off “mysterious European ships” that were allegedly dumping barrels of toxic waste offshore. UN envoy Ould-Abdallah told Johann Hari of The Independent in 2009 that “somebody is dumping nuclear material here. There is also lead, and heavy metals such as cadmium and mercury – you name it.” After the 2005 tsunami, “hundreds of the dumped and leaking barrels washed up on shore. People began to suffer from radiation sickness, and more than 300 died,” Hari reports.
Finnish Minister of Parliament Pekka Haavisto, speaking to ECSP last year, urged UN investigation of the claims. “If there are rumors, we should go check them out,” said the former head of the UN Environment Program’s Post-Conflict Assessment Unit:I think it is possible to send an international scientific assessment team in to take samples and find out whether there are environmental contamination and health threats. Residents of these communities, including the pirate villages, want to know if they are being poisoned, just like any other community would.
To date, there has been no action to address these claims.
Drought, Deforestation, and Migration
While foreign entities may have been exploiting Somalia’s oceans, the climate has played havoc with the rest of the country. Reuters and IRIN report that the worst drought in a decade has stricken some parts of the interior, while others parts of the country face heavy flooding from rainfall further upstream in Ethiopia.
Land management has also broken down. A 2006 Academy for Peace and Development study estimated that the province of Somaliland alone consumes up 2.5 million trees each year for charcoal, which is used as a cheaper alternative to gas for cooking and heating. A 2004 Somaliland ministry study on charcoal called the issue of deforestation for charcoal production “the most critical issue that might lead to a national environmental disaster.”
West of Mogadishu, Al Shabab has begun playing the role of environmental steward, instituting a strict ban on all tree-cutting – a remarkable decree from a group best known for their brutal application of Sharia law rather than sound governance.
The result of this turmoil is an ever-increasing flow of displaced people – nearly 170,000 alone so far this year, according to the Washington Post – driven by war, poverty, and environmental problems. The burden is beginning to weigh on Somalia’s neighbors, says the UNHCR.
The Neighborhood Effect
One of the largest flows of displaced Somalis is into the Arabian peninsula country of Yemen – itself a failing state, with 3.4 million in need of food aid, 35 percent unemployment, a massive youth bulge, dwindling water and oil resources, and a burgeoning Al Qaeda presence.
In testimony on Yemen earlier this year, Assistant Secretary of State Jeffrey Feltman said that the country’s demographics were simply unsustainable:Water resources are fast being depleted. With over half of its people living in poverty and the population growing at an unsustainable 3.2 percent per year, economic conditions threaten to worsen and further tax the government’s already limited capacity to ensure basic levels of support and opportunity for its citizens.
Other neighboring countries face similar crises of drought, food shortage, and overpopulation – Ethiopia has 12 million short of food, Kenya, 3.5 million, says Reuters. UNHCR reports that in Djibouti, a common first choice for fleeing Somalis, the number of new arrivals has more than doubled since last year, and the country’s main refugee camp is facing a serious water crisis.
A Case Study in Collapse
The ballooning crises of Somalia encompass a worst-case scenario for the intersection of environmental, demographic, and conventional security concerns. Civil war, rapid population growth, drought, and resource depletion have not only contributed to the complete collapse of a sovereign state, but could also lead to similar problems for Somalia’s neighbors – threatening a domino effect of destabilization that no military force alone will be able to prevent.
Speaking at a naval conference in Abu Dhabi this week, Australian Vice Admiral Russell Crane told ASD News that, “The symptoms (piracy) we’re seeing now off Somalia, in the Gulf of Aden, are clearly an outcome of what’s going on on the ground there. As sailors, we’re really just treating the symptoms.”
Sources: Academy for Peace and Development, AP, ASD News, Carnegie Endowment for International Peace, Christian Science Monitor, Foreign Policy, High Seas Task Force, Independent, IRIN, New York Times, Population Action, Population Reference Bureau, Reuters, Telegraph, Time, UN, US State Department, War is Boring, Washington Post.
Photo Credits: “Don’t Swim in Somalia (It’s Toxic)” courtesy of Flickr user craynol and “Somalia map states regions districts” courtesy of Wikimedia Commons.
 A Publication of the Stimson Center.
A Publication of the Stimson Center.