Showing posts from category UN.
-
How Did We Arrive at 7 Billion – and Where Do We Go From Here? [Part One]
›October 26, 2011 // By Elizabeth Leahy MadsenThe United Nations Population Division has estimated world population will reach seven billion on Monday. Which changes in demographic trends led us to this milestone? What do the past and present tell us about how human numbers will change in the future?
The “Day of Seven Billion” was announced this spring following the release of the latest revision of UN population projections. Although the seven billionth person will not be precisely identified, this estimate is based on careful demographic modeling. Every two years, the UN revises its projections to incorporate the latest trend data and modify its assumptions, as seemingly small changes can make a huge difference demographically.The UN estimates that the seven billionth person alive today will be born on October 31. Demographer Elizabeth Leahy Madsen explains how we got to that number, its significance, and where our demographic path might take us from here. Read part two here.
The United Nations Population Division has estimated world population will reach seven billion on Monday. Which changes in demographic trends led us to this milestone? What do the past and present tell us about how human numbers will change in the future?
The “Day of Seven Billion” was announced this spring following the release of the latest revision of UN population projections. Although the seven billionth person will not be precisely identified, this estimate is based on careful demographic modeling. Every two years, the UN revises its projections to incorporate the latest trend data and modify its assumptions, as seemingly small changes can make a huge difference demographically.
Demography Is Driven by Fertility and Population Momentum
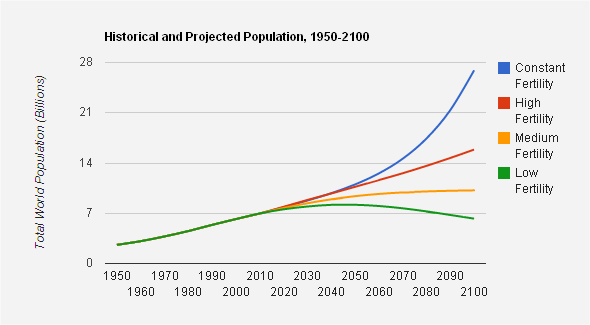
Since world population reached three billion in 1959, the rate of growth has increased, peaked, and begun to slow. Each succeeding milestone was reached more quickly than the last: It took 15 years to reach four billion, 13 years to hit five billion, and only 11 years to get to six billion at the end of 1998. The interval leading to seven billion was slightly longer, at 13 years, as the global rate of population growth has slowed.
Although mortality and migration also affect population trends, the factor with the greatest influence by far is fertility – the average number of children born to each woman. The decline in the global fertility rate from an average of nearly 5 children per woman in the early 1960s to 2.5 children today has in turn slowed the pace of world population growth. However, demographic momentum from previous generations of high fertility can drive population growth for decades to come. Even if Nigeria reached replacement-level fertility today, its population would still grow by one-third by 2050 as the number of births continued to exceed the number of deaths.
Assumptions Matter
Population projections consider: 1) current data about fertility and 2) assumptions about the ways fertility will change in the future. These assumptions vary depending on the source, so how much of a difference do they make? As it turns out, quite a lot.
Projections of world population in 2050 range from 8.1 billion (if fertility rates fall to a global average of 1.7 children per woman) to 10.9 billion (if they remain unchanged). The gap of nearly three billion between those possibilities is greater than the combined populations of China and India today.
Estimates vary even more widely for the end of the century, with the UN projecting that by 2100 world population could total anywhere between 6 billion (if total fertility falls to an average of 1.55 children per woman) and 27 billion (if every country’s fertility rates remain constant at today’s levels).
While demographers parse the details of the projections, policymakers would like to know which of these scenarios is more likely. After all, the economic, environmental, and political consequences of a population of 8 or 11 billion two generations hence are not the same, and a world of 27 billion is difficult for anyone to fathom.
If we simply projected past trends into the future at a steady rate, the population estimates on the low end of the fertility spectrum seem more likely. The global fertility rate has fallen from 4.5 children per woman in the early 1970s to 2.5 today, a decline of 43 percent, so the 14 percent decline projected in the medium-fertility variant between now and 2050 seems reasonable at first glance, perhaps even conservative. The medium-fertility variant assumes that all countries’ fertility rates will begin moving towards replacement level, around 2.1 children per woman, regardless of whether they are currently above or below that number.
However, even a 14 percent decline in fertility assumes that areas where fertility rates remain stalled at high levels will soon begin rapid declines, paralleling the past experience of other regions. As Population Reference Bureau demographer Carl Haub writes, “the assumption that the developing world will necessarily follow the path of the industrialized world…is far from a sure bet.”
In the last 40 years, fertility rates in the Caribbean, northern and southern Africa, Latin America, and all of Asia declined by 50 percent or more. The pace of decline in sub-Saharan Africa, while still notable, was much slower, at 23 percent. In order to meet the UN medium-variant projections, the region’s fertility rate would need to fall by nearly 40 percent by mid-century.
Some of the largest, fastest-growing populations in the developing world would need to experience a major acceleration from recent trends. In Nigeria, fertility edged down by 15 percent between 1970 and 2010, but the medium variant projection depends on a decline of 37 percent over the next four decades; Ethiopia’s fertility rate will need to fall by half.
Gender Matters, Too
The great irony of fertility trends is that gender inequities play an important role at both ends of the scale. In countries with the highest fertility rates, women tend to have less education than men and less autonomy. Their fertility choices may be greatly affected by the preferences of their husbands or other family members. In Niger, which has the highest fertility rate in the world, married men would, on average, like three more children than married women. In Uganda, where women average more than six children each, 60 percent of men report that domestic violence is justified.
By contrast, in countries with the lowest fertility rates, women have achieved equal access to education and the labor market, with more autonomy about how to earn income and what to do with it. Yet cultural expectations that place the burden for child and elder care and housework almost entirely on women can make marriage an unappealing option. In Japan, which is among the 10 lowest fertility countries in the world, more women are choosing to stay single: The marriage rate has fallen by almost half since the 1970s. Japanese women who do marry are waiting until their late 20s and tend not to give birth until they are 30, both of which result in lower average family size.
Even at this end of the demographic spectrum, the assumptions embedded within population projections seem optimistic. Japan’s fertility rate was last above replacement level in the early 1970s; it has fallen steadily to 1.3 children per woman today. The UN projections assume that fertility will immediately reverse track and begin rising to over 1.8 children per woman in 2050, rebounding above two children per woman before the end of the century.
The stalled high fertility rates in much of sub-Saharan Africa and parts of the Middle East, together with unprecedented low fertility in Eastern Europe and parts of East Asia, indicate that we are currently in an era of remarkable demographic diversity, despite the UN’s projection of future convergence.
Continue reading part two here.
Elizabeth Leahy Madsen is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and former senior research associate at Population Action International.
Sources: Boling (2008), Haub (2011), Japan Statistics Bureau, Measure DHS, UN Population Division, UN Population Fund, Washington Post.
Image Credit: Chart data from UN Population Division, arranged by Elizabeth Leahy Madsen. -
Watch: Dennis Taenzler on Four Key Steps for REDD+ to Avoid Becoming a Source of Conflict
›The UN Program on Reducing Emissions from Deforestation and Forest Degradation (REDD) provides financial incentives to developing countries to conserve their forests and invest in low-carbon pathways to sustainable development. However, it may also be a potential new source of conflict, says Dennis Taenzler, a senior project manager at adelphi in Berlin, who works on climate and energy policies as well as peace and conflict issues.
-
John Donnelly, Global Post
Family Planning and Seven Billion at the Aspen Institute
›September 9, 2011 // By Wilson Center Staff
The original version of this article, by John Donnelly, appeared on Global Post.
Sometime this fall, the world’s population will reach 7 billion people. Experts now forecast that by 2050, the population could be 10 billion.
Those numbers, said the former presidents of Chile and Latvia at an event in Washington D.C., Wednesday night, should force policy makers to focus more intently on making family planning much more widely available in the developing world.
“When we are 9, 10 billion people, what are we going to do? Go to Mars? Go to the moon?” said Michelle Bachelet, the former president of Chile and now the Under Secretary-General and Executive Director of UN Women, the latest agency created by the United Nations. “We are really going to have huge problems. Family planning is a huge issue.”
Her comments came during a series of discussions organized by Aspen Global Health and Development called “7 Billion: Conversations that Matter.” The talks, funded in part by the U.S. Agency for International Development, have often centered on global health issues, and Wednesday’s event was no different.
Continue reading on Global Post.
Video Credit: The Aspen Institute. -
Alex Evans, Global Dashboard
Is it Time for Sustainable Development Goals?
›September 8, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Alex Evans, appeared on Global Dashboard.
From MDGs to…SDGs? That’s one of the ideas swirling around in discussions ahead of the Rio 2012 sustainable development summit next year, anyway.
You can see the attraction. With less than a year to go, there are precious few concrete ideas on the table for what the summit might produce, especially in the area of “institutional framework for sustainable development,” one of two key themes for the event (sure, there’s much talk of a new World Environment Organization, but color me very unconvinced of the case for that). So might SDGs help to fill the gap?
Well, that would depend on what they cover. The government of Colombia has set out a proposal for SDGs that would cover various sectors – atmosphere, climate resilience, land degradation, sustainable agriculture, biotech, waste and so forth. This would mainly be about ‘reaffirming’ (that awful word – who, other than diplomats, ever ‘reaffirms’ anything?) commitments made at Rio 1992. But you have to wonder: important though delivery of existing commitments undoubtedly is, is ‘reaffirmation’ of stuff agreed 20 years ago really going to set any pulses racing outside the sustainable development priesthood?
Continue reading on Global Dashboard.
Sources: UN.
Image Credit: Adapted from UNSCD 2012 official logo. -
Youth Bulge and Societal Conflicts: Have Peacekeepers Made a Difference?
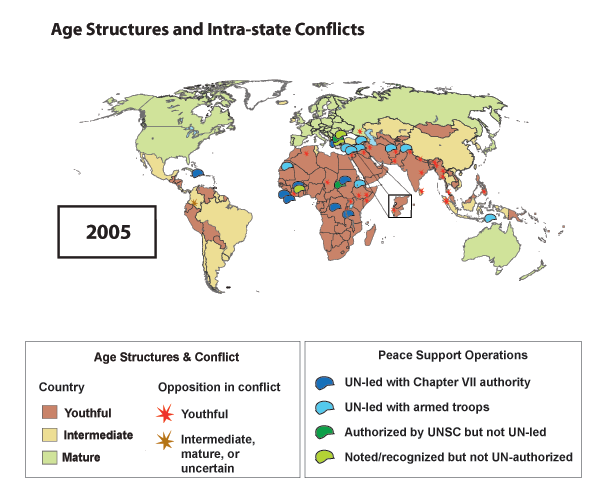
›August 22, 2011 // By Richard CincottaUntil recently, the question of which countries are at the most risk of violent societal conflict could be answered with a terse, two-part response: “the young and the war-torn.” This simple characterization regarding youth and conflict worked well, until the first decade of the 21st century. The proportion of youthful countries experiencing one or more violent intrastate conflicts declined from 25 percent in 1995 to 15 percent in 2005. What’s behind this encouraging slump in political unrest? One hypothesis is that peace support operations (PSOs) – peacekeepers, police units, and specialized observers that are led, authorized, or endorsed by the United Nations – have made a difference.
From the 1970s through the 1990s, more than 90 percent of all societal conflicts broke out in countries with a youthful age structure – a population with a median age of 25 years or less. And wherever civil and ethnic wars emerged, they tended to persist. The average societal conflict that began between 1970 and 1999 continued without a one-year break in battle-associated fatalities for about six years. Some – including the Angolan civil war, Northern Ireland’s “Troubles,” Peru’s war against the Shining Path, and the Afghan civil war – endured for decades. In contrast, inter-state conflicts that began between 1970 and 1999 lasted, on average, less than two years (see the UCDP/PRIO Conflict Database).
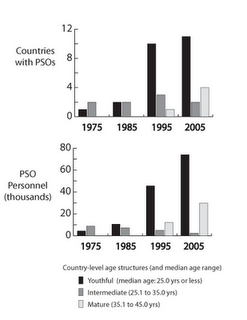
Taking on Intra-State Conflicts Beginning in the early 1990s, however, there was a marked expansion in size and number of PSOs deployed in the aftermath of societal warfare, which appears to have dampened the persistence of some conflicts and prevented the reemergence of others. The annual number of active PSOs deterring the re-emergence of societal conflict jumped from just 2 missions during 1985 to 22 in 2005. In contrast, those led, authorized, or endorsed by the UN to maintain cease-fire agreements between neighboring states during that same period only increased from three active missions to four. By 2009, nearly 100,000 peacekeepers were stationed in countries that had recently experienced a societal conflict. About 70 percent were deployed in countries with a youthful population (see Figures 2A and B). Why the sudden expansion in use of PSOs?
Beginning in the early 1990s, however, there was a marked expansion in size and number of PSOs deployed in the aftermath of societal warfare, which appears to have dampened the persistence of some conflicts and prevented the reemergence of others. The annual number of active PSOs deterring the re-emergence of societal conflict jumped from just 2 missions during 1985 to 22 in 2005. In contrast, those led, authorized, or endorsed by the UN to maintain cease-fire agreements between neighboring states during that same period only increased from three active missions to four. By 2009, nearly 100,000 peacekeepers were stationed in countries that had recently experienced a societal conflict. About 70 percent were deployed in countries with a youthful population (see Figures 2A and B). Why the sudden expansion in use of PSOs?
According to William Durch and Tobias Berkman, this upsurge was less a change of heart or modification of a global security strategy and more an outcome of the unraveling web of Cold War international relations. Before the 1990s, the majority of PSOs were United Nations-led operations that were mandated to monitor or help maintain cease-fires along mutual frontiers. Because insurgents were typically aligned with either the Soviets or a Western power, Security Council authorization to mediate a societal conflict was difficult to secure.
This situation changed with the breakup of the Soviet Union and the initiation of PSOs by regional organizations, including operations by the Economic Community of West African States (ECOWAS) in Liberia and Sierra Leone and the NATO-led Kosovo Force in 1998-99.
Demographic Forecasting
What do national demographic trends suggest for the demand for PSOs over the next two decades? For societal conflict, political demographers foresee that the demand for PSOs will continue to decline among states in Latin America and the Caribbean – with the exception of sustained risk in Guatemala, Haiti, Bolivia, and Paraguay. Similarly, demand for peacekeeping is expected to continue to ebb across continental East Asia.
Gauged by age structure alone, the risk of societal warfare is projected to remain high over the coming two decades in the western, central, and eastern portions of sub-Saharan Africa; in parts of the Middle East and South Asia; and in several Asian-Pacific island hotspots – Timor-Leste, Papua New Guinea, the Philippines, and Solomon Islands. But even in some countries that are losing their youthful blush, domestic political relations could turn out less rosy than this simple age-structural model forecasts.
In other words, there are roadblocks to a “demographic peace.” Among them is an increasing propensity for a specific demographic configuration of ethnic conflict: warfare between state forces and organizations that recruit from a minority that is more youthful than the majority ethnic group. Examples of these conflicts include the Kurds in Turkey, the Shiites in Lebanon, the Pattani Muslims in southern Thailand, and the Chechens of southern Russia.
However, this twist on the youth bulge model of the risks of societal conflict is a discussion for another installment on New Security Beat. Suffice it to say that when political demographers look over the UN Population Division’s current demographic projections, they see few signs of either the waning of societal warfare, or the withering of the current level of demand for PSOs.
Richard Cincotta is a consultant on political demography for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Program and demographer-in-residence at The Stimson Center.
Sources: PRIO, The Stimson Center, UN Population Division.
Chart Credit: Data courtesy of the UN Population Division 2011, PRIO, and Durch and Berkman (2006). Arranged by Richard Cincotta. -
Deirdre LaPin, Niger Delta Working Group
Next Step, Clean Up the Niger Delta: The UNEP Ogoni Environmental Report
›August 12, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Deirdre LaPin, appeared on the Niger Delta Working Group and AllAfrica.
The long-awaited report from the United National Environmental Program (UNEP) on oil damage in the Ogoni area was presented to President Goodluck Jonathan on August 4 in Abuja. This important study, the first of its kind in the Niger Delta, was conceived well before 2006 by the Federal Government as part of the Ogoni reconciliation and peace process led by Father Matthew Kukah (recently named Bishop of Sokoto). Intended as a major assessment of the impacts of oil production in the Ogoni region, UNEP in an early statement described the aim as to “clarify and de-mystify concerns expressed by local communities.” [Audio Below]
Shell Petroleum Development Company (SPDC) suspended active production in Ogoniland in late 1993 as a response to growing resistance to industry presence led by the martyred freedom fighter and writer Ken Saro-Wiwa. However, the company remained responsible during its withdrawal for monitoring and maintaining its installations, and especially the critical Trans-Niger pipeline serving Bonny Terminal. It also left behind a number of spill sites.
Deirdre LaPin on the History of Inequality in the Niger Delta [Excerpted Version] by ECSP WWC
Over the years the company had mixed success in negotiating with local communities access to spills sites or achieving their complete remediation. The impoverished local population also pursued informal oil production that centered on bunkering (oil pipeline tapping) and bush refining – increasing opportunities for further spills and pollution. In keeping with the “polluter pays” principle, the operator SPDC joint venture funded the U.S. $9.5 million UNEP study.
Last week the press had a field day with the freshly unveiled report.
Journalists whisked together highlights and added spice from the region’s contested history. Some articles cooked in the press kitchen missed key ingredients or simply got them mixed up. The best among them focused on the findings from the study’s careful scientific analysis, which led UNEP to the conclusion that “pollution has perhaps gone further and penetrated deeper than many may have previously supposed.”
This forceful opinion stated in the foreword by UNEP’s executive director Achim Steiner represents a long step beyond the study’s original technical terms of reference or the limited policy aims supporting reconciliation and “de-mystification.”
Now in 2011, UNEP’s thoughtful recommendations, while not assigning blame, point clearly to the need for a genuine shift in the priorities and practices of the oil industry and governmental regulatory agencies operating throughout the Niger Delta. The muscular sub-text rippling throughout the report makes clear that nothing less than ending pollution and full remediation of Ogoniland (and indeed the whole Niger Delta region) should be accepted as an end point.
Continue reading on the Niger Delta Working Group.
For more on the Niger Delta, be sure to also read “Nigeria’s Future Clouded by Oil, Climate Change, and Scarcity,” which includes the full audio interview with Deidre LaPin (excerpted above) on the history of the Niger Delta.
Sources: UNEP.
Photo Credit: NASA Space Shuttle Overflight photo of the Niger Delta, courtesy of NASA. -
UN Security Council Debates Climate Change
› Today the UN Security Council is debating climate change and its links to peace and international security. In this short video, ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko outlines his hopes for today’s session and its follow-on activities. He suggests it is time to move from problem identification to problem solving by developing practical steps to respond to climate-security links.
Today the UN Security Council is debating climate change and its links to peace and international security. In this short video, ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko outlines his hopes for today’s session and its follow-on activities. He suggests it is time to move from problem identification to problem solving by developing practical steps to respond to climate-security links.
This Security Council debate was held at the instigation of the German government, chair of the Security Council this month. But it is not the first time this body has debated climate and security. In 2007, the United Kingdom used its prerogative as chair to introduce the topic in the security forum. Opinions from member states diverged on whether the Security Council was the appropriate venue for climate change.
Largely at the instigation of the Alliance of Small Island States, the UN General Assembly tackled climate and security links in 2009. The resulting resolution also spurred the UN Secretary-General to produce a summary report on the range of climate and security links.
Sources: Reuters, UN. -
World Population Day 2011: The Year of Seven Billion
›July 11, 2011 // By Schuyler NullThe UN Population Fund established World Population Day as a day of awareness about global population in 1987. As we approach seven billion just 24 years later, the UN is kicking off their 7 Billion Actions campaign, designed to raise awareness about the resource, health, and environmental challenges raised by our numbers. Population and its more detailed cousin-indicator, demography, impact the world in a great many ways – from contributing to resource scarcity and environmental destruction to creating social imbalances that can lead to civil instability.
Check out a few of New Security Beat’s most recent stories on population to get a sense of why it’s such an important but oft-simplified and misunderstood indicator and where it matters most.
Photo Credit: “World population,” courtesy of flickr user Arenamontanus.- One in Three People Will Live in Sub-Saharan Africa in 2100, Says UN
- Ten Billion: UN Updates Population Projections, Assumptions on Peak Growth Shattered
- Tunisia Predicted: Demography and the Probability of Liberal Democracy in the Greater Middle East
- Watch: Demographic Security 101 With Elizabeth Leahy Madsen
- Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions
- Guest Contributor Michael Kugelman: Pakistan’s Population Bomb Defused?
- Dot-Mom: USAID Egypt’s Health and Population Legacy Review
- Watch: Eric Kaufmann on How Demography Is Enhancing Religious Fundamentalism
- Consumption and Global Growth: How Much Does Population Contribute to Carbon Emissions?