-
Joan Castro on Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management in the Southern Philippines
› In the southern Philippines, the innovative IPOPCORM program “worked in areas where there is high…marine biodiversity, high population, and high population momentum, which means…about 40 percent of the population are 15 years and below,” Joan Castro told ECSP in this interview. Castro, the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., recently spoke at the Wilson Center on the state of integrated development efforts in her country and elsewhere.
In the southern Philippines, the innovative IPOPCORM program “worked in areas where there is high…marine biodiversity, high population, and high population momentum, which means…about 40 percent of the population are 15 years and below,” Joan Castro told ECSP in this interview. Castro, the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., recently spoke at the Wilson Center on the state of integrated development efforts in her country and elsewhere.
From 2000-2006, IPOPCORM (which stands for “integrated population and coastal resource management”) sought to integrate population, health, and environment (PHE) development efforts in Philippine communities. They had four primary objectives, said Castro: 1) improve the reproductive health of the community members; 2) improve management of the coastal resources; 3) increase knowledge of the linkages between population, health, and the environment; and 4) increase the capacity of community leaders to advocate for these links.
“The aspect of livelihoods was very essential,” said Castro, especially for empowering women in the communities. Through family planning services and micro-credit finance initiatives, women were able to better space their pregnancies and contribute to household incomes, she said. In addition, by establishing locally managed, marine protected areas, IPOPCORM increased the protection of high biodiversity zones and improved the likelihood that there will be enough fish to feed future generations.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Youth Revolt in Egypt: A Country at the Turning Point
›March 2, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Farzaneh Roudi-Fahimi, Shereen El Feki, and Tyjen Tsai, appeared at the Population Reference Bureau.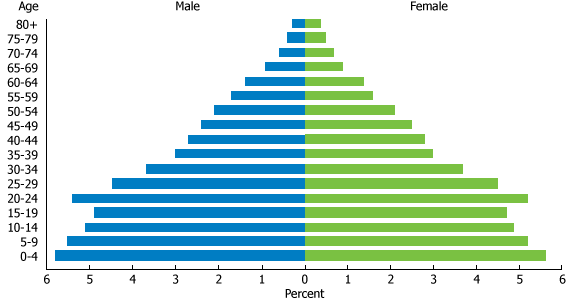
Egyptians know some dates by heart: July 26, 1952, marks the overthrow of Egypt’s last monarch; October 6, 1973, is the date of the country’s attack to reclaim the Sinai Peninsula. Now another date can be added to that list: January 25, 2011, the first day of anti-government protests that led to President Hosni Mubarak’s resignation 18 days later. Mubarak ruled Egypt for nearly 30 years, during which the country’s population grew by 90 percent – from 45 million to 85 million according to UN estimates, despite concerted government campaigns to slow population growth. The demographic strength of Egypt is undeniable, not just in absolute numbers but in its age distribution. Egypt is experiencing a “youth bulge:” One in five Egyptians is between ages 15 and 24, and one-half of the population is below age 25 (see figure above), a powerful engine of renewal for the country.
Youth as the Drivers of Change
Egyptians of all ages and walks of life participated in the protests, unified in aspirations and demands including political freedom, better wages, and better working conditions. But it was the astonishing numbers of young people participating in demonstrations that gave the uprising its momentum, and were key to sustaining it, as hundreds of thousands gathered in Tahrir (Liberation) Square in Cairo and other cities across the country. Egypt’s youth are the faces behind this leaderless revolution; the revolt, in large part, was spurred by their finesse in using social media to organize and make their voices heard.
Young people arguably have the most at stake in the outcome of this revolution. The results have immediate impact and future implications in how they construct their lives. Recent studies show the frustrations young Egyptians feel at the stagnancy of their lives. They are a generation waiting for better access to quality education, secure employment, and the financial stability necessary to get married and start their own families.
Continue reading at the Population Reference Bureau.
Sources: UN Population Division.
Image Credit: Population pyramid from PRB, data from the UN Population Division. -
The Middle East’s Demographic Destiny
›February 25, 2011 // By Jennifer Dabbs SciubbaThe original version of this article, by Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba, appeared on her blog. Sciubba will be speaking at the Wilson Center on March 14 about her newest book The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security.
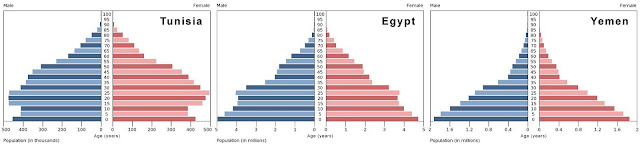
The so-called “arc of revolution” sweeping across the Middle East and North Africa has some demographers feeling smug. In Egypt, Tunisia, Algeria, Jordan, and Lebanon the population ages 15-29 – a key group for demographers – is very large, about 41-50 percent of all adults ages 15-59. No matter where you’re born, this life period is significant because during this time young adults expect to finish their education, get a job, get married, maybe start a family, and have some say in the way they are governed. As many have noted, the problem in each of these countries is that the desires of young adults are being dashed as they are shut out of economic, political, and even social opportunities. The result is all over the headlines.
Aside from structural failures like corruption and inattention of politicians to creating jobs, why are young people so disadvantaged? The answer lies in demography. Opportunities for young adults are limited in these countries because of what demographers refer to as “cohort crowding,” a situation that results when an age group, in Tunisia’s case those aged 25-29, is significantly larger than the preceding age group. Generally, jobs cannot be created fast enough to keep pace with this demographic bump, so those in the large cohorts are “crowded” out of the labor market. This situation turns into protest and violence when youth from large cohorts fall short of the living standards of preceding generations, which are smaller. In a 2009 Pew Global Attitudes survey, 50 percent of respondents ages 18-29 in Egypt said they thought children born today would be worse off than their parents. In Jordan and Lebanon, 38 and 40 percent, respectively, of respondents had a similarly depressed attitude.
Continue reading on The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security blog.
Sources: Pew Research Center, U.S. Census Bureau.
Photo Credit: “DS-RY028 World Bank,” courtesy of flickr user World Bank Photo Collection (Dana Smillie). -
Watch: Laurie Mazur on a Pivotal Moment for the Global Environment and World Population
›February 24, 2011 // By Hannah Marqusee“It’s increasingly clear that we are living in a pivotal moment,” said Laurie Mazur, director of the Population Justice Project, in this interview with ECSP about her new book, A Pivotal Moment: Population, Justice, and the Environmental Challenge. Currently, “nearly half the world’s population – about three billion people – are under the age of 25,” she said, and the choices these young people make, and the choices that are available to them “will determine whether world population grows from the current almost 6.9 billion to anywhere between 8 billion and 11 billion.”
“Numbers do matter,” said Mazur. “Clearly, a world population of 8 billion would be better than 11 billion for both human beings and the environment.” What’s more, “everything we need to do to slow population growth is something we should be doing anyway.”
Investments in family planning, girls’ education, women’s empowerment, and sustainable, equitable development are all means to slowing population growth, as well as being an end in and of themselves. Population growth “is an issue of really broad appeal” and should be of concern to environmental and reproductive health advocates, people of faith, or anyone who cares about development, justice, and eliminating poverty, said Mazur. -
QDDR Coverage Wrap-up: Institutional Shifts, Development-as-Security, Women’s Empowerment, and Complex New Threats
›February 23, 2011 // By Schuyler NullSomewhat lost in the wake of turmoil in the Middle East and the budget battle in Congress has been the State Department’s most aggressive attempt yet to reshape itself for the dynamic foreign policy challenges of the 21st century.
-
Yemen’s Revolt Won’t Be Like Egypt or Tunisia
›February 15, 2011 // By Schuyler NullInspired by the success of the recent Tunisian and Egyptian revolts, another key state in the Middle East is under pressure from youth-led unrest: Yemen. Again the United States must decide whether to support a corrupt autocrat (albeit one that has been helpful in the war on terror) or face the uncertainty of life without. The Saleh regime in Yemen has been in power for three decades, but major protests led by multiple opposition groups have forced recent concessions, including agreement that neither President Ali Abdullah Saleh nor his son will run for re-election in 2013.
-
More on Tunisia’s Age Structure, its Measurement, and the Knowledge Derived
›February 4, 2011 // By Richard CincottaThis post is a response to the questions and comments that my fellow demographers Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, Jack Goldstone, and Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba put to my recent assessment of Tunisia’s chances for democracy. I’ve divided my response to address the principal questions. (Note: Throughout, “young adults” refers to 15-24 year olds, and “working age population” refers to those between 15-64 years old.)
1. Tunisia’s age structure is still quite young – aren’t the effects associated with youth bulge still at work?
Tunisia’s age structure (median age, 29 years) is in the early stages of transiting between the instability that typically prevails in countries with youthful age structures (median age <25), and the stability that is typical of mature structures (median age between 35 to 45). I classify Tunisia’s age structure as intermediate (between 25 to 35). The Jasmine Revolution has featured a mix of both types of sociopolitical behavior: some violence and property damage, perpetuated by both the state and demonstrators; evidence of a mature, professionally-led institution (the Tunisian army); and demonstrations that are peaceful and in which women and older people participate.
By any legitimate youth bulge measure, Tunisia’s age-structure is similar to that of South Korea, Taiwan, and Thailand’s during the mid-1990s. In 2010, Tunisia’s proportion of young adults in the working age population was almost precisely the same as South Korea’s in 1993. South Korea’s median age in 1993 was 28.5, compared to Tunisia’s 29 today.
Consistent with these numerical similarities, Tunisia’s political behavior is not much different than the sociopolitical events observed in South Korea, Taiwan, or Thailand in the early 1990s when these countries experienced an age structure of similar maturity. As these countries matured, political violence and destructive protests occurred less frequently but dissidence lingered in more peaceful, isolated incidents. For example, South Korea experienced several deadly anti-U.S. demonstrations in 1988-89 and only a few minor incidents in the early 1990s. By 1993, the public was demonstrating against extremism, and public protest had turned peaceful and symbolic.
Even today, public protest in Thailand (median age, 33 years) is commonplace. Thai political rights are constrained, and accordingly the country has been dropped in Freedom House’s annual assessment of political freedoms from “free” to “partly free.” However, unlike the student and worker riots that occurred sporadically throughout the 1970s and 80s, Thai demonstrations are typically non-confrontational political rallies attended by T-shirt-clad grandparents and families who bus into town for the event.
2. Why use the population’s median age rather than the youth bulge measures that political demographers (including me) have previously employed with considerable success?
I’m experimenting, and so far, I’ve found that median age replicates prior published results concerning civil conflict and stable liberal democracy. Median age’s ability to span the entire length of the demographic life-cycle of the state is its primary advantage. Youth bulge indicators do not; neither do indicators focused on working-age adults, nor those measuring seniors. In addition, median age integrates many factors that change in parallel with the age-structural transition, including income, education, women’s participation in society, secularization, and technological progress. Still, median age doesn’t track the youth bulge measures perfectly, so why use it?
Currently, foreign affairs policymakers see few linkages between a country’s (1) risk of civil and political violence; (2) its propensity to accumulate savings and human capital; (3) its chances of attaining stable liberal democracy; (4) the challenges that arise to adequately funding pensions and senior healthcare; and (5) rapid ethnic change in low fertility societies. Political demographers understand that these effects on the state are indeed related and that the rising and ebbing probabilities associated with these effects occur sequentially. Understanding this sequence is key to understanding the world’s international relations future. Median age allows political demographers to view that sequence.
As Jennifer Sciubba points out, the disadvantage of median age is its apparent lack of resonance with theories that have historically informed political demography, including theories of cohort crowding, dependent support, and life-cycle savings. I don’t believe that political and economic demographers should (or will) abandon these indicators, which help them observe the inner workings of age-structural phenomena. Nonetheless, I find it useful to make analysts aware of the advantageous and disadvantageous pressures that age structure exerts across the entire demographic life cycle of the state.
3. Can the deposed regime’s multi-faceted problems be captured by the age-structural transition?
No, age-structure cannot account for leadership – clumsy or deft, corrupt or honest. The method is limited to predictions that draw on sociopolitical behaviors that are associated with age structures, or by knowledge gained from deviations from these predictions. Nonetheless, I question the value of many of the after-the-fact observations of the Ben Ali Regime. Tunisia’s fallen regime was indeed oppressive, corrupt, and nepotistic – but so are most authoritarian regimes in Asia and Africa. Lack of job creation and preferential access to employment are valid grievances across much of the developing world, but the lack of informal sector statistics renders country comparisons difficult.
Some analysts have hypothesized that global warming has been a contributor (also applied to Egypt), others point to economic globalization and pressures on Tunisia’s middle class. Whether these assertions are wrong or right, it is difficult for me to see how such post hoc observations add to analysts’ knowledge of regime change or democratization or help them explain why other countries with similar problems have not undergone similar sociopolitical dynamics. In contrast, hypotheses based on quantitative relationships between age structural indicators and sociopolitical behaviors generate testable and repeatable predictions that can be checked and held accountable after an event.
What I find most surprising about the age-structural approach to predicting liberal democracy is how often states ascend to liberal democracy as they approach, or pass, the 0.50 probability mark. If either “triggers” of regime change or key institutions were very important, this observation would be unlikely.
A Concluding Note on Political Demography
If political demographers are serious about advancing policymakers’ ability to understand the present and future of global politics and security, political demography will have to become a scientific discipline – a field of study in which assertions are consistently tied to data and tested whenever possible. In many cases, though not all, we’re lucky – demographers provide us with timely estimates and projections at the national level. Nonetheless, for our field to succeed, political demographers must take full advantage of these data, encourage sub-national data to be collected and published, and make a clean break from the tradition of conjecture that currently pervades international relations.
Richard Cincotta is a consulting political demographer for the Wilson Center’s Environmental Change and Security Project and demographer-in-residence at the Stimson Center.
Sources: CIA World Factbook, Freedom House, Jadaliyya.
Image Credit: Adapted from “Viva the Tunisian Revolution,” courtesy of flickr user freestylee (Michael Thompson). -
Book Preview: ‘The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security’
›February 3, 2011 // By Christina DaggettThe word “population” doesn’t come up too often in national security debates, yet, a shift may be coming, as global population reaches the seven billion mark this year, youth-led unrest rocks the Middle East, and questions of aging enter the lexicon of policymakers from Japan and South Korea to Europe and the United States. What does a population of nine billion (the UN medium-variant projection for 2050) mean for global security? How will shrinking populations in Europe affect Western military alliances and operations? Is demography destiny?
The latter question has plagued demographers, policymakers, and academics for centuries, resulting in heated debate and dire warnings. Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba continues this debate in her new book, The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security, but with a decidedly more measured and optimistic tone (full disclosure: Sciubba was one of my professors). The book is targeted at policymakers but is accessible to anyone with an interest in the field of demography and national security. She will launch her book at an event hosted by the Wilson Center on March 14.
Turning Challenge Into Opportunity
The main themes of The Future Faces of War are challenge and opportunity. Yes, national security will be tested by a series of evolving demographic trends in the decades ahead, but with proper insight and preparation, states can turn these challenges into opportunities for growth and betterment. Sciubba writes, “How a state deals with its demographic situation – or any other situation for that matter – is more important than the trends themselves” (p.125).
Part of turning these population challenges into opportunity is understanding long-term trends – a daunting task given the range and number of trends to consider. Drawing on her own experiences in the defense community, Sciubba writes how policymakers were “receptive” to the idea of population influencing national security, but that the “overwhelming number of ways demography seemed to matter” made them hesitant to act (p.3). With the publication of this book, which clearly and concisely outlines the basics of each population trend with demonstrative examples, hopefully that hesitation will be turned into action.
Youth and Conflict
The first population trend Sciubba highlights is perhaps the one of most immediate concern to national security policymakers given recent world events. In the chapter “Youth and Youthful Age Structures,” Sciubba discusses the security implications of those countries (in particular those in Africa, the Middle East, and Central Asia) with a majority of their population under the age of 29. She writes, “Most important for national security, countries with youthful age structures are generally the least developed and least democratic in the world, and tend to have the highest risk of civil conflict” (p. 18). In fact, between 1970 and 1999 countries with very young and youthful age structures were two to four times more likely to experience civil conflict than countries with more mature age structures.
The risks of very young and youthful populations are well documented (Sciubba cites the examples of Somali piracy, religious extremism, and child soldiers in Africa), but what has not been as widely discussed are the opportunities. Youthful states have a large pool of potential recruits for their armies, plenty of workers to drive economic development, and even an opportunity to grow democratically through social protest. Sciubba writes, “Youth can also be a force for positive political change as they demand representation and inclusion in the political process… social protest is not always a bad thing, even if it does threaten a country’s stability, because it may lead to more representative governance or other benefits” (p. 23). (For more on youth and the transition to democracy, see “Half a Chance: Youth Bulges and Transition to Democracy,” by Richard Cincotta, and his recent blog post about the Jasmine Revolution in Tunisia).
Graying of the Great Powers
At the other end of the demographic transition is population aging. Sciubba points out that the countries with the highest proportions of people aged 60 and older are also “some of the world’s most powerful and economically or politically strategic states” (p. 42). Europe, Japan, and the United States are all getting older (though the United States to a slightly lesser extent), and Sciubba states that the “graying” of these countries has the potential to greatly limit military preparedness, size, and funding. She points out that the number of recruits available will be much smaller and more money will have to be spent on pensions and health care for the growing number of elderly persons.
To counteract these challenges, Sciubba recommends that aging states seek out alliances with each other and countries with younger populations. She writes, “As part of strong alliances, states have strength in numbers, even if they are individually weakened by aging” (p. 47). Another alternative would be to improve military technology and efficiency to compensate for the drop in personnel.
Migration and Security: A “Unique” Relationship
Migration, the third pillar of demographic change after fertility and mortality, has what Sciubba calls a “unique relationship to national security” (p.83). Migration “is the only population driver that can change the composition of a state or a community within months, weeks, or even days” (p. 83). Mass migrations (such as those caused by a natural disaster or violent conflict) are the best examples of this trend. Some of the security challenges Sciubba highlights about migration are refugee militarization, competition for resources, and identity struggles among the native and migrant populations.
However, Sciubba also argues that both migrants and receiving countries can benefit. Origin states release pressure on their crowded labor markets and earn income from remittances, while receiving countries increase their labor market and mitigate population decline (a key component of U.S. growth).
Much of this has been studied before, but two new developments in migration trends that Sciubba calls to our attention are what she calls the “feminization of migration” (the increasing number of women who are likely to move for economic reasons) and migration as a result of climate change. Both are intriguing new areas of inquiry that deserve further study, but only get a passing mention in the book.
Making Her Case
The basic trends outlined above are only a small sampling of the wealth of information to be found in The Future Faces of War. Other noteworthy topics include a discussion on transitional age structures, urbanization, gender imbalances, HIV/AIDS, differential growth among ethnic groups, and many more. The topics are varied and wide-ranging and yet, Sciubba manages to connect them and makes her case convincingly for their inclusion in the broader national security dialogue. Sciubba has briefly written about many of these topics before, but this is the first time she (or anyone else, for that matter) has brought them together in one comprehensive book with such a focus on national security.
Christina Daggett is an intern with ECSP and a former student of Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba’s at Rhodes College.
Sources: Population Action International.
Photo Credits: “Children at IDP Camp Playful During UNAMID Patrol,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo. Book cover image provided by, and used with the permission of, Jennifer Dabbs Sciubba and ABC-CLIO.
Showing posts from category youth.