Showing posts from category population.
-
Lakis Polycarpou, Columbia Earth Institute
The Year of Drought and Flood
›August 1, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Lakis Polycarpou, appeared on the Columbia Earth Institute’s State of the Planet blog.
On the horn of Africa, ten million people are now at risk as the region suffers the worst drought in half a century. In China, the Yangtze – the world’s third largest river – is drying up, parching farmers and threatening 40 percent of the nation’s hydropower capacity. In the U.S. drought now spreads across 14 states creating conditions that could rival the dust bowl; in Texas, the cows are so thirsty now that when they finally get water, they drink themselves to death.
And yet this apocalyptic dryness comes even as torrential springtime flooding across much of the United States flows into summer; even as half a million people are evacuated as water rises in the same drought-ridden parts of China.
It seems that this year the world is experiencing a crisis of both too little water and too much. And while these crises often occur simultaneously in different regions, they also happen in the same places as short, fierce bursts of rain punctuate long dry spells.
The Climate Connection
Most climate scientists agree that one of the likely effects of climate will be an acceleration of the global water cycle, resulting in faster evaporation and more precipitation overall. Last year, the Proceedings from the National Academy of Sciences published a study which suggested that such changes may already be underway: According to the paper, annual fresh water flowing from rivers into oceans had increased by 18 percent from 1994 to 2006. It’s not hard to see how increases in precipitation could lead to greater flood risk.
At the same time, many studies make the case that much of the world will be dramatically drier in a climate-altered future, including the Mediterranean basin, much of Southwest and Southeast Asia, Latin America, the western two-thirds of the United States among other places.
Continue reading on State of the Planet.
Sources: Associated Press, The New York Times, Proceedings from the National Academy of Sciences, Reuters, Science Magazine, University Corporation for Atmospheric Research.
Photo Credit: “Drought in SW China,” courtesy of flickr user Bert van Dijk. -
Watch: Alecia Fields on Population, Health, and Environment Advocacy with the Sierra Club
›July 29, 2011 // By Roza Essaw “The issues of population, health, and environment are pretty foreign to a lot of people,” said Alecia Fields, a recent University of Kentucky graduate who participated in a Sierra Club Global Population and Environment Study Tour of Ethiopia last summer as a student fellow.
“The issues of population, health, and environment are pretty foreign to a lot of people,” said Alecia Fields, a recent University of Kentucky graduate who participated in a Sierra Club Global Population and Environment Study Tour of Ethiopia last summer as a student fellow.
“I learned about the program, how to be an effective advocate, and I took those tools back to my university on campus and shared it with young people,” said Fields in this interview with ECSP.
Fields came from a women’s health background but found the connections between population, health, and environment (PHE) compelling enough that she wanted to become an advocate on campus. “At first, people don’t think they have a connection to the issue, but once you start talking with people, they really start to see how they are central to a larger issue,” said Fields.
“It is challenging in the United States to see some of the population and environmental issues…but when you go to a developing country, you see the effects right in front of you,” explained Fields. The Sierra Club’s Global Population and Environment Study Tours bring a select group of student advocates abroad to see PHE projects in the field with the aim of creating pro-active messengers of the importance of integrated development in the United States.
Fields visited various sites and organizations in Ethiopia including the Gauraghe People’s Self-help Development Organization (GPSDO), located in the southwest region. “People in Ethiopia have had tremendous success in connecting population, health, and environment within communities and starting integrated programs that work towards development,” said Fields.
Going to Ethiopia provided Fields with concrete examples of the importance of PHE and allowed her to share her experience with young people through meaningful illustrations and moving stories.
“A lot of it deals with figuring out where people are in their attachment to the subject…and try to figure out how that program can connect to them,” she said. -
Farahnaz Zahidi Moazzam on the Population Reference Bureau’s “Women’s Edition” Trip to Ethiopia
›The original version of this article, by Farahnaz Zahidi Moazzam, appeared on the Population Reference Bureau’s Behind the Numbers blog.
My name is Farahnaz Zahidi Moazzam, and I’m a freelance journalist, writer, and editor from Pakistan. My passion is writing about human rights with a special focus on gender issues and reproductive health. Blogging is a personal joy to me, as I put my heart into my writing and blogging allows for a more personalized style. Digital journalism is a sign of evolution – one I happily accept. My pet peeve is marginalization on any grounds. I am a mother of a teenage daughter and live in Karachi.
As part of the Population Reference Bureau’s (PRB) group of journalists in Women’s Edition 2010-2012, I recently had the chance to travel to Ethiopia on a visit that was unforgettable. The visit inspired a series of seven brief travel-blogs, based on my seven days there. Women’s Edition is a wonderful opportunity to connect with other like-minded female journalists from developing countries around the world, and learn solutions to the problems from this interaction. The program has reaffirmed my belief that our commonalities are more than the differences.
Read Farahnaz Zahidi Moazzam’s posts from her trip to Ethiopia on her blog, Impassioned Ramblings, and view photos from the trip on PRB’s Facebook page.
Photo Credit: PRB. -
Failed States Index 2011
›“The reasons for state weakness and failure are complex, but not unpredictable,” said J.J. Messner, one of the founders of the Fund for Peace’s Failed States Index, at the launch of the 2011 version of report in Washington last month. The Index is an analytical tool that could aid policymakers and governments seeking to prevent and mitigate state collapse by identifying patterns of underlying drivers of state instability.
The Index ranks 177 countries according to 12 primary social, economic, and political indicators based on analysis of “thousands of news and information sources and millions of documents” and distilled into a form that is meant to be “relevant as well as easily digestible and informative,” according to the creators. “By highlighting pertinent issues in weak and failing states,” they write, the Index “makes political risk assessment and early warning of conflict accessible to policymakers and the public at large.”
Common Threats: Demographic and Natural Resource Pressures
The Index reveals that half of the 10-most fragile states are acutely demographically challenged. The composite “Demographic Pressures” category takes into account population density, growth, and distribution; land and resource competition; water scarcity; food security; the impact of natural disasters; and public health prevention and control. Additional population indices are found in “Massive Movement of Refugees or Internally Displaced Persons (IDPs),” and health indicators, including infant mortality, water, and sanitation, are spread across several categories.
Not surprisingly, some of the most conflict-ridden countries show up at the top of the list. The Index highlights some of the lesser known issues that contribute to their misery: demographic and natural resource stresses in Afghanistan, Iraq, Nigeria, Pakistan, and Yemen (a list that would include Palestine, if inclusion in the Index were not contingent on UN membership); the DRC’s conflict minerals; and Somalia and Sudan’s myriad of environmental and migration problems, which play major roles in their continued instability.
Haiti, with its poor health and lack of infrastructure and disaster resilience, was deemed the Index’s “most-worsened” state of 2011. The January 2010 earthquake and its ensuing “chaos and humanitarian catastrophe” demonstrated that a single event can trigger the collapse of virtually every other sector of society, causing what Messner termed the “Humpty Dumpty effect” – while a state can deteriorate quickly, it is much harder to put it back together again.
The inclusion of natural resource governance within the social and economic indicators would render the Index a more complete analytical tool. In a 2009 report, the UN Environment Program (UNEP) found that “since 1990, at least eighteen violent conflicts have been fueled by the exploitation of natural resources,” and that effective natural resource management is a necessary component of conflict prevention and peacebuilding operations.
The Elephant in the Room: Predicting the Arab Spring
Why did the Index fail to predict the Arab Spring sweeping the Middle East and North Africa? Many critics assert that the inconsistent ranking of the states, ranging from Yemen (ranked 13th) to Bahrain (ranked 129th), demonstrates that the Index is a poor indicator of state instability. Particularly, critics argue that many of the countries experiencing revolutions were ranked artificially low.
“Of course, the Failed States Index did not predict the Arab Spring, and nor is it intended to predict such upheavals,” said Messner at the launch event. “But by digging down deeper into the specific indicator analysis, it was possible to observe the growing tensions in those countries.” The Index has consistently highlighted specific troubling indicators for the region, such as severe demographic pressures, migration, group grievance, human rights, state legitimacy, and political elitism.
Blake Hounshell, a correspondent with Foreign Policy (long-time collaborators with the Fund for Peace on the Index), wrote that the Index was never meant to be a “crystal ball” – even the best statistical data cannot truly encapsulate the complex realities that lead to inherently unpredictable events, such as revolutions. “It’s thousands of individual decisions, not rows of statistics, that add up to political upheaval,” Hounshell continued.
Demographer Richard Cincotta’s work on Tunisia’s revolution illuminates how the Index’s linear indicators can mask a complex reality. Whereas the Failed States Index simply measures “demographic pressure” as a linear function of how youthful a population is, Cincotta pointed out at a Wilson Center event that it was actually Tunisia’s relative demographic maturity that paved the way for its revolution and gives it a good chance of achieving a liberal democracy. Other countries in the region are much younger than Tunisia (Yemen being the youngest). The Arab Spring demonstrates that static indicators alone often do not have the capacity to predict complex social and political revolutions.
Sources: Foreign Policy, The Fund for Peace, UNEP.
Image Credit: Failed States Index 2011, Foreign Policy. -
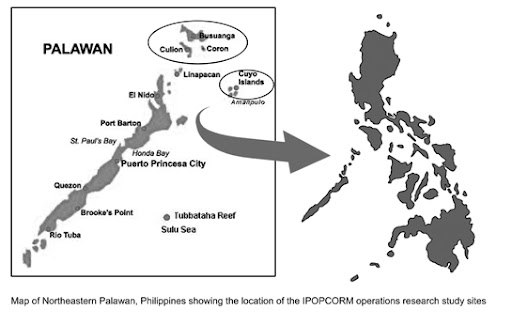
Leona D’Agnes on Evaluating PHE Service Delivery in the Philippines
›“By reducing population growth, we are going to have a better chance of sustaining the gains of an environmental conservation project,” said Leona D’Agnes in this interview with ECSP. D’Agnes, a technical advisor to PATH Foundation Philippines, served as lead author on a research article published late last year in Environmental Conservation titled, “Integrated Management of Coastal Resources and Human Health Yields Added Value: A Comparative Study in Palawan (Philippines).” The study provided concrete statistical evidence that integrated development programming incorporating population, health, and the environment (PHE) can be more effective in lowering population growth rates and preserving critical coastal ecosystems than single-sector development interventions.
“What set this research apart from earlier work on integrated programming was the rigorous evaluation design that was applied,” said D’Agnes. “What this design aimed to do is to evaluate the integrated approach itself. Most of the previous evaluations that have been done on integrated programming were impact evaluations — they set out to evaluate the impact of the project.” This most recent research project, on the other hand, sought to evaluate the effectiveness of cross-sectoral interventions based on “whether or not synergies were produced,” said D’Agnes.
Although it took her team six years to generate statistically significant findings in Palawan, D’Agnes reports that the synergies of PATH Foundation Philippines’ PHE intervention took the form of reduced income poverty, a decreased average number of children born to women of reproductive age, and the preservation of coastal resources, which helped bolster the region’s food security.
Going forward, D’Agnes said, an integrated approach to environmental conservation should also prove appealing because of its cost effectiveness. “This has huge implications for local governments in the Philippines, where they are struggling to meet the basic needs of their constituents in the face of very small internal revenue allotments that they get from the central government,” she said. “They can really pick up on this example to see that at the local level, if somehow they can do this integrated service delivery that was done in the Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management (IPOPCORM) model, that they’ll be able to achieve the objectives of both their conservation and their health programs in a much more cost-effective way, and, in the process, generate some other [positive] outcomes that perhaps they didn’t anticipate.”
D’Agnes expects the study’s results will prompt a fresh look at cross-sectoral PHE programming. “I hope that this evidence from this study will help to change the thinking in the conservation community about integrated approaches to conservation and development,” she said.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Life on the Edge: Climate Change and Reproductive Health in the Philippines
›July 18, 2011 // By Hannah MarquseeHigh population growth and population density have placed serious stress on natural resources in the Philippines. No one lives far from the coast in the 7,150-island archipelago, making the population extremely dependent on marine resources and vulnerable to sea-level rise, flooding, and other effects of climate change. The coastal megacity of Manila – one of the most densely populated in the world – is beset by poor urban planning, lack of infrastructure, and a large population living in lowland slums, making it particularly vulnerable to increased flooding and natural disasters. [Video Below]
The Philippines is now home to 93 million people and by 2050 is expected to reach 155 million, according to the UN’s medium fertility variant projections. Development programs in the country have made great strides towards increasing access to family planning and reproductive health services as well as improving management of marine resources, but the underlying trends remain troubling.
The Battle Over Reproductive Health
Since 1970, the government’s Commission on Population has been addressing population growth, reproductive health, and family planning. “The impact of the high rate of population growth is intricately linked to the welfare and sustainable development for a country like the Philippines, where poverty drives millions of people to overexploit their resource base,” wrote the commission. As a result of these efforts and others, total fertility rate has dropped from 6.0 children per woman in 1970, to the present 3.2.
The Philippines has also made great gains towards achieving Millennium Development Goal targets, “particularly in the alleviation of extreme poverty; child mortality; incidences of HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria; gender equality in education; household dietary intake; and access to safe drinking water,” according to the United Nations Development Program (UNDP). Yet, “glaring disparities across regions persist,” UNDP states.
One of the poorest regions in the country, the Autonomous Region of Muslim Mindanao, is also home to a violent separatist movement. With limited access to health services, fertility and population growth rates are the highest in the country. Women in Mindanao average 4.2 children per woman; one in four married women has an unmet need for contraception; and 45 percent of households live in poverty (compared to 24 percent nationally).
Nationally, “serious challenges and threats remain with regard to targets on maternal health, access to reproductive health services, nutrition, primary education, and environmental sustainability,” according to UNDP–in particular, indicators on maternal health are “disturbing” and of all the MDGs, are labeled “least likely to be achieved.”
Out of three million pregnancies that occur every year, half were unplanned and one-third of these end in abortions, according to a 2006 report of the Allan Guttmacher Institute conducted in the Philippines. Induced abortion was the fourth leading cause of maternal deaths, and young women accounted for 17 percent of induced abortions. Over half of births occurred at home and one-third of them were assisted by traditional birth attendants. Around 75 percent of the poorest quintile did not have access to skilled birth attendants compared to only 20 percent of the richest quintile.
The politically influential Catholic Church recently blocked passage of a reproductive health bill, despite support by President Benigno Aquino and a majority of Filipinos. The bill seeks to provide universal access to contraception and would make sex education required from fifth grade onwards, a provision that has angered Church officials.
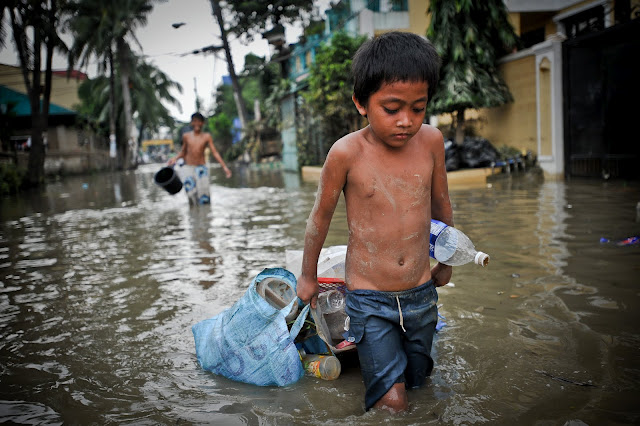
Manila Under Water
The Philippines’ combination of high population growth and limited land area (nearly all of which is near the coast) makes the country extremely vulnerable to the effects of climate change. Sixty-five percent of Filipinos live in coastal areas and 49 percent live in urban areas. Paul Hutchcroft, in Climate Change and Natural Security, writes that “even in the best of times, the frequency of typhoons, floods, earthquakes, and volcanic eruptions makes the Philippines one of the most disaster-prone countries in the world” (p. 45).
Population growth, climate change, and deforestation will only increase the severity of these disasters, he concludes. Hutchcroft points out that by 2080, projected temperature increases of between 1.2 to 3.9 degrees Celsius could raise sea levels by an estimated 0.19 to 1.04 meters – a scary thought for the 15 million living within a one-meter elevation zone (p. 46).
In 2009, metropolitan Manila, currently home to 11 million people (18,650 per square kilometer) and projected to grow to 19 million by 2050, was hit by tropical storms that caused devastating flooding – at their peak, waters reached nearly seven meters, according to a World Bank report. “More than 80 percent of the city was underwater,” write the authors, “causing immense damage to housing and infrastructure and displacing around 280,000-300,000 people.”
“Even if current flood infrastructure plans are implemented, the area flooded in 2050 will increase by 42 percent in the event of a 1-in-100-year flood,” says the World Bank report. Climate change could also increase the cost of flooding as much as $650 million, or 6 percent of GDP. Only by considering climate-related risks in urban planning can the Philippines hope to mitigate the effects of climate change, the report concludes.
Integrated Development: One Piece of the Puzzle?
Population, health, and environment (PHE) programs that integrate family planning and natural resource management are one way to help the majority of Filipinos that live in densely populated and resource-stressed coastal areas.
In ECSP’s FOCUS Issue 15, “Fishing for Families: Reproductive Health and Integrated Coastal Management in the Philippines,” Joan Castro and Leona D’Agnes explain how Path Foundation Philippines, Inc.’s IPOPCORM project – which ran from 2000 to 2006 – helped “improve reproductive health and coastal resource management more than programs that focused exclusively on reproductive health or the environment – and at a lower total cost.” A recent peer-reviewed study, co-authored by Castro and D’Agnes and published in Environmental Conservation, proved the same point with rigorous analysis.
“When we started IPOPCORM, there was really nothing about integrating population, health, and environment,” said Castro in an interview with ECSP. IPOPCORM provided some of the first evidenced-based results showing there is value added to implementing coastal resource management and family planning in tandem rather than separately. In part due to the success of the IPOPCORM, the Philippines have become one of the major PHE development implementers in the world.
Creating sustainably managed marine sanctuaries while improving access to family planning provides a way forward for many coastal communities. However, the Philippines’ urban woes – 44 percent of urban dwellers live in slums, according to the Population Reference Bureau – internal divisions, and natural vulnerability will likely make it difficult to dodge considerable climate-related effects in the near future. Already the archipelago’s vast biodiversity is in crisis, according to studies over two thirds of native plant and animal species are endemic to the islands and nearly half of them are threatened; only seven percent of its original old-growth less than 10 percent of the islands’ original vegetation remains; and 70 percent of nearly 27,000 square kilometers of coral reefs are in poor condition.
Sources: CIA, Conservation International, Field Museum, The Guardian, The Huffington Post, Philippines National Statistics Office, Population Reference Bureau, United Nations, U.S. Census Bureau, World Bank, World Wildlife Fund.
Photo Credit: “Climate Risk and Resilience: Securing the Region’s Future” courtesy of Flickr user Asian Development Bank. -
Michael Kugelman, Foreign Policy
Pakistan’s Demographic Dilemma
›July 15, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Michael Kugelman, appeared on Foreign Policy’s AfPak Channel.
Pakistan’s 2011 census kicked off in April, but less than three months later, it is embroiled in controversy. Several members of the Sindh Census Monitoring Committee have rejected as “seriously flawed” the recently completed household count. They allege that census workers, directed by an unspecified “ethnic group,” have counted Karachi’s “inns, washrooms, and even electric poles” as households in an effort to dilute the city’s native “Sindhi” presence.
These Census Monitoring Committee members are not the only Pakistani politicians to be concerned about the census. Pakistan is experiencing rapid urbanization; while a third of the country’s people have long been rurally based, at least 50 percent of the population is expected to live in cities by the 2020s. Pakistan’s political leadership draws much of its power from rural landholdings, power that could be greatly reduced if a census confirms this migration toward cities.
This politicization underscores the perils of census-taking in Pakistan. In many other nations, it is a routine process completed regularly. Yet in Pakistan, myriad factors – from catastrophic flooding and insufficient funding to the turbulent security situation and intense political opposition – have conspired to delay it for three consecutive years, making the country census-less since 1998.
Accurate census data enables governments to make decisions about how to best allocate resources and services. In Pakistan, such decisions are critical. Consider that its current population, estimated at about 175 million, is the world’s sixth-largest. It has the highest population growth, birth, and fertility rates in South Asia – one of the last regions, along with sub-Saharan Africa, still experiencing young and rapidly rising populations. Additionally, with a median age of 21, Pakistan’s population is profoundly youthful. Two-thirds are less than 30 years old, and as a percentage of total population, only Yemen has more people under 24.
Continue reading on Foreign Policy.
Michael Kugelman is a program associate for the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson Center and co-editor of Reaping the Divided: Overcoming Pakistan’s Demographic Challenges.
Sources: UN Population Division.
Photo Credit: “Pakistan Diaster Relief,” courtesy of flickr user DVIDSHUB. -
World Population Day 2011: The Year of Seven Billion
›July 11, 2011 // By Schuyler NullThe UN Population Fund established World Population Day as a day of awareness about global population in 1987. As we approach seven billion just 24 years later, the UN is kicking off their 7 Billion Actions campaign, designed to raise awareness about the resource, health, and environmental challenges raised by our numbers. Population and its more detailed cousin-indicator, demography, impact the world in a great many ways – from contributing to resource scarcity and environmental destruction to creating social imbalances that can lead to civil instability.
Check out a few of New Security Beat’s most recent stories on population to get a sense of why it’s such an important but oft-simplified and misunderstood indicator and where it matters most.
Photo Credit: “World population,” courtesy of flickr user Arenamontanus.- One in Three People Will Live in Sub-Saharan Africa in 2100, Says UN
- Ten Billion: UN Updates Population Projections, Assumptions on Peak Growth Shattered
- Tunisia Predicted: Demography and the Probability of Liberal Democracy in the Greater Middle East
- Watch: Demographic Security 101 With Elizabeth Leahy Madsen
- Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions
- Guest Contributor Michael Kugelman: Pakistan’s Population Bomb Defused?
- Dot-Mom: USAID Egypt’s Health and Population Legacy Review
- Watch: Eric Kaufmann on How Demography Is Enhancing Religious Fundamentalism
- Consumption and Global Growth: How Much Does Population Contribute to Carbon Emissions?