-
Imelda Abano on Environmental Reporting in the Philippines
›“What we are trying to do is to explore more strategies on how to improve environmental reporting in the Philippines – and on how to reach the government and communities as well,” said Imelda Abano, president of the Philippine Network of Environmental Journalists, Inc. (PNEJ) and senior correspondent at Business Mirror, in an interview with ECSP.
With an overwhelmingly coastal population of around 95 million, the 7,150 island archipelago of the Philippines is seen as highly vulnerable to environmental and climate-related threats. One of Albano’s major aims as president of the PNEJ is therefore to “empower local journalists to report more on environmental issues like biodiversity, climate change, disaster, and other environmental challenges in the Philippines,” she said.
Compelling reporting, she said, comes from “try[ing] to understand what the government is trying to say or what researchers or other organizations are trying to say,” and then relating that information back to the people “in the layman’s terms.”
Environmental issues require a lot of context, she said. One of the most important related issues in the Philippines is population growth.
“When you talk about environment issues, it really resonates or links to population issues,” Abano said. Current UN projections estimate that by 2050, the population could balloon to nearly 155 million. “This really affects our jobs, women, culture, and of course the population around the coastal areas.” -
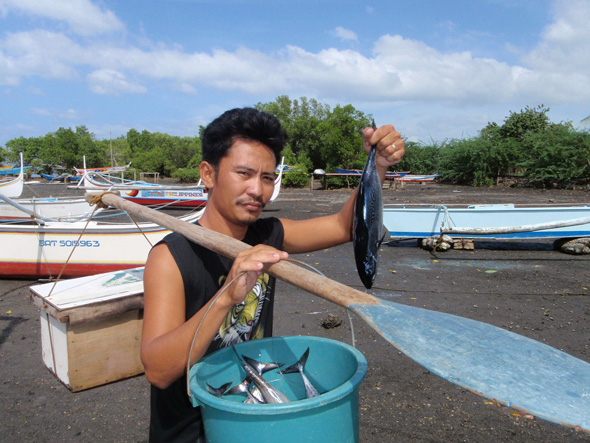
Philippines’ Bohol Island Demonstrates Benefits of Integrated Conservation and Health Development
›
In March 2012, I participated in a study tour to the island of Bohol, near the unique Danajon double barrier reef ecosystem – the only one of its kind in the Philippines and one of only three in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. Nowhere is the connection between population dynamics and biodiversity more evident than in the Philippines, one of the most densely-populated countries on the planet, with more than 300 people per square kilometer. Nearly every major species of fish in the region shows signs of overfishing, according to the World Bank.
-
Improving Food Security Through Land Rights and Access to Family Planning
›“In a future world affected by climate change, population growth is one lever that can be addressed to ameliorate the impacts of climate change, particularly in the area of food security,” write Scott Moreland and Ellen Smith in “Modeling Climate Change, Food Security, and Population,” a recent study for MEASURE Evaluation and USAID. Moreland and Smith combine demographic changes, food needs, and economic capacity into a single aggregate model to assess how family planning and climate change might affect food security from now until 2050. Using Ethiopia as an example, the model finds that if access to family planning services were increased to meet existing needs, the subsequent decrease in demand for food would reduce child malnutrition and effectively counteract a projected 25 percent shortfall in caloric availability from climate change’s impact on agriculture. Programs designed to increase access to family planning should therefore be incorporated into national adaptation and food security strategies, they conclude. “Family planning, especially in countries with high unmet need, provides a potential solution not only for women’s reproductive health, but also for adapting to the effects of climate change.”
The Food and Agriculture Organization’s Committee on World Food Security recently endorsed a set of voluntary guidelines for land tenure governance in the context of food security that aims to strike a balance between encouraging productive investment and ensuring equitable and sustainable development. Population growth, climate change, and environmental degradation are putting pressure on the legal and cultural systems that govern land rights, resulting in “inadequate and insecure tenure rights” which can “increase vulnerability, hunger and poverty, and can lead to conflict and environmental degradation when competing users fight for control of these resources.” The guidelines, drawn from consultations with hundreds of people from both the private and public spheres and representing more than 130 countries, emphasize the need to safeguard access to land, fisheries, and forests – as well as the resources they provide – in a way that respects customary tenure systems, which are not always reflected in official tenure policies or records. They also emphasize strengthening the ownership rights of women and other traditionally marginalized groups in order to enhance food security and minimize the risk of instability and conflict in the future. -
The Global Water Security Assessment and U.S. National Security Implications
›
“Water security is about much more than access to H2O,” said Jane Harman, director, president, and CEO of the Wilson Center at the May 9 meeting, “Global Water Security: The Intelligence Community Assessment.” The event – part of the Wilson Center’s National Conversation Series – brought together a number of experts to discuss a recently released intelligence community assessment of global water security. [Video Below]
-
“Afghanistan, Against the Odds: A Demographic Surprise” Launches ECSP Report 14
›A few months ago, Elizabeth Leahy Madsen broke down Afghanistan’s first-ever nationally representative survey of demographic and health issues in a two-part series here on the blog. Now, we’ve published her analysis in a rich new policy brief format. It is the first issue of Environmental Change and Security Program Report 14, the latest volume of ECSP’s flagship publication.
In “Afghanistan, Against the Odds,” Madsen examines the surprising results of this fall’s demographic survey and how the country’s statistics compare to neighboring Pakistan.
“Just as Afghanistan and Pakistan’s political circumstances have become more entwined,” writes Madsen, “their demographic paths are more closely parallel than we might have expected. For Afghanistan, given its myriad socioeconomic, political, cultural, and geographic challenges, this is good news. But for Pakistan, where efforts to meet family planning needs have fallen short of capacity, it is not.”
The publication of this brief marks the re-launch of ECSP Report as an online-only volume, with individual issues scheduled to be released throughout the year. Forthcoming ECSP Report 14 briefs will address the demographic roots of the Arab Spring; the links between population dynamics and environmental resources like water, biodiversity, and food; and the potential impact of climate change mitigation efforts on conflict.
Published since 1996 in hard copy and online, the new ECSP Report will now be available on the Wilson Center website, New Security Beat, and Issuu. You can read the previous 13 volumes of the ECSP Report on the Wilson Center website.
Download ECSP Report 14: “Afghanistan, Against the Odds” from the Wilson Center. -
John May, Center for Global Development
‘People and the Planet’ Study Re-Introduces Demography to Sustainability Debate
›May 15, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by John May, appeared on the Center for Global Development’s Global Health Policy blog.
Population issues have been conspicuously absent from the discussions on the environmental sustainability of our globalized economy in the run-up to the Rio+20 Conference on Sustainable Development, which will take place in Brazil, June 20-22, under the auspices of the United Nations.
Fortunately, the new report, People and the Planet by the Royal Society, should help change this woefully shortsighted approach. The report demonstrates clearly and convincingly that demographic trends cannot be separated from consumption patterns, and that there is no chance to achieve a path of equitable and sustainable development without tackling population growth and consumption at the same time. In short, population and the environment cannot and should not be considered as two separate issues.
This strong and long overdue pitch to bring back the “p” word into the environmental debate is most welcome. In recent decades, international attention has shifted from rapid population growth to other urgent issues, such as the HIV/AIDS epidemic, humanitarian crises, climate change, and good governance. But reproductive health and voluntary family planning programs are still very much needed, especially in high fertility countries, and they require political leadership and long-term financial commitment. Broader access to family planning services will be needed to accelerate the decline of high fertility rates, particularly in countries where unmet needs for contraception are high.
Continue reading at the Center for Global Development.
Image Credit: People and the Planet cover, courtesy of the Royal Society. -
Nigeria Beyond the Headlines: Environment and Security [Part Two]
›
In the coming years, Nigeria’s cohort of unemployed youth has equal potential to “be converted into either a religious or a regional clash, as certain youths get opportunities and other youths do not,” said Pauline Baker, President Emeritus of the Fund for Peace, during the day-long “Nigeria Behind the Headlines” event at the Wilson Center on the April 25 (read part one here). [Video Below]
-
Nigeria Beyond the Headlines: Demography and Health [Part One]
›
“Nigeria is a country of marginalized people. Every group you talk to, from the Ijaws to the Hausas, will tell you they are marginalized,” said Peter Lewis, director of the African Studies Program at the Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies. Lewis spoke at an April 25 conference on Nigeria, co-hosted by ECSP and the Wilson Center’s Africa Program, assessing the country’s opportunities for development given its demographic, governance, natural resource, health, and security challenges. [Video Below]
Showing posts from category population.