-
A Tough Nut to Crack: Agricultural Remediation Efforts in Afghanistan
›April 5, 2010 // By Julien Katchinoff“It was pretty much a normal day in Afghanistan on Monday.
Though only earning a glancing mention in The New York Times, it is heartening to see a response to the environmental and economic loss of Afghanistan’s once abundant wild pistachio forests. As a result of wide-spread environmental mismanagement and war, the past 30 years have seen a dramatic decline in the wild pistachio woodlands native to Northwestern Afghanistan.
“A couple of civilian casualties caused by insurgents. More investigations into corrupt former ministers. The opening of six new projects in Herat Province by the Italians and the Spaniards, which are the NATO countries in the lead in western Afghanistan. All right, not six, projects, but two or three, and the Spanish announced a pistachio tree-growing program to replace poppies. Pistachios, poppies… maybe pine nuts will be next.”
— At War: An Airborne Afghan Folk Tale, Alissa J. Rubin, New York Times, April 1, 2010
In a 2009 survey of Afghanistan’s environmental challenges, UNEP found that, while in 1970 “the Badghis and Takhar provinces of northern Afghanistan were covered with productive pistachio forests and earned substantial revenue from the sale of nuts,” few remain as the forests have since succumbed to mismanagement, war, and illegal logging.
In this video by the Post-Conflict and Disaster Management Branch of UNEP, scenes of dusty and denuded hillsides clearly show that rural Afghan farmers in search of sustainable livelihoods have few options remaining.
The project mentioned in the New York Times is a recent foray into remediation efforts by a Spanish Provincial Reconstruction Team (PRT) that targets communities previously involved in the production of illegal drugs. In conjunction with the Spanish Agency of Coordination and Development (AECID), the Spanish PRT is working in over 13 sites in Baghdis province–a region once covered in pistachio trees–to help farmers transition to legal crops and restore the traditional pistachio forests to their former prominence. AECID joins the Afghan Conservation Corps (ACC), USAID, NATO and additional partners in promoting remediation projects to reverse deforestation.
Unfortunately, these programs face daunting obstacles, as pistachio and other traditional Afghan cash crops –such as raisins, figs, almonds and other nuts– require substantial re-investments of time, money, and infrastructure development. Furthermore, convincing desperate rural farmers to transition to nearly untested alternative crops is difficult when they are currently counting the days to the spring opium harvest.
Recently, eradication efforts targeting small-scale farms have abated, and increased attention is being paid to facilitating shifts toward new products through free seeds, loans, technical assistance, and irrigation investments. If successful, these projects will grant rural Afghan communities the ability to sustainably and legally provide for their families, providing long-term employment and returns for a region lacking in both money and hope for the future.
Video Credit: UNEP Video, “UNEP observes massive deforestation in Afghanistan” . -
‘Wilson Center on the Hill:’ Haiti’s Long Road Ahead
›March 25, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffNearly two months after the devastating 7.0 magnitude earthquake in Port-au Prince, Haiti, the country still needs assistance to provide basic healthcare and shelter, in addition to rebuilding Haiti’s economy, government, and institutions. As the international community and NGOs make the transition from emergency disaster relief to long-term reconstruction and capacity-building efforts, donor coordination and long-term commitment are crucial. Recently, on Capitol Hill, a panel of experts organized by Wilson Center on the Hill and the Wilson Center’s Latin American Program discussed Haiti’s continuing problems and challenges.
Patience Necessary
Johanna Mendelson Forman, a senior associate for the Americas Program at the Center for Strategic and International Studies, stressed that progress in Haiti will take time—perhaps five years to rebuild and 10 years to see positive economic growth. This timeline is often frustrating for donors—including Congress and U.S. citizens—who want to see immediate results, she noted. Nevertheless, Mendelson Forman discounted the myth that “because Haiti is a weak state it is not a sovereign state,” and emphasized that developing and strengthening the Haitian government remains necessary.
She observed that the post-earthquake efforts in Haiti have been different from previous United Nations interventions, particularly in terms of the Latin American community’s involvement. Brazil, for example, is leading relief operations. Other Latin American countries—including Haiti’s neighbor, the Dominican Republic—have committed to promoting a stable and secure Haiti. Here Mendelson Forman noted a new partnership initiated by the Dominican and Haitian governments. “[Dominican officials] understand that they are doomed if Haiti is doomed,” she said. “As members of the international community, it is our job to foster that reconciliation.”
Costs Are Rising
Andrew Philip Powell, a regional economic advisor in the Caribbean Country Department at the Inter-American Development Bank (IDB), said that while the IDB initially estimated damage from the earthquake at about $8 billion, the complete destruction of the government and commerce centered in Port-au-Prince could push that number much higher. The IDB and partner organizations are currently conducting a Post-Disaster Needs Assessment that will ultimately identify the official damages and ballpark the cost of reconstruction.
Powell stated that Haiti is “not starting from a blank slate,” citing a development strategy agreed upon in April 2009 by the Haitian government and international donors. In keeping with the strategy, he emphasized the need for effective coordination between donors and the Haitian government. At the same time, he said it is vital to encourage population dispersion by shifting government agencies and private-sector jobs to other parts of the country. Haiti needs roads and communication networks outside of the capital area, as well as export processing zones in outlying regions, to increase the economic opportunities outside of Port-au-Prince, he said.
However, with the large amounts of aid flowing into the country, Powell warned donors and Haitian officials to remain on the lookout for “Dutch disease”—a decline in the manufacturing sector following a sharp increase in natural resource prices, foreign assistance, or foreign direct investment. Its occurrence could increase Haiti’s dependency on aid in the future.
Challenges for Healthcare
Sheri Fink, a public policy scholar at the Woodrow Wilson Center and senior fellow at the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, offered her perspective on Haiti’s continuing health crisis based on two trips to the country in the earthquake’s aftermath. There are signs of hope, including some normalcy and commerce returning to the camps, she noted, but problems in the health sector as a whole are increasing. As field hospitals put in place after the earthquake close, “there is a fear among Haitians that attention is starting to turn elsewhere,” she said.
According to Fink, “the work is far from done” in Haiti, a sentiment she said is shared by many departing health workers. The hospitals left standing are not prepared to deal with the influx of patients arriving at their doors following the closure of field hospitals, and government health workers are currently working without pay.
Fink also pointed out the risk of long-term earthquake-related health problems, including injuries suffered during aftershocks or from falling debris, inflamed chronic diseases, horrible conditions and lack of basic health services in camps, and the “looming nightmare” of infectious disease epidemics.
Fink called for more international involvement to avert a widening of the health crisis. “We’ve made a big commitment and to follow-up on the investment, to make it mean something; let’s not be satisfied with just bringing things back to where they were,” she said.
By Sarah Huston and David Klaus of Wilson Center on the Hill at the Woodrow Wilson International Center for Scholars.
Photo: Courtesy Flickr user United Nations Development Programme -
Tapping In: ‘Secretary Clinton on World Water Day’
›March 23, 2010 // By Julien Katchinoff “It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a World Water Day event hosted by the National Geographic Society and Water Advocates.
“It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a World Water Day event hosted by the National Geographic Society and Water Advocates.Alongside speeches by representatives from government and the non-profit sector, Secretary Clinton repeatedly emphasized America’s support for water issues. “As we face this challenge, one thing that will endure is the United States’ commitment to water issues,” she asserted. “We’re in this for the long haul.” Beyond simply highlighting the importance of the issue, Secretary Clinton also affirmed commitment to new programmatic, cross-cutting initiatives that will target water as a keystone for development and peace.
ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko, who attended the event, noted that Secretary Clinton’s speech ran counter to the much publicized notion that water scarcity is an unavoidable catalyst for conflict.
She came down squarely on the side of inclusion by identifying water as both a ‘human security’ and ‘national security’ issue. At the same time, she did not fall prey to the common pitfall of arm-waving about water wars. She flagged conflict and stability concerns, but also raised solutions through meeting needs associated with water and development. She went out of her way to emphasize water’s potential for peace and confidence-building, reflecting a commitment to capturing opportunities rather than merely identifying threats.
Secretary Clinton highlighted five crucial areas that comprise the United States’ whole-of-government approach to water issues:
1. Building capacity:
Through efforts with international partners, the United States hopes to strengthen the abilities of water-stressed nations to manage vital water resources. Agencies such as the Millennium Challenge Corporation and USAID are implementing initiatives that will enhance national ministries and encourage regional management cooperatives.2. Elevating diplomatic efforts:
A lack of coordination between the numerous UN agencies, governments, and multilateral funding organizations hinders global water progress. By bringing this work together, the United States can act as a leader, demonstrating a positive diplomatic precedent for fragile and water-stressed nations.3. Mobilizing financial support:
Relatively small grants have achieved large impacts. Work by the United States to strengthen capital markets in the water sector shows that it is possible to earn large returns on water investments. Successful examples range from educational and awareness-building programs, to desalinization and wastewater treatment plants.4. Harnessing the power of science and technology:
Although there is no silver technological bullet to solve the global water crisis, simple solutions, such as ceramic filters and chlorine disinfection systems, do help. Additionally, sharing government-accumulated technological knowledge can have significant impacts, as demonstrated in a recent NASA-USAID project establishing an Earth-observation monitoring and visualization system in the Himalayas.5. Broadening the scope of global partnerships:
By encouraging partnerships and elevating water in its global partnership initiatives with NGOs, non-profits, and the private sector—all of which are increasingly engaged in water issues—the Department of State hopes to maximize the effectiveness of its efforts.The holistic approach advocated by Secretary Clinton reflects a distinct evolution of American diplomacy within this area, which is strongly supported by the water community. “The policy directions outlined in the speech, the five streams, represent a victory for those in and outside of government who have argued for a broad, rather than narrow, view of water’s dimensions,” said Dabelko. “The diversified strategy focuses on long-term and sustainable interventions that respond to immediate needs in ways most likely to make a lasting difference.”

In her concluding remarks, Secretary Clinton sounded a positive note, noting that for all of the press and attention devoted to the dangers of the global water crisis and the possible dark and violent future, dire predictions may be avoided through a smart, coordinated approach. “I’m convinced that if we empower communities and countries to meet their own challenges, expand our diplomatic efforts, make sound investments, foster innovation, and build effective partnerships, we can make real progress together, and seize this historic opportunity.”
Photo Credits: State Department Official Portrait; UNEP.
-
Visualizing Natural Resources, Population, and Conflict
›Environmental problems that amplify regional security issues are often multifaceted, especially across national boundaries. Obtaining a comprehensive understanding of the natural resource, energy, and security issues facing a region is not fast or easy.
Fortunately, the Environment and Security Initiative (ENVSEC) has created highly informative, easy-to-understand maps depicting environmental, health, population, and security issues in critical regions.
Published with assistance from the United Nations GRID-Arendal, these maps offer policymakers and the public a snapshot of the complex topography of environmental security hotspots in Central Asia, Eastern Europe, Southeastern Europe, and the Southern Caucasus.
Some that caught our eye:
• Environmental Issues in the Northern Caspian Sea: Overlaying environmental areas and energy production zones, this map finds hydrocarbon pollution in sturgeon spawning grounds, seal habitats in oil and gas fields, and energy production centers and waste disposal sites in flood zones.
• Water Withdrawal and Availability in the Aral Sea Basin: Simple and direct, this combination map and graph contrasts water usage with availability in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, and Kazakhstan—which stand in stark comparison to the excess water resources of Tajikistan and Kyrgyzstan.
• Environment and Security Issues in Belarus: In addition to noting the parts of the country with poor water quality and potassium mining, the map also delineates wildfires that occurred in areas contaminated by the Chernobyl explosion, thus threatening downwind populations.
Maps: Illustrations courtesy of the Environment & Security Initiative. -
Video—Integrating Population, Health, and Environment (PHE) to Conserve Ethiopian Wetlands
›February 1, 2010 // By Julia GriffinIn our latest video interview about PHE programs in Ethiopia, Zuna–a village elder from the Mettu Woreda region of Ethiopia—describes how an integrated intervention by the Ethio-Wetlands and Natural Resources Association (EWNRA) has benefited her community.
EWNRA aims to raise awareness within Ethiopian communities and governmental organizations of the importance of sustainable wetlands management. The organization also imparts local-level training on resource conservation and wise-use labor techniques.
Zuna recounts how EWNRA provided welcome training in sanitation and housekeeping practices that increased both safety and sustainability within her community. The more efficient, cleaner-burning wood stoves introduced in Mettu Woreda, for example, have improved local air quality while decreasing the frequency of skin burns and amount of harvested fuel required for cooking and other activities.
“We are benefiting from all this and I think the benefits from this intervention are good,” she says through an interpreter. “I want them to keep doing this and hopefully we will improve our activities working with them.” -
Gates: More Money for Global Health Is Good for the Environment
›January 28, 2010 // By Gib Clarke Bill Gates gave the PHE community a much-needed upgrade in his foundation’s 2nd Annual Letter, released this week. Unfortunately it still has a few bugs.
Bill Gates gave the PHE community a much-needed upgrade in his foundation’s 2nd Annual Letter, released this week. Unfortunately it still has a few bugs.
“In the long run, not spending on health is a bad deal for the environment because improvements in health, including voluntary family planning, lead people to have smaller families, which in turn reduces the strain on the environment,” concludes Gates.
This statement could dramatically raise awareness of and funding for population-environment programs. Any time Bill Gates talks, the world listens, as evidenced by the barrage of coverage from Reuters, AFP, and top IT newswires. For the public, it offers a rare glimpse into development strategy, so Gates’ thoughts (and financial commitments) could be seen as representative of the foundation community’s approach to global health problems.
Although it may seem obvious that fewer people place less strain on the environment, this connection has been largely absent from the environmental agenda, including the efforts to combat climate change. Some environmental leaders and organizations have dismissed population as an unimportant distraction from the real business at hand. Others have noted that population growth’s impact on climate change is far greater in the rich world than in poor countries, whose per capita emissions are a fraction of developed countries’.
Gates’ comment may cause those in the first camp to re-evaluate the importance of family planning, and it is likely to energize the converted. But it will have less impact on those focused on consumption. But if it encourages the environmental community to put population and family planning issues back on the table, it will have gone a long way.
However, Gates could have gone further, by explaining that family planning is a relatively inexpensive way to mitigate climate change, compared to complex and emerging technological solutions. He also could have pointed out that climate change is expected to increase the prevalence of vector-borne diseases such as malaria, or that sick or malnourished individuals may be forced to mismanage natural resources.
Because Gates didn’t make these explicit connections, many in the media missed his point. The wire headlines pit health against environment, when Gates was in fact pointing out how interdependent they are. This distortion is symptomatic of the media’s tendency to highlight the horserace. But maybe they would pay closer attention if the Gates Foundation put its money where its mouth is—and funded programs that integrate family planning and the environment.
Perhaps several years from now, we will look back and say that this letter marks the start of the Gates Foundation’s integrated approach to development. But we may need to wait for Letter 3.0 for a complete install.
Photo: Courtesy Flickr User World Economic Forum -
Collier and Birdsall: Plunder or Peace
›January 22, 2010 // By Julien Katchinoff In a preview of his new book The Plundered Planet: Why We Must – and How We Can – Manage Nature for Global Prosperity, Paul Collier dispelled the common perception that Africa’s indentified resource reserves are the world’s largest. In actuality, it is estimated that up to four-fifths of the value of subsoil assets in the African continent are yet to be discovered. “That is the big story,” Collier remarked. “Here are assets which could finance transformation….but historically haven’t.” Instead, these resources have been plundered.
In a preview of his new book The Plundered Planet: Why We Must – and How We Can – Manage Nature for Global Prosperity, Paul Collier dispelled the common perception that Africa’s indentified resource reserves are the world’s largest. In actuality, it is estimated that up to four-fifths of the value of subsoil assets in the African continent are yet to be discovered. “That is the big story,” Collier remarked. “Here are assets which could finance transformation….but historically haven’t.” Instead, these resources have been plundered.
In a recent event hosted by the U.S. Institute of Peace, Paul Collier, professor of economics and director of the Center for the Study of African Economies at Oxford University, and Nancy Birdsall, president of the Center for Global Development, discussed how resource-rich environments in developing countries have been traditionally misused. The two also proposed strategies to disrupt these processes and transform resource “curses” into deeply needed support for peace and stable development.
Conflict and instability in countries whose economies are heavily invested in natural resource have often hindered local development and security. Many of these countries—including Cambodia, Angola, Indonesia, and DRC—have suffered from one of two forms of plunder:
Types of Natural Resources Plunder:
1. Where the few steal from the many:
Natural assets are, by definition, without natural owners, and therefore lie as easily taken common goods. “This process of expropriation opens up a whole array of dysfunctional variants, many of which are violent,” Collier noted.
2. Where the present steals from the future:
Intertemporal mismanagement is a possibility, as unlike man-made assets, natural assets belong to all generations.
Operating from a worldview of weak sustainability, where profits from natural assets are reinvested for the benefit of future generations, Collier suggested that natural resource rights are more akin to “rights of stewardship” than traditional property rights. “We may well transform that value into something that is more productive, but if we pull up natural assets from the ground, we should leave to the future something that is equivalently valuable.”
Collier argued that the successful harnessing of natural resources for stable and sustainable development depends on the application of a tenuous decision chain:
Natural Resources Decision Chain:
1. Discovery Process:
Failure in this phase stems from poor property rights, and the time consistency problem—uncertainty that conditions and regulations that make expensive upfront investments profitable today will remain in place in the future.
2. Appropriate Taxation:
Currently, as a result of poor negotiations or limited information regarding the status of resources, governments are unable to craft tax regimes which effectively capture resource rent.
3. Avoiding the Delta:
Sustainable management any discovered subsoil assets must avoid a local “Nigerian Delta” catastrophe. Clearly designating the government as the sole responsible agent for resource rents may limit such failures.
4. Saving the money:
To avoid plunder of the future by the present, Collier suggested that, though politically difficult, a proportion of revenue streams must be delineated from general accounts.
5. Building the capacity to invest in the country:
Collier deemed the inability of resource-rich countries to attract diversified investment as the “killer link.” Governments must use returns from subsoil assets to fund “investment in investment”—directing public capital toward transportation and utility infrastructure, education, health, and other short-term projects. Once in place, such projects encourage future public and private investments, thereby multiplying long-term returns.
As with many complex systems, Collier warned that the chain is only as strong as its weakest link. If one link fails, “the chain won’t pull the country from poverty to prosperity.” On the other hand, if each link holds, the value is tremendous. ”[Y]ou really can pull the country from poverty to prosperity over the course of a generation. There are no fixes in economics that are faster than that.”
Ultimately, Collier and Birdsall emphasized that success depends upon the development of an informed and competent “critical mass” of people. Even the strongest decision chain will fail if it is not underwritten by a majority of the population. Birdsall reiterated the need for public participation in the process, possibly through direct income distribution or responsible interventions by non-vested third parties.
Photo: Courtesy of Oxford University Press. -
VIDEO—How the World’s Poor Live on $2 a Day
›January 22, 2010 // By Dan Asin“Most people think that if you’re living on $1 a day or $2 a day, it’s impossible to save,” Jonathan Morduch tells ECSP Director Geoff Dabelko in a discussion of his book, Portfolios of the Poor: How the World’s Poor Live on $2 a Day. The Woodrow Wilson Center hosted Morduch and his co-author, Daryl Collins, for presenations at the Center and on Capital Hill last September. “[I]n fact, because of being poor—not despite it—households were spending a lot of time building up for the future.”
“What was really critical about what this new work was showing was that poor households were strategizing, they were making decisions,” says Morduch. “They were, essentially, juggling, active in ways that had been hidden from sight with the bigger surveys.” Now revealed, this knowledge creates opportunities for policymakers to help poor households in new ways, such as reducing regulatory costs for financial institutions seeking to service poor communities.
Morduch says microfinance and microcredit schemes are doing well, but that they are not enough to serve poor communities’ entire financial needs. “The next steps involve embracing what’s already going on and making products, devising products, that are even more flexible or even more appropriate,” he says. Households have a diverse range of needs, from food and water to financing health care and education, and Morduch says these diverse needs merit diverse solutions.
Showing posts from category development.



 “It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a
“It’s not every day you find an issue where effective diplomacy and development will allow you to save millions of lives, feed the hungry, empower women, advance our national security interests, protect the environment, and demonstrate to billions of people that the United States cares. Water is that issue,” declared Secretary of State Hillary Clinton at a 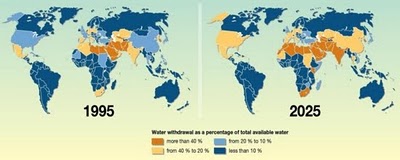



 Bill Gates gave the
Bill Gates gave the 


