Showing posts from category *Main.
-
Babatunde Osotimehin Answers Seven Questions on Population
›PSI’s Impact magazine has an interview up with UNFPA Executive Director Babatunde Osotimehin asking him seven questions about population. It’s not likely this will be the last seven-something-themed story as we approach October and the expected seven billion mark for global population, but Karl Hofmann, president and CEO of PSI, asks some good questions, including on the prospect of harnessing the “demographic dividend” and about the barriers facing more integrated development efforts – a critical topic in population, health, and environment (PHE) circles.
On the demographic dividend:Karl Hofmann: Demography can be a key to progress with the right policy environment in place, but it can also be a burden when we don’t have the right framework in place to take advantage of growing populations. Some have described this as the demographic dividend – growing populations as a potent driver of economic growth and development. Give us your perspective on that.
And on integrated development:
Babatunde Osotimehin: I spoke at the 17th African Union Summit this year and one of my messages was that we have the opportunity right now to take advantage of the demographic dividend of young people. It’s important for African governments to understand that they have a youthful population. Most of Africa is under the age of 35. If 85 percent of the African population is under 35, the implication is that you have to have education, social services, housing, all of that, tailored to meet the needs of this population.
Beyond that, given what we’ve seen with the Arab spring uprising and others in many parts of the developing world, young people who are out of work want education and economic opportunities. We want to appeal to member states to provide skills appropriate to development and also ensure that we have continuing conversations with young people about their reproductive health and rights so they can make the choices that will ensure they plan for their families.KH: There are lots of conversations going on in global health circles these days around the synergy of integration. From your perspective, what are the barriers to this integration?
Read the full interview on Impact.
BO: I think it’s bipolar. Some countries are satisfied with vertical programs. Others are resistant to changing their system at the request of a donor. One argument for integration is that you can have the one-stop shop situation where one, two, three trained providers can deliver services at the same time. These include integration of HIV counseling, testing and treatment with family planning, with health education for non-communicable diseases, with immunization for children or with maternity services.
When you look at the components of an integrated system, it is very easy to sell. In terms of investment, it makes sense for the governments to build and put this together. The supervision becomes a lot easier, and the training of health workers would then capture all of the skill sets that would be required. Some countries, like India, Ethiopia and Nigeria have started this kind of integration.
Sources: PSI.
Image Credit: Adapted from UNFPA. -
Edward Carr, Open the Echo Chamber
Food Security and Conflict Done Badly…
›The original version of this article, by Edward Carr, appeared on Open the Echo Chamber.
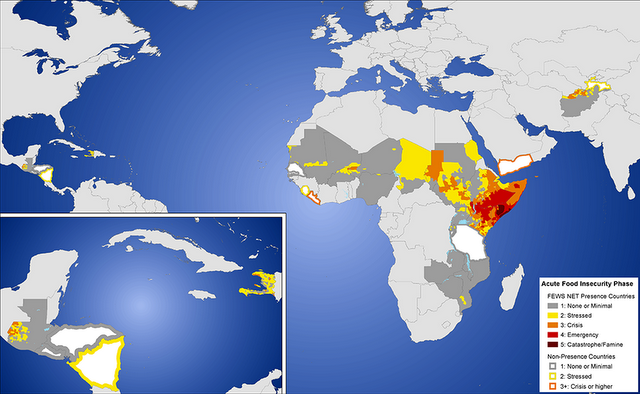
Over at the Guardian, Damian Carrington has a blog post arguing that “Food is the ultimate security need.” He bases this argument on a map produced by risk analysts Maplecroft, which sounds quite rigorous:The Maplecroft index [represented on the map], reviewed last year by the World Food Programme, uses 12 types of data to derive a measure of food risk that is based on the UN FAO’s concept. That covers the availability, access and stability of food supplies, as well as the nutritional and health status of populations.
I’m going to leave aside the question of whether we can or should be linking food security to conflict – Marc Bellemare is covering this issue in his research and has a nice short post up that you should be reading. He also has a link to a longer technical paper where he interrogates this relationship…I am still wading through it, as it involves a somewhat frightening amount of math, but if you are statistically inclined, check it out.
Instead, I would like to quickly raise some questions about this index and the map that results. First, the construction of the index itself is opaque (I assume because it is seen as a proprietary product), so I have no idea what is actually in there. Given the character of the map, though, it looks like it was constructed from national-level data. If it was, it is not particularly useful – food insecurity is not only about the amount of food, but access to that food and entitlement to get access to the food, and these are things that tend to be determined locally. You cannot aggregate entitlement at the national level and get a meaningful understanding of food insecurity – and certainly not actionable information.
Continue reading on Open the Echo Chamber.
Image Credit: “Estimated food security conditions, 3rd Quarter 2011 (August-September 2011),” courtesy of the Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWS NET) and USAID. -
Development or Security: Which Comes First?
› “Let’s take an area of conflict of great concern to us: Afghanistan. One of the very concrete questions is, do you invest your development efforts predominantly in the relatively secure parts of Afghanistan, which gives you more security gains in terms of holding them, or in the relatively insecure parts, where you’re most concerned with winning against the Taliban and the battle seems most in the balance?” With that question, Richard Danzig, the chairman of the board for the Center for a New American Security (CNAS), got to the heart of the issues being debated at a recent panel on development assistance and national security.
“Let’s take an area of conflict of great concern to us: Afghanistan. One of the very concrete questions is, do you invest your development efforts predominantly in the relatively secure parts of Afghanistan, which gives you more security gains in terms of holding them, or in the relatively insecure parts, where you’re most concerned with winning against the Taliban and the battle seems most in the balance?” With that question, Richard Danzig, the chairman of the board for the Center for a New American Security (CNAS), got to the heart of the issues being debated at a recent panel on development assistance and national security.
The discussion, hosted on September 5 by the Aspen Institute in conjunction with the Brookings Blum Roundtable on Global Poverty, brought together Rajiv Shah, the administrator of the U.S. Agency for International Development; Susan Schwab, professor at the University of Maryland and former U.S. trade representative; Sylvia Mathews Burwell, president of the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation’s Global Development Program; and CNAS’ Danzig. Most of the hour-long discussion was spent debating whether assistance could be successful in insecure situations (like Afghanistan), or if a place has to have some kind of stability before assistance can really take root and successfully spur development.
Short vs. Long term
Administrator Shah, not surprisingly, made the argument that development assistance is valuable in either instance. That said, he also strongly cautioned against overpromising what aid in a place like Afghanistan can accomplish, saying that “one big mistake we’ve made is to oversell what any civilian agency can do in an environment where there’s an active military campaign.” He pointed out that “it not only raises the cost of doing the work…but it also puts people at real risk.”
Danzig took a more aggressive tone, saying that “in the great majority of cases I think it is misleading and distortive to argue for development on the grounds that it will predominantly enhance security.” He argued that more often than not, security should be a prerequisite for development: “You need to distinguish cart and horse here…in most instances…the security needs to precede the development.”
Shah and Danzig, who dominated the panel, were more in sync about what development assistance can accomplish in longer-term scenarios, when security and stability are assured. Shah in particular spoke forcefully about development assistance over time, stressing that “in the long view, in the medium term, the development priorities are national security priorities.”
Enabling Success
However, Shah did warn that aid could fall short of our goals if it not carried out in a reliable way. “Stability and predictability of finance is the single thing that’s most highly correlated with good outcomes,” he said. When our aid to a country comes and goes unreliably, flowing one year and stopping abruptly the next, it’s much harder to have the kind of positive impact we want it to have, he explained.
“Through the years, where these questions have been debated back and forth, there has been one constant,” said moderator Jessica Tuchman Mathews, president of the Carnegie Endowment for International Peace. “We have always multiplied the objectives vastly beyond the resources – always.”
Video Credit: Aspen Institute. -
Jan Eliasson, Huffington Post
What Somalia Teaches Us: Sanitation, Health, and Conflict
›September 15, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Jan Eliasson, appeared on Huffington Post.
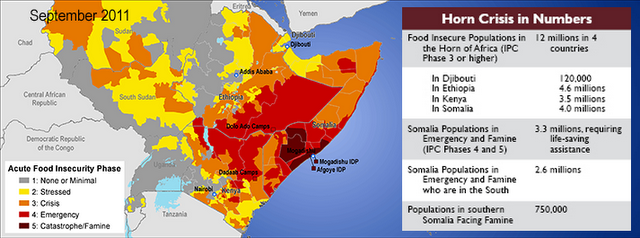
The confirmation of cholera deaths in Somalia offers a chilling reminder of what happens when there is no safe water and inadequate sanitation. The refugee crisis in Somalia is fueled by the worst drought in the horn of Africa in over 60 years.
This humanitarian disaster is a glaring example of the international community’s failure to uphold basic needs and rights of some of our planet’s most vulnerable people. As we struggle to respond to this humanitarian catastrophe, we must remember that Somalis are in need of more than access to food, but also safe water, sanitation, shelter, and healthcare.
For many of Somalia’s poorest citizens, who have walked for days and miles, drinking contaminated water, and staying in crowded camps, deadly diseases including cholera may be a tragic but predictable end result. Up to 100,000 people have crowded into Mogadishu, seeking shelter, food, and water. More arrive each day in Mogadishu and in overflowing camps in neighboring Kenya.
Experts estimate that more than 29,000 children under the age of five have already died from the combination of drought, famine, and illness. Diarrhea is on the rise in overcrowded shelters where there is a shortage of safe water and large numbers of weak and malnourished children. These conditions provide a breeding ground for infectious diseases, including measles, cholera and pneumonia. On August 18th, Tarik Jasarevic, a spokesperson for the World Health Organization, said, “We don’t see the end of it.”
Continue reading on Huffington Post.
Sources: AP, The New York Times, UN.
Image Credit: “The Horn of Africa food security crisis in numbers,” courtesy of the Famine Early Warning Systems Network (FEWS NET) and USAID. -
Water: Asia’s New Battleground
›“Asia faces a daunting water crisis,” warns Brahma Chellaney, professor at the Center for Policy Research (New Delhi) and author of the new book, Water: Asia’s New Battleground. It is a crisis that imperils the region’s economic and political rise, and that deepens environmental risk in a part of the world marked by melting glaciers and densely populated coastal areas.
In his book, Chellaney, regarded as one of India’s most distinguished strategists, surveys the water landscape across Asia; examines the security implications of water-based territorial disputes; and offers policy recommendations to help prevent water conflict. On September 12, Chellaney spoke about Water at a Wilson Center event organized by the Asia Program and co-sponsored by the China Environment Forum and Environmental Change and Security Program. Steven Solomon, a journalist and author who last year published Water: The Epic Struggle for Wealth, Power, and Civilization, offered commentary.
According to Chellaney, Water “fills a void in the literature” by, for the first time, focusing on water issues across the entire continental region of Asia – an immense expanse that includes not only Northeast, Southeast, and South Asia, but also Central Asia and the Middle East. The book, he explained, defines Asia “as it looks on a map.”
The World’s Dam Center
What drives the water crisis in this vast region? One factor is population. Asia is the world’s largest and most populous continent but also the most water-deficient; its freshwater levels per capita are one-third those of Europe’s, and slightly less than Africa’s. Another is tied to economic development. Asia is the world’s fastest developing continent, yet its most rapidly developing nations, particularly India and China, are already afflicted by serious water challenges.
Rising income levels and attendant growth in consumption rates are additional drivers. Asians are consuming more resources, including meat, which requires prodigious amounts of water to produce. A fourth factor is intensive irrigation. Seventy percent of the world’s total irrigation originates in Asia, and 80 percent of the region’s “water withdrawals” are allocated to agriculture. (The latter figure is only 30 percent in Europe.) Such large-scale irrigation has enabled Asia to evolve from “a land of recurrent famine” to a major food exporter, yet it has also spawned ruinous agricultural conditions such as waterlogging and soil salinity.
Chellaney contended that Asia’s water ills can also be attributed to the “large-scale impoundment of water” by dams, barrages, and other storage-creating structures. Asia is the world’s “dam center,” he said, with China boasting half the world’s dams and now planning to construct “mega dams,” including one “higher than the Eiffel Tower.” Impounding water triggers riverwater depletion, which in turns promotes “the reckless use” of sub-surface groundwater resources, said Chellaney. With water tables plummeting, millions of groundwater pumps are depleting what used to be a pristine and plentiful resource.
“We Need Better Politics”
In a region rife with transboundary rivers yet devoid of mechanisms to promote transboundary water-sharing, Asia’s water troubles pose grave geopolitical risks.
According to Chellaney, “water wars” are already being waged across the region via non-military means, fostering mistrust and hampering efforts toward greater cooperation. He argued that in order to forestall water conflict, Asia must develop a set of norms on shared resources based on the 1997 UN Convention on the Non-Navigational Uses of International Watercourses – the only available instrument for international water management. Chellaney also called for the creation of “inclusive water institutions,” that emphasize transparency and dispute settlements, and for the adoption of “holistic planning” on central and provincial governmental levels that aim for better water efficiency.
Playing devil’s advocate, Solomon faulted Chellaney for according insufficient attention to Asia’s crisis of energy – a resource that, he pointed out, is “extraordinarily water-intensive.” He also countered Chellaney’s criticism of dams by observing that Asia desperately needs storage – a deficiency that makes the region highly vulnerable to drought. And he questioned whether China’s dam-building activities on the Brahmaputra River truly imperil lower riparian India’s water security, noting that only 15 percent of the river’s flows entering India are impacted by Chinese dams.
Ultimately, Chellaney said, alleviating Asia’s water crisis will also require improving the region’s poor political environment. While Asian economies are coming together, its politics are more divided. Transboundary water cooperation – and any treaty meant to undergird it – cannot be expected to last if co-riparians do not get along. “We need better politics,” he concluded.
Event ResourcesMichael Kugelman is a program associate with the Wilson Center’s Asia Program.
Photo Credit: David Hawxhurst/Wilson Center. -
Debts, Deficits, and Development
›The debates surrounding the U.S. national debt and deficit bring with them implications for both overall U.S. development policy and the budgets of USAID and the Department of State. These implications were the focus of the Wilson Center on the Hill event that took place on August 2, “Debts, Deficits, and Development,” moderated by Wilson Center Senior Scholar John Sewell. Sewell said that Congressional action on deficit reduction could potentially reduce funding for development-related initiatives just as the U.S. government “for the first time…is taking development and the notion of development very seriously.”
After an introduction from Sewell, Gordon Adams, distinguished fellow at the Henry L. Stimson Center, began by talking about the lack of attention that international affairs and the civilian side of U.S. international engagement usually receive in the government budget. He noted the growth in personnel and funding at USAID and the Department of State over the past ten years as a success, adding that a fair amount of this growth was related to the conflicts in Iraq and Afghanistan and the global effort against terrorist organizations.
“Foreign policy, development, foreign assistance, [and] diplomacy have increasingly been viewed as a key part of a broadly defined security budget,” said Adams. The first Quadrennial Diplomacy and Development Review had the potential to restructure the Department of State and USAID in line with these goals, he said, but lacked the force to prioritize programs and allocate funds effectively.
In post-conflict environments, Adams emphasized the need to build the capacity to govern effectively, efficiently, and accountably first. “Where we fall down,” added George Ingram, co-chair of the Modernizing Foreign Assistance Network, “is in rushing too much money in right as the conflict ends for two or three years and then getting distracted by other crises from year five to ten; when the country’s built up a capacity and probably could use the assistance, our interest falls off.” In his opinion, that sequencing should be reversed.
Focus on Priorities
Adams continued to emphasize the need for goals and priorities when he addressed the topic of belt-tightening at USAID or the Department of State. According to Adams, the four categories to consider in allocating resources are: security assistance; the individual priorities of foreign assistance and development funds; conflict prevention and resolution; and better preparation and training of personnel. He lauded the military’s commitment to training its servicemen and women throughout their careers and suggested a similar program for members of the Foreign Service. To coordinate these priorities, however, a coherent U.S. development strategy (currently lacking) is essential, said Ingram.
Focusing on how the current budget environment is impacting development, Ingram said that the decade of growth in the international affairs budget for development may have just hit a brick wall. He described the FY 2012 budget as “skewed heavily toward reducing the development accounts and protecting the security accounts,” resulting in an 11 percent overall cut from 2011 levels and some development accounts being reduced by 20 or 30 percent.
Ingram noted that USAID’s overall operating expenses were cut by 27 percent from FY 2011 levels. This operating expense reduction will likely halt planned increases in USAID staff and may ultimately lead to staff cuts. The failure to build up staff at USAID will reduce its ability to manage key development programs and slow the Department of Defense’s efforts to shift responsibilities for development work to civilian hands.
Adams added that in light of shrinking resources, legislators will probably ask supporters of development about the tangible outcomes of investment in development and about the link between development and American interests, so they should be prepared with answers. Ingram cited the successes of U.S. aid over the last decades – such as the Green Revolution and oral rehydration – and noted how they benefited from a long-term perspective rather than approaching development on a project-by-project basis.
Given the tumult in the Middle East since the start of the Arab Spring, the need for expertise in governance is high, said Adams. “The problem of governance in failing, fragile, weak, brittle authoritarian states,” he said, “is a great risk to stability.”
Event Resources:Erica Pincus is an intern at the Wilson Center’s Program on America and the Global Economy.
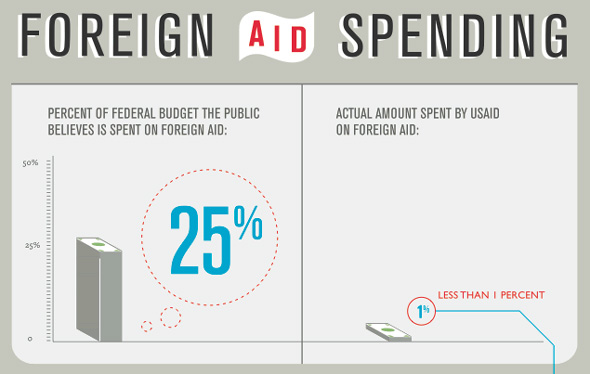
Image Credit: “Foreign Aid Spending,” courtesy of visual.ly user maggie, published by USAID. -
Rich Thorsten on Water Sanitation, Population, and Urbanization in the Developing World
› “For the first time in human history, more than one half of the world’s population now lives in urban areas, and some of the largest and fastest growing population centers in the world – countries like India, China, parts of sub-Saharan Africa – are in areas where water resources are becoming more and more scarce,” said Water.org’s Rich Thorsten in a recent interview with ECSP.
“For the first time in human history, more than one half of the world’s population now lives in urban areas, and some of the largest and fastest growing population centers in the world – countries like India, China, parts of sub-Saharan Africa – are in areas where water resources are becoming more and more scarce,” said Water.org’s Rich Thorsten in a recent interview with ECSP.
Thorsten serves as director of international programs for Water.org, which partners with local communities, governments, and NGOs across Central America, South Asia, and Africa to bring improved water sanitation to at-need rural and urban populations. He emphasized that ensuring access to clean water has a number of positive spillover effects, ranging from improved prospects for economic development to greater social stability, since access to non-polluted water supplies removes one potential source of tension within and between communities.
Community Health
The greatest benefit of improved sanitation services, however, comes in the form of enhanced public health outcomes. “I would definitely say there is a strong correlation” between the two, Thorsten asserted. “Water and sanitation-related diseases are related to the deaths of at least 3.5 million people every year in the developing world – not to mention millions of hours and dollars that are lost to treating health problems and coping with health problems as a result of poor [water] access and hygiene practices.”
Thorsten said that community participation has been a key aspect of ensuring the sustainability of Water.org’s projects. To pave the way for continued gains in economic development and public health, he said they work alongside water users, engineers, and government officials in target communities to make those parties stakeholders in the infrastructure development process. Fostering a sense of community ownership of sanitation projects helps reduce the likelihood that infrastructure will fall into disrepair or disuse after the initial programming intervention has been conducted.
Given that improving water-sanitation access for the world’s poor is a key element of the UN Millennium Development Goals, Thorsten said he is pleased the subject seems to be attracting more attention within the policymaking and development communities. Despite the positive momentum, however, he acknowledged the fight to ensure clean-water access for the developing world will remain an uphill battle.
“When one considers that….about 2.6 billion people lack access to basic sanitation, that there’s more people in the world that have access to a cell phone than a pit latrine or a toilet, it’s still a very daunting task that will require a lot more investment, commitment, and attention in order to improve the situation for billions of people,” Thorsten said.
Sources: UN.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
John Donnelly, Global Post
Family Planning and Seven Billion at the Aspen Institute
›September 9, 2011 // By Wilson Center Staff
The original version of this article, by John Donnelly, appeared on Global Post.
Sometime this fall, the world’s population will reach 7 billion people. Experts now forecast that by 2050, the population could be 10 billion.
Those numbers, said the former presidents of Chile and Latvia at an event in Washington D.C., Wednesday night, should force policy makers to focus more intently on making family planning much more widely available in the developing world.
“When we are 9, 10 billion people, what are we going to do? Go to Mars? Go to the moon?” said Michelle Bachelet, the former president of Chile and now the Under Secretary-General and Executive Director of UN Women, the latest agency created by the United Nations. “We are really going to have huge problems. Family planning is a huge issue.”
Her comments came during a series of discussions organized by Aspen Global Health and Development called “7 Billion: Conversations that Matter.” The talks, funded in part by the U.S. Agency for International Development, have often centered on global health issues, and Wednesday’s event was no different.
Continue reading on Global Post.
Video Credit: The Aspen Institute.