-
‘New Security Beat’ Is Five Years Old
›January 26, 2012 // By Wilson Center Staff
ECSP’s Sean Peoples, Meaghan Parker, and Schuyler Null accepted the Population Institute’s Global Media Award for Best Online Commentary at a January 12 ceremony in New York City. Five years ago, in January 2007, we launched New Security Beat. Since then we’ve established a strong editorial focus on a key but neglected niche: where population, environment, and security meet.
-
Move Beyond “Water Wars” to Fulfill Water’s Peacebuilding Potential, Says NCSE Panel
›January 26, 2012 // By Schuyler NullOne of the best talks of last week’s NCSE Environment and Security Conference was thewater security plenary on Friday. Moderator Aaron Salzberg, who is the special coordinator for water resources at the Department of State, led with a provocative question: how many in attendance think there will be war over water in the future?
-
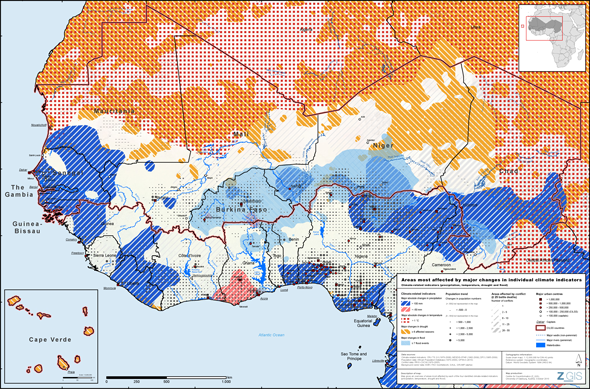
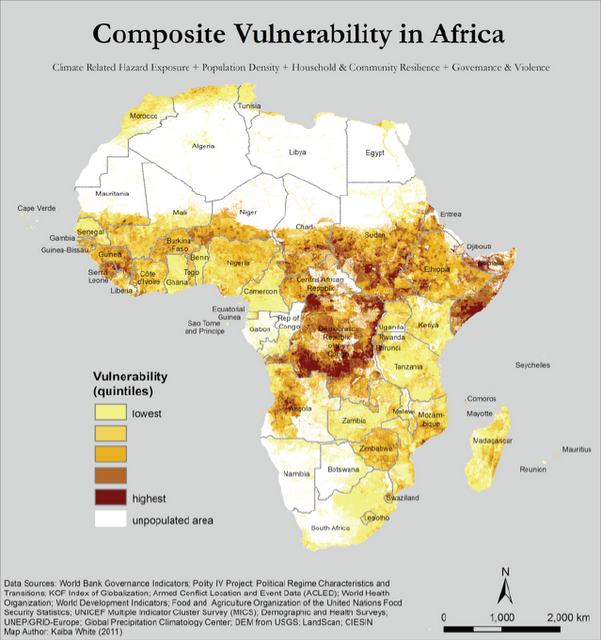
UNEP Maps Conflict, Migration, Environmental Vulnerability in the Sahel
›A new set of maps from the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP) identifies “climate hotspots” – areas vulnerable to instability exacerbated by climate change – in 17 sub-Saharan countries in and bordering the Sahel region. The maps reflect the fact that, more often than not, the impact of climate change on local populations is compounded by changes in migration, conflict, or both. According to Livelihood Security: Climate Change, Migration and Conflict in the Sahel, the UNEP report accompanying the maps, understanding “the exacerbating effect of changes in climate on population dynamics and conflict in the region” will be essential to developing successful adaptation strategies throughout the region.
UNEP’s maps analyze 40 years of data to pinpoint where the region’s most at-risk populations are located based on environmental, population, and conflict trends dating back to 1970. In a single map pinpointing the Sahel’s 19 hotspots, UNEP synthesizes subnational data from four environmental indicators over time – rainfall (from 1970 to 2006), temperature changes (1970 to 2006), drought (1982 to 2009), and flooding (1985 to 2009) – which are then layered on top of population trends (1970 to 2010) and conflict data (1970 to 2005) in order to identify the region’s most insecure areas.
Composite Vulnerability
At first glance, the map can appear hard to decipher; it is flooded with different colors and symbols, each indicating something different about the extent of climate change, migration, and conflict in the region. A Google Earth version of the map (available for download here) makes all this information easier to process by allowing users to select which indicators they want to see mapped out, cutting back on the number of lines, dots, colors, and pie charts the user has to decode.
Given the vast amount of the information being condensed into these maps, the report is a helpful and worthwhile read. For instance, eight hotspots are in places with growing populations and another seven are located in places that have experienced conflict; altogether, 4 of the 19 hotspots have both past conflict and growing populations. The report digs deeper into the confluence of climate, conflict, and migration by discussing case studies that highlight how the three intersect in local communities (at the same time, the report is careful to avoid suggesting that there is a causal relationship between the three issues.). In Niger, Nigeria, and Chad, for example, tensions have been mounting between northern pastoralists and southern farmers as each group has moved further and further afield in search of water and arable land to sustain their livelihoods.
Holes In the Data
While the hotspot maps include a wealth of information, the report makes clear that it is by no means exhaustive. Rising sea levels are, for instance, a major impending threat to coastal populations in the Sahel, but only the downloadable Google Earth map – not the hotspot map in the report or the Google Earth map as presented online – incorporates this factor. Compounded with a skyrocketing population in the coastal areas – the coast between Accra and the Niger delta is expected to be “an urban megalopolis of 50 million people” by 2020, according to the report – an increase in sea levels could have a huge impact on the region’s stability.
The report also readily admits that the datasets for population trends and conflict have shortcomings. Population data is largely based on censuses, which both the report and its data sources (UNEP’s African Population Database and the Gridded Population of the World, version 3) acknowledge can be inconsistent in their accuracy. Additionally, after 2000, population data is based on projections rather than estimates, which, as last year’s update from the UN Population Division showed, have often proven inaccurate, particularly in sub-Saharan Africa.
Regarding conflict, the UNEP report is straightforward in admitting its limits. The report lacks data on small-scale conflict (fewer than 25 battle deaths, following the Uppsala Conflict Data Program’s threshold that separates conflicts from lower-level violence), even as it acknowledges that such conflict is “often the first to occur” when climate change threatens communities’ access to resources and livelihoods.
Ultimately, however, these maps give valuable data on specific locations that are uniquely vulnerable to trends in population, climate, migration, and conflict. They add focus to the conventional wisdom that climate change will impact the region’s stability, and, taken together, the maps and the report provide a valuable resource for scholars and policymakers attempting to craft adaptation policies that take into consideration these complex links.
Sources: Socioeconomic Data and Applications Center at Columbia University’s Earth Institute, UNEP, Uppsala Conflict Data Program.
Image Credit: UNEP. -
Ethan Goffman, SSPP Blog
Securing a Sustainable Future: The Military Takes On a New Mission
›January 25, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Ethan Goffman, appeared on the Sustainability: Science, Practice, and Policy blog.
In a time of polarized politics in the United States, over the environment and just about everything else, an overlooked development is how much the military, as well as the national security apparatus, has taken on climate change and other environmental challenges. “Environment and Security” was thus a profoundly important choice of theme for the 2012 National Conference on Science, Policy, and the Environment, held last week in Washington, DC. With the early effects of climate change apparently already occurring, notably in an increase in natural disasters and in a new northwest passage through the Arctic, those responsible for our security can’t afford to sit around and engage in speculation that climate change is caused by sunspots or isn’t really occurring. It is the military’s job, after all, to take action against potential threats rather than getting immersed in domestic politics.
The concern with climate change is the next step in a widening of the concept of security from strict military matters, to include such interrelated strands as food and water access, public health, and the environment. Much of the military has already acknowledged that armed force alone won’t make us safe. “Energy security, economic security, environmental security, and national security are all inextricably linked. Address one and you need to think of the others,” explained Vice-Admiral Dennis McGinn at the conference.
One obvious linkage is the connection of our oil dependency with security risks that can easily draw us into conflict in politically unstable parts of the world. Just how much the recent wars in the Middle East are about oil, and how much about a clash of civilizations, is a matter of considerable debate, although undoubtedly both factors play a part. The Iranian threat to close the Strait of Hormuz, choking outgoing oil deliveries, underscores vulnerability on the energy issue. From another angle, in Afghanistan, the military experienced the fragility of supply lines for a force strongly dependent on large quantities of oil. The Air Force, in particular, is working on algal jet fuel to free us from such reliance. And the Navy’s need for more icebreakers and other capacity shows concern regarding shipping and resource exploitation enabled by the melting of Arctic ice and the new passage.
Continue reading on the SSPP blog.
Photo Credit: Sherri Goodman and Rear Admiral Neil Morisetti, courtesy of Sean Peoples/Wilson Center. -
New Research on Climate and Conflict Links Shows Challenges for the Field
›
“We know that there will be more conflicts in the future as a result of climate change than there would have been in a hypothetic world without climate change,” said Marc Levy, deputy director of the Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) at Columbia University’s Earth Institute, although existing data and methodologies cannot predict how many additional conflicts there will be, or which causal factors will matter most. [Video Below]
-
John Donnelly, Global Post
A Call for Young People to “Get Angry” About Global Warming
›January 18, 2012 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by John Donnelly, appeared on Global Post.
The elder called on the younger generation to speak up.
At a session on climate change and family planning Thursday, Mary Robinson, the former president of Ireland, said that she keeps hoping that more young people will demand action on global warming.
“Maybe there’s a need to link the more thoughtful aspects of the Occupy movement with this, to get some of that more radical thinking,” she said. “As younger people increasingly understand the issues, I would say, ‘get angry’ so that we feel the need to do something more urgent. Let us know this is your future and for goodness sake it is absolutely urgent.”
She spoke at a session called “The Road to Rio: Climate Change, Population and Sustainability,” part of the Aspen Institute’s “7 Billion: Conversations that Matter” roundtable series (watch above). The discussion, organized by Aspen Global Health and Development, focused on strategies leading up to the Rio+20 United Nations Conference on Sustainable Development Summit in June – as well as what should be happening beyond Rio.
Continue reading on Global Post.
Video Credit: The Aspen Institute. -
Jon Barnett: Should Climate Change Be Addressed by the UN Security Council?
›For a small island state like Tuvalu, climate change is an enormous security issue and they have told the UN Security Council as much, said Jon Barnett, professor of resource management and geography at the University of Melbourne, in an interview with ECSP. But, despite debate in 2007 and 2011, the Council has been unable to reach agreement on whether climate change is an international security issue or not.
-
Jon Barnett: Climate Adaptation Not Just Building Infrastructure, But Expanding Options
›“I think it’s appropriate to think about [climate change] adaptation or investments in adaptation as investments to open up the range of choices available to people to deal with an uncertain future,” said Jon Barnett, associate professor of geography at the University of Melbourne, in an interview with ECSP. “In some circumstances it might be appropriate to build infrastructure and hard options where we’re very certain about the nature of the risk…but in other cases, expanding the range of choices and freedoms and opportunities that people have to deal with climate change in the future is perhaps the better strategy.”
Showing posts from category environment.