Showing posts from category gender.
-
Judith Bruce on Empowering Adolescent Girls in Post-Earthquake Haiti
› “The most striking thing about post-conflict and post-disaster environments is that what lurks there is also this extraordinary opportunity,” said Judith Bruce, a senior associate and policy analyst with the Population Council’s Poverty, Gender, and Youth program. Bruce has spent time this year working with the Haiti Adolescent Girls Network (HAGN), a coalition of humanitarian groups conducting workshops focused on the educational, health, and security needs of the country’s vulnerable female youth population.
“The most striking thing about post-conflict and post-disaster environments is that what lurks there is also this extraordinary opportunity,” said Judith Bruce, a senior associate and policy analyst with the Population Council’s Poverty, Gender, and Youth program. Bruce has spent time this year working with the Haiti Adolescent Girls Network (HAGN), a coalition of humanitarian groups conducting workshops focused on the educational, health, and security needs of the country’s vulnerable female youth population.
Gender-based violence has long been an issue in Haiti, but the problem became even more pronounced in the wake of the January earthquake. HAGN has sought to address the problem by concentrating its community-based programming on “high priority” groups, including girls who are disabled, serve as de facto heads of households, or are aged 10-14.
Bruce asserted that protecting and empowering young girls is critical because upon reaching puberty, “their access to a safe world shrinks dramatically.” With the post-disaster environment adding another layer of challenge, she said “there could be no ambiguity in anyone’s mind that we have to create dedicated spaces for girls who, at least for a few hours a week, feel secure to be themselves and to plan for their long-term safety as well as their development.”
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
The World’s Toilet Crisis
›Forty percent of the world’s population – 2.6 billion people – do not have access to toilets, and some in the international aid community are finally dispensing with the euphemisms and calling this sanitation crisis what it is: “shit.”
In “The World’s Toilet Crisis” (trailer above), Adam Yamaguchi sets off in an episode of Current TV’s Vanguard program to tell the story of “the deadliest killer in the world…something no one wants to talk about.” All around the developing world, thanks in part to rapid population growth and poor development and environmental standards, “people are literally eating their own shit,” he said.
His journey takes him to India, where more people own cell phones, than toilets. The 55 percent of Indians who practice open defecation have contributed to another grim statistic: an estimated 840,000 children under the age of five die in India each year from diarrheal diseases.
India’s water quality is especially affected by lack of sanitation. In the documentary, Yamaguchi visits the Yamuna River, which is Delhi’s primary source of drinking water, and has become a “giant toilet” literally bubbling with methane gas. This phenomenon is not unique to India. Approximately 80 percent of sewage in developing countries goes untreated, polluting local water resources.
But it is women who feel the effects of lack of access to clean water and toilets most keenly. In 72 percent of households around the world, women are the primary water collectors, often travelling long distances for drinkable water. They face shame and harassment when going to the bathroom, causing them to suppress their need until dark, causing negative health effects. Waiting until nightfall also means that when women openly defecate, they often face molestation, violence, and rape. Teenage girls also often drop out of school once they begin to menstruate because toilets are not private, unsafe, or are simply nonexistent.
Reflecting on his motivations for making the documentary, Yamaguchi said that in order to expose this “global public health crisis,” he needed to be as graphic, shocking, and disgusting as possible.If you’re not grossed out by, or incensed by the fact that there is shit everywhere, you’re not really moved to act or change your ways. And that’s ultimately what’s happened in many places in the world. It’s a normal fact of life. You see it everywhere, and you think nothing of it. There are causes out there that are deep sexy causes or marketable causes. Shit or toilets – not the most marketable thing in the world.
“The World’s Toilet Crisis” forms part of a broader trend among sanitation advocates to use crude language to address a problem the international health and development community has traditionally shied away from talking about directly.
Tales of shit: Community-Led Total Sanitation in Africa, published shortly before World Toilet Day by the International Institute for Environment and Development, takes an equally direct approach to sanitation.
Community-Led Total Sanitation (CLTS) is an approach begun with great success by Dr. Kamal Kar in Bangladesh that relies on “triggering” to change community behavior. The report, which is prefaced by a three-page “International Glossary of Shit” listing the words for shit in other languages, emphasizes the need to “explicitly [talk] about and [make] visible the shit that is normally hidden beneath taboos and polite language.” By almost literally thrusting people’s shit right under their noses, communities learn what they have been ignoring: that they are “eating each others’ shit.”
Traditional sanitation programs often fail because “a high proportion of latrines constructed with subsidies are never used as toilets, but as storage space, animal shelters, or prayer rooms – the buildings are too high quality to be wasted on toilets!” says the report. CLTS, on the other hand, focuses on changing behavior at the community, rather than the individual level to create sustainable change that responds and adapts to a community’s distinct culture and needs.
“The World’s Toilet Crisis” shows the promise CLTS has of meeting the needs of the billions without toilets. In East Java, Yamaguchi joins a community leader to collect a “specimen” from a well-traveled river bank near the town, which he proceeds to show to a group of women in the town who are, predictably, revolted. The community then takes collective action to become “open-defecation free” and invest in toilets.
“The World’s Toilet Crisis” is not easy to watch, nor was it easy to film – seven minutes in, Yamaguchi vomits on the banks of the polluted Yamuna River. Disgust, however, is central to raising awareness and affecting change on both the community and global levels. As Yamaguchi explains, “You’re going to get grossed out by seeing this piece, and that’s part of the point.”
Sources: Community-Led Total Sanitation, Current TV, Earth Times, IIED, Water.org, World Toilet Organization, WHO, United Nations University.
Video Credit: “The World’s Toilet Crisis – Vanguard Trailer,” courtesy of Current TV’s Vanguard. -
An Integrated Climate Dialogue
COP-16 Cancun Coverage Wrap-up
›December 13, 2010 // By Schuyler NullAfter focused last-minute negotiations, the UNFCCC COP-16 parties meeting in Mexico finally reached an agreement on a package being called “The Cancun Agreements” on Saturday. One of the most important impacts of the agreement (also referred to as the “balanced package”) is the establishment of a green climate fund which will help developing countries adapt to and mitigate the effects of climate change.
For more on the green fund as well as the integration of gender, population, development, and even a little bit of security in the broader climate dialogue, see The New Security Beat’s coverage of Cancun below.- Interview with Karen Hardee: Climate-Proofing Development
- Pop Audio: From Cancun: Roger-Mark De Souza on Women and Integrated Climate Adaptation Strategies
- Guest Contributor Alex Stark: From Cancun: Getting a Climate Green Fund
- The Number Left Out: Bringing Population Into the Climate Conversation
Kicking off our coverage was an email interview with Karen Hardee, visiting fellow with the Population Reference Bureau, on “climate-proofing” development. Hardee gives a brief overview of the UN National Adaptation Programmes of Action system and the current state climate adaptation integration in international development. She points out that one of the enduring positives from COP-15 was a renewed focus on financing tools that has permeated to the top levels of the UN.
Hardee also touched on the nascent but largely unfulfilled connection between population growth and resilience, noting that “of the first 41 programs submitted to the UNFCCC…37 noted that population growth exacerbated the effects of climate change, but only six explicitly stated that meeting an unmet demand for RH/FP should be a key priority for their adaptation strategy and only two proposed projects that included RH/FP.”
Next, Population Action International’s Roger-Mark De Souza was kind of enough to speak with us briefly over the phone from the conference itself, providing a run-down on a PAI-sponsored side event focusing on empowering women in climate debates.
“When you look at the negative impacts of climate change, the impacts on the poor and the vulnerable – particularly women – increase, so investing in programs that put women at the center is critical,” De Souza said.
Leaving gender issues, like child and maternal health and education, out of deliberations like those COP-16 are missed opportunities to get more “power for your peso,” he said.
Alex Stark, formerly of CNAS and now with the Adopt a Negotiator program in Cancun, provided an update and a strong argument for one of the most critical elements of the “balanced package” that many are hoping will come out of Cancun – the establishment of an international fund to help pay for adaptation and mitigation programs in developing countries.
Stark provides an insight into some of the chatter on the floor at COP-16 and also outlines the moral, development, and security advantages to supporting a green fund, pointing out that “by managing displacement, migration, and violent conflict driven by the effects of climate change, such as water scarcity, climate change adaptation can help bolster international security and stability.”
“Within the UN process itself,” she writes, “a robust, well-run, equitable green fund would help rebuild the trust lost between developed and developing countries at Copenhagen last year.”
Lastly, Bob Engelman, of the Worldwatch Institute, provides a broad argument for more inclusion of a key variable in climate debates – population (and not in the Ted Turner mold). He enumerates the common pitfalls of population debates, from sensitivities about personal choices to squeamishness about sexuality and reproductive health, and just plain gender bias.
But despite these barriers, says Engelman, population – and not just growth but demographics too – matters in the climate debate and therefore needs to be part of the conversation (an argument he makes more comprehensively in a new report, Population, Climate Change, and Women’s Lives). Echoing De Souza, he concludes by pointing out that although the discussion may be difficult, the solution is relatively simple: “On population, the most effective way to slow growth is to support women’s aspirations.”
“As societies, we have the ability to end the ongoing growth of human numbers – soon, and based on human rights and women’s intentions,” Engelman said. “This makes it easy to speak of women, population, and climate change in a single breath.”
Sources: Population Action International, Slate, UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, The Washington Post, Worldwatch Institute.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Trees Dead on Shore of Timor-Leste Lake,” courtesy of flickr user United Nations Photo; Roger-Mark De Souza, courtesy of David Hawxhurst/Wilson Center; “Will you back a climate fund?,” courtesy of flickr user Oxfam International; and “Met Office Climate Data – Month by Month (September),” courtesy of flickr user blprnt_van. -
Expanding Access to Maternal Health Commodities
›“This is not just about getting quantities of drugs out, this is about saving women’s lives with really simple products that work,” said Julia Bunting, team leader of AIDS and reproductive health at the UK Department for International Development and coalition chair of the Reproductive Health Supplies Coalition, at the ninth meeting of the Global Health Initiative’s 2009-2010 Advancing Policy Dialogue on Maternal Health series. Joined by panelists Melodie Holden, president of Venture Strategies Innovations (VSI), and Elizabeth Leahy Madsen, senior research associate at Population Action International (PAI), the panel discussed the challenges and strategies for expanding access to maternal health commodities.
Integrating Maternal Health and Family Planning Supply Chains
“It is often said that the family planning and the maternal health communities have very different views of supplies… but actually [both communities] recognize that we need to explore the continuum,” said Bunting, addressing the need to integrate maternal health commodities into existing reproductive health supply chains. “I really think the stars are aligned right now for advancing this agenda,” added Bunting.
“Many of the commodities that we talk about in terms of reproductive and maternal health cost tiny amounts to deliver, but actually save lives and are some of the most cost-effective interventions we have both in public health and in broader development,” said Bunting.
No Product, No Program
“Supplies are a key element in programs to improve maternal health and they are also a tangible and visible hook to increase awareness and commitment,” said Madsen. “Policymakers whose eyes glaze over when they hear the term ‘health systems strengthening’ can grasp… much better when they learn that supply shelves in clinics are bare and that women are making great efforts to reach facilities, only to leave empty- handed,” said Madsen.
Presenting research conducted by PAI, Madsen discussed the availability of four key maternal health medicines and products in Bangladesh and Uganda including:
By focusing on supplies that target the three leading causes of maternal mortality, Madsen and her colleagues identified factors that inhibit access to these commodities and developed recommendations for strengthening maternal health supply chains.- Oxytocin: used to prevent post-partum hemorrhage
- Misoprostol: used to prevent post-partum hemorrhage
- Magnesium Sulfate: used to treat pre-eclampsia
- Vacuum Aspirators: used for treatment of early and incomplete abortion
Madsen identified several strategies to strengthen supply chains for maternal health commodities including forecasting and preparing for growing demand, advocating for government and donor support, encouraging scaling-up of community-based approaches, promoting family planning, and focusing on human resource training.
“In maternal health, if a supply to prevent or treat a life-threatening complication is in stock, there must also be a way for a woman to reach it in time… and in most cases a provider who knows how to administer it,” said Madsen.
“This research is intended to lay the groundwork for future advocacy and policy initiatives by providing an evidence base that is informed by local expertise,” said Madsen. “We hope that this information will inform program implementation, funding decisions, and awareness raising.”
Getting the Product to People: The Case of Misoprostol
“The story of Misoprostol is still being written. The goal is to invest in creating access to interventions that are low-cost and relatively simple to use,” said Holden. By sharing lessons learned, Holden described VSI’s experience registering and procuring Misoprostol and demonstrated how community mobilization is imperative to overcoming major challenges for large-scale implementation.
“Making products available is not without challenges,” said Holden. To increase access to Misoprostol in rural communities, maternal health experts must work to “engage communities, educate and mobilize women, train providers at all levels of the health care system, and provide support to distributors to jump start sales,” said Holden. “By looking holistically across entire health systems, bringing in great interventions, addressing the components of supply and demand, and working with local partners, we can have lasting impact.”
While the price of Misoprostol has decreased significantly, Holden stressed the need to identify creative ways along the supply chain that reduce costs to the end user. Additionally, “establishing policies around this new intervention not only establishes its reach, but also makes its use institutionalized, which means it will be part of the system even if governments or individuals change,” said Holden.
“If there is a gap between what could be achieved with Misoprostol and what is being achieved, we need to go back to the model and figure out what pieces aren’t working,” concluded Holden. “The work is complex and takes time, but it’s worth it.”
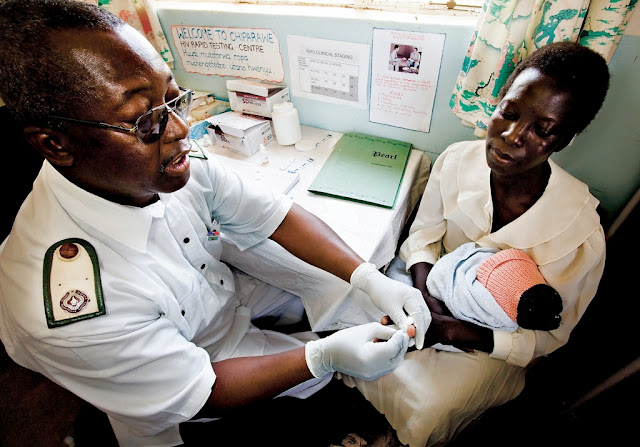
Photo Credit: “Rapid HIV testing,” courtesy of flickr user DFID – UK Department for International Development. -
Robert Engelman, Worldwatch Institute
The Number Left Out: Bringing Population Into the Climate Conversation
›December 9, 2010 // By Wilson Center Staff Numbers swirl around climate change.
Numbers swirl around climate change.
So many parts per million of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. So many gigatons of carbon dioxide emitted. So many degrees Celsius of temperature rise that we hope won’t happen. Yet one number rarely comes into play when experts or negotiators talk about the changing atmosphere and the warming of the planet: the number of humans putting heat-trapping gases into the air.
The original version of this article, by Robert Engelman, appeared on the Worldwatch Institute’s Transforming Cultures blog.
The UK Met Office’s data set for September 2009 of more than 1,600,000 temperature readings from 1,700+ stations.
Numbers swirl around climate change.
So many parts per million of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. So many gigatons of carbon dioxide emitted. So many degrees Celsius of temperature rise that we hope won’t happen. Yet one number rarely comes into play when experts or negotiators talk about the changing atmosphere and the warming of the planet: the number of humans putting heat-trapping gases into the air.
The relative silence isn’t hard to understand. Population is almost always awkward to talk about. It’s fraught with sensitivity about who has how many children and whether that is anyone else’s business. It’s freighted with sexuality, contraception, abortion, immigration, gender bias, and other buttons too hot to press into conversation. Yet two aspects of population’s connection to climate change cry out for greater attention – and conversation.
One is that population – especially its growth, but other changes as well – matters importantly to the future of climate change, a statement that as far as I can tell is not challenged scientifically. (The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, for example, accepts the accuracy of the so-called Kaya identity, which names population among the four factors that determine emissions growth from decade to decade.) And, two, addressing population in climate-friendly ways is also fundamentally people-friendly, in that it involves no “population control,” but rather the giving up of control – especially control of women’s bodies by people other than themselves.
A new Worldwatch Institute report, which I authored, offers details, findings, and recommendations on both the importance of population in climate change and how to address it. The report looks at some of the history of the population-climate link – in particular, interesting work by William Ruddiman, who hypothesizes that the agricultural revolution contributed to global warming thousands of years ago. And it addresses the common objection that population growth can’t be that important in greenhouse gas emissions growth because countries with high per capita emissions tend to have smaller families than low-emitting countries.
Equity in per capita emissions, I argue, is an essential goal – and without it, no global effort to shrink emissions can succeed. The imperative of an equal sharing of atmospheric carbon space is among the most powerful arguments for a smaller world population. When greenhouse gases other than carbon dioxide – such as methane and “black carbon” – are considered, per capita emissions gaps are not as wide as many writers believe. And the amount of all these gases that equal emitters can contribute without altering the atmosphere shrinks in direct proportion to population’s growth.
Arguments about population’s role in climate change are unnecessarily heated, however. Even if the growth of human numbers played only a minor role in emissions growth, it would be worth discussing – not because addressing population will somehow resolve our climate predicament, but because ultimately no other strategy on its own will either. We need the widest possible range of strategies – economic, political, technological, and behavioral – that are both feasible and consistent with shared human values.
On population, the most effective way to slow growth is to support women’s aspirations. Almost all women aspire to gain an education, to stand in equality with men, and to make decisions for themselves – including whether and when to give birth. Policies and programs to help women achieve these aspirations exist in many places. But they don’t get the attention, support and funding they deserve. And they are rarely seen as climate-change strategies.
As societies, we have the ability to end the ongoing growth of human numbers – soon, and based on human rights and women’s intentions. This makes it easy to speak of women, population, and climate change in a single breath.
Robert Engelman is vice president for programs at the Worldwatch Institute and the author of “Population, Climate Change, and Women’s Lives.” Please contact him if you are interested in a copy of the report.
Sources: UK Met Office, World Resources Institute.
Image Credit: Adapted from “Met Office Climate Data – Month by Month (September),” courtesy of flickr user blprnt_van, and report cover, courtesy of the Worldwatch Institute. -
From Cancun: Roger-Mark De Souza on Women and Integrated Climate Adaptation Strategies
› “When you look at the negative impacts of climate change, the impacts on the poor and the vulnerable – particularly women – increase, so investing in programs that put women at the center is critical,” said Roger-Mark De Souza, vice president of research and director of the climate program at Population Action International (PAI), speaking to ECSP from the UN Climate Change Conference in Cancun, Mexico. “There are a number of missed opportunities here in Cancun and in climate change deliberations overall that are not including women and are missing an opportunity to have a bigger bang for the buck, or power for the peso, as we say in Mexico.”
“When you look at the negative impacts of climate change, the impacts on the poor and the vulnerable – particularly women – increase, so investing in programs that put women at the center is critical,” said Roger-Mark De Souza, vice president of research and director of the climate program at Population Action International (PAI), speaking to ECSP from the UN Climate Change Conference in Cancun, Mexico. “There are a number of missed opportunities here in Cancun and in climate change deliberations overall that are not including women and are missing an opportunity to have a bigger bang for the buck, or power for the peso, as we say in Mexico.”
PAI hosted a side session with five panelists from Denmark, Ethiopia, Kenya, Suriname, and Uganda on “Healthy Women, Healthy Planet: Women’s Empowerment, Family Planning, and Resilience.” The session attracted more than 100 attendees and prompted incisive, informative questions, said De Souza.
“There was a call for additional research that is policy relevant that identifies some of the key entry points and added benefits at a country level,” said De Souza. “And there is a very strong call for youth partnerships from a number of youth advocates who are looking at medical and public health interventions and are desirous of including reproductive health programming as part of that.”
“One concrete next step for Cancun is to work with other civil society partners who are here who are tracking how gender is being integrated into the negotiating language, particularly with regard to financing mechanisms,” De Souza said.
Besides financing and the need for more research, De Souza said the key issues that emerged from the panel were: the importance of linking programs of different scales; ensuring women’s empowerment and ownership; and recognizing and replicating effective partnerships.
For more from Roger-Mark De Souza, see ECSP Focus Issue 19, “The Integration Imperative: How to Improve Development Programs by Linking Population, Health, and Environment.”
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Empowering Women in the Muslim World
›December 2, 2010 // By Wilson Center StaffOriginally featured in the Wilson Center’s Centerpoint, November 2010.
For decades, women in the Middle East have actively struggled for equal status before the laws of their respective countries. They have strived to attain equal participation in politics and society, and progressive justice throughout the region. While they have made progress in some parts of the region, many challenges remain. The Wilson Center’s Middle East Program recently held three meetings to discuss challenges as well as progress to empowering women across the Muslim world.
A Modern Narrative
The American Islamic Congress (AIC) recently published a report, “A Modern Narrative for Muslim Women in the Middle East: Forging a New Future,” that highlights past and present triumphs and difficulties – economic, legal, political, religious, and social –for women’s rights throughout the region. On September 30, the Middle East Program co-sponsored a meeting with the AIC to review the status of women in Saudi Arabia and Jordan, based on findings in the AIC’s report.
Fawziah Al-Hani, manager of the Gherass Center for Social Education in Saudi Arabia, expressed frustration about the progress women have made in her native Saudi Arabia. She said women there are perceived as second-class citizens by the country’s legal, economic, political, religious, and social institutions. Women’s issues are rarely discussed in Saudi political and social spheres, and women are not represented in government or the business sector. She said if women are allowed to be active outside the home, they are mostly restricted to educational and health activities.
While she is frustrated about these restrictive Saudi policies toward women, Al-Hani said she maintains hope, as changes take place within the society and government through new initiatives and movements.
Rana Husseini, a human rights activist, author, and journalist, detailed the changes to the status of women in Jordan over the past 20 years. Husseini, whose human rights activities over the past two decades in Jordan have focused on honor crimes and other women’s issues, said Jordan has made substantial progress on women’s rights as a result of intense media and civil society activism. While there is room for improvement, she said women are now participating in government and significant reforms have been made to the judicial system.
Though the effectiveness of quotas for women in government may be debated, Husseini noted that quotas facilitate women’s participation in elections and government service. In fact, she said, there are some 50 women judges in Jordan. She noted that honor killings, except in extreme cases, are becoming rarer, and harsher sentences are being imposed for honor crimes.
With constant pressure on the government and society, reforms will continue, said Husseini, who is optimistic about the future for women rights in Jordan and in the Middle East as a whole.
Demographic Realities
Why do many Middle Eastern women not enjoy the same economic opportunities as women of other regions? Can they be empowered to participate at a greater level? Nadereh Chamlou, a senior adviser at the World Bank, attributed the gender inequality to restrictive social norms. She said the region’s women must be empowered to participate in a more significant way if their countries are to effectively exploit, instead of squander, the current economic “window of opportunity.”
At a September 13 discussion, Chamlou said the good demographic news is that there are high numbers of working-age people and thus the potential for rapid economic growth. However, Middle Eastern countries have the highest dependency rates in the world, a fact that Chamlou attributed to the low economic participation of Middle Eastern women relative to female citizens’ participation in other parts of the world. This reality means the Middle East’s demographic composition will not be exploited to its full potential.
Increasing economic opportunities for women will require changing social norms, said Chamlou. She cited a study conducted by the World Bank in three Middle Eastern capitals – Amman, Jordan; Cairo, Egypt; and Sana’a, Yemen – that revealed the biggest reason for the poor representation of women in the workforce is the negative male attitude regarding women working outside the home. Notably, social norms and such negative male attitudes proved to restrict women’s participation far more than the need to attend to child-rearing duties. Despite the successful efforts of most Middle Eastern states to improve education opportunities, conservative social norms still pose a barrier to female empowerment.
Some simple changes could have a substantial impact. Chamlou recommended focusing on educated, middle-class women, undertaking more efforts to bring married women into the workforce, and emphasizing changing attitudes – particularly among conservative younger men – toward women working outside the home.
Lessons from Tunisia
In Tunisia, the progress of women’s empowerment can serve as a model for the region, noted women’s rights advocate Nabiha Gueddana, president and director-general of the National Agency for Family and Population in Tunisia.
Speaking at a September 8 meeting, Gueddana said the Arab world can learn much from her native Tunisia regarding the positive effects of empowering women. Gueddana, also a candidate for undersecretary-general of UN Women at the United Nations, described how Tunisian women have been empowered politically, economically, and socially, and how this empowerment has benefited Tunisian society.
Tunisia has undergone substantial changes since achieving independence from France in 1956. Tunisian women had second-class status in the years prior, a time Gueddana described as one that relegated them to a life of constant child-rearing, illiteracy, and economic dependence.
Yet Tunisia has become a beacon for other Muslim societies: the country’s labor code allows full female participation in the economy and education is open equally to boys and girls. Family planning programs and important strides in health have considerably lowered the birth rate and lengthened the life expectancy of the average woman. Gueddana also noted that Tunisia’s economic growth is now five times greater than the growth rate of its population.
Measures to empower women in Tunisia have benefited not only women but Tunisian society as a whole, with significant shifts in men’s attitudes regarding women’s rights and roles in society. Gueddana indicated that her efforts extend beyond Tunisia, as she strives to help empower women throughout the world. She said such efforts will persist so long as women anywhere find themselves disadvantaged, dependent, and living as second-class citizens.
Women’s empowerment in society rests increasingly not in the political but in the economic and business domains (Editor’s note: one could add that women’s empowerment has the potential to considerably impact the environmental domain as well). While women have made considerable progress in the political arena, economic power is still male-dominated throughout the region.
Gueddana said the discussion of women’s rights should take place within the broader context of human rights. Violence against women, particularly sexual violence, is a widespread phenomenon across all societies and, unfortunately, often considered taboo for discussion. She said all citizens benefit when all have equal rights and can use them to expand their opportunities and achievements to enhance their societies.
Dana Steinberg is the editor of the Wilson Center’s Centerpoint.
Photo courtesy of Centerpoint. -
World AIDS Day 2010: Not Yet in a Position to Say “Mission Accomplished”
›December 1, 2010 // By Schuyler NullToday is World AIDS day. More than 33 million people are currently living with HIV around the world, according to the UN, and the vast majority of them (22 million) are located in sub-Saharan Africa.
“We have halted and begun to reverse the epidemic. Fewer people are becoming infected with HIV and fewer people are dying from AIDS,” said Executive Director Michel Sidibé in the 2010 edition of UNAIDS’ annual report.“However we are not yet in a position to say ‘mission accomplished.’ Growth in investment for the AIDS response has flattened for the first time in 2009. Demand is outstripping supply. Stigma, discrimination, and bad laws continue to place roadblocks for people living with HIV and people on the margins.”
Particularly in sub-Saharan Africa, “people on the margins” often means women and children. As a result, there has been more and more integration of HIV/AIDS programs with gender and maternal health. The environmental community has also worked closely with HIV/AIDS interventions in places where the destruction of natural resources makes certain populations more vulnerable than others and valuable conservation efforts are threatened.
As development efforts become more cross-sectoral, it’s important to keep in mind and maximize these connections between community, economic, and environmental health.
Check out The New Security Beat’s coverage of HIV/AIDS integration with other health and environment programs including coverage from the Global Health Initiative’s “Integrating HIV/AIDS and Maternal Health Services” event last year, a sit-down interview on the challenges facing HIV-positive adolescents with Harriet Birungi of the Population Council in Kenya, and an examination of how gender-based violence contributes to women’s vulnerability to HIV.
Sources: Population Reference Bureau, UN, World Wildlife Federation.
Map Credit: World AIDS Campaign.