Showing posts from category food security.
-
VIDEO: Leona D’Agnes on Population, Health, and Environment
›April 15, 2009 // By Wilson Center StaffIntegrated population-health-environment (PHE) programs “are very cost-effective ways” to develop “community capacity—to strengthen their know-how, and bring…in some additional appropriate technologies” to promote livelihoods, says Leona D’Agnes in this short expert analysis from the Environmental Change and Security Program.
“It doesn’t require a lot of money, but it does require capacity building and being able to motivate communities and help them to understand that it is not just the government that’s responsible for their development. Their own food security and environmental security rests with their abilities to manage their assets, their natural resources, to plan their families, and make sure their children finish school.”
In this expert analysis, D’Agnes, currently a consultant to CDM International on PHE and forestry in Nepal, discusses the linkages between population, health, and environment involved in her work as a technical adviser for PATH Foundation Philippines and its IPOPCORM project.
To learn more about population, health, and environment issues, please visit our PHE page. -
Weekly Reading
›“A New Military Mission: Clean Energy,” part of the Center for American Progress’ “It’s Easy Being Green” series, highlights the military’s attempts to become more energy-efficient. Read more about the U.S. military’s environmental initiatives.
Simon Dalby, a professor at Carleton College, discusses the evolution of environmental security with John Tessitore, executive editor of the Carnegie Council, in a video interview (transcript available).
Climate Change, Food Security, and the Right to Adequate Food examines climate change’s expected impact on food production, with a special focus on Africa and Asia.
The BDA Foundation, a Canadian charity, and PharmAfrica, a pharmaceutical company, are working to create a medicinal plants industry that will lift local people out of poverty in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. -
In Land Grab, Food Is Not the Only Consideration
›March 3, 2009 // By Will Rogers Global cereal production – including stable items like wheat, coarse grains, and rice – is projected to shrink in 2009 due to drought and adverse weather in the world’s major producers. With shrinking food stocks, a growing demand for biofuels, and a need for cheaper sources of raw materials like rubber and other natural resources, governments and corporations in many developed countries are seeking to secure access to these coveted commodities by leasing large tracts of land in developing countries.
Global cereal production – including stable items like wheat, coarse grains, and rice – is projected to shrink in 2009 due to drought and adverse weather in the world’s major producers. With shrinking food stocks, a growing demand for biofuels, and a need for cheaper sources of raw materials like rubber and other natural resources, governments and corporations in many developed countries are seeking to secure access to these coveted commodities by leasing large tracts of land in developing countries.
In Indonesia, PT Daewoo Logistics Indonesia, a subsidiary of South Korea’s Daewoo Logistics Corporation, and Cheil Jedang Samsung recently announced a partnership to invest US $50 million to grow and process energy crops on the islands of Buru and Samba. The two companies will produce 30,000 tons of corn grain a year on 24,000 hectares and will export their entire production back to South Korea. The announcement comes on the heels of a report from the International Food Policy Research Institute, The Challenge of Hunger: The 2008 Global Hunger Index, that raises concerns about Indonesia’s already precarious food security.
Meanwhile, Saudi investors have been lobbying government officials in the Philippines to grow and export “basmati rice, corn, cassava, sugar, animal fodder, fisheries, red meat, Philippine bananas and mangoes,” reports Neil Morales in BusinessWorld. Philippine officials are hoping to leverage Saudi Arabia’s growing demand for food against the harsh economic climate to boost much-needed foreign direct investment. “Tell me an item that the whole world needs regardless of the economic situation, it is food,” said Peter Favila, the Philippine Trade Secretary, in an interview with BusinessWorld.
But securing food stocks is not the only motive behind the massive leasing of land in developing countries. A surging demand for biofuels to meet energy needs, as well as access to new sources of raw materials for manufacturing goods, appears to be driving recent land grabs. Recently, Sinopec and The Chinese National Overseas Oil Corporation, two state-owned oil giants, made investments of US $5 billion and $5.5 billion, respectively, in Indonesia to grow and process corn into biofuel to be exported to China.
Meanwhile, several Chinese companies have secured deals in Southeast Asia to grow rubber trees so that they can process and export the sap to meet China’s rising manufacturing demands (China is expected to consume 30 percent of the world’s rubber by 2020). In Cambodia, domestic rice fields have been cleared to make way for rubber trees, with nearly all the sap to be exported to China. And in Burma – which according to the UN’s Food and Agriculture Organization is plagued by severe localized food insecurity – concessions have been made to lease land to two Chinese companies to establish rubber plantations. According to Agweek, Burmese “troops are forcibly evicting farmers to make way for rubber plantations.”
Governments in these developing countries should exercise caution when granting land concessions to foreign governments and corporations. Despite the short-term investments, most – if not all – of the production will be exported, making the long-term food security situation even worse in these host countries. And according to a recent report from the U.N. Environment Programme, From Conflict to Peacebuilding: The Role Natural Resources and the Environment, environmental conditions – like severe food insecurity – linked with these poor government policies and claims of “neo-colonialism” could exacerbate existing trends and tensions in the host countries and spark violent conflict.
A recent attempt by South Korea’s Daewoo Logistics Corporation to negotiate a 99-year lease on 3.2 million hectares of farmland in Madagascar has stalled due to severe domestic outcry. Since mid-January, the country has been in a state of emergency; riots have erupted throughout the capital city of Antananarivo, killing, by some estimates, close to 100 and injuring more than 200; and Madagascar’s President Marc Ravalomanana is struggling to maintain power amidst fierce criticism by opposition leaders like Antananarivo Mayor Andry Rajoelina for even considering the deal.
Even with the prospect of political unrest, however, current economic woes will likely dictate policymaking in these developing countries, with short-term payoffs eclipsing the long-term political, social, economic and security consequences.
Photo: In the northeastern coastal city of Tamatave, political unrest has stirred since mid-January over negotiations between the Malagasy government and South Korea’s Daewoo Logistics Corporation to lease nearly half the country’s arable farmland to the company to grow and export food to South Korea. Courtesy of flickr user foko_madagascar.
-
Reading Radar — A Weekly Roundup
›February 27, 2009 // By Wilson Center Staff A new study published in Conservation Biology (abstract) calculates that more than 80 percent of major armed conflicts from 1950-2000 have taken place in one of the world’s 34 biodiversity hotspots. “The fact that so many conflicts have occurred in areas of high biodiversity loss and natural resource degradation warrants much further investigation as to the underlying causes, and strongly highlights the importance of these areas for global security,” says coauthor Russell A. Mittermeier. He and lead author Thor Hansen argue that protecting nature during war can help recovery, and call for integrating conservation “into military, reconstruction and humanitarian programs in the world’s conflict zones.”
A new study published in Conservation Biology (abstract) calculates that more than 80 percent of major armed conflicts from 1950-2000 have taken place in one of the world’s 34 biodiversity hotspots. “The fact that so many conflicts have occurred in areas of high biodiversity loss and natural resource degradation warrants much further investigation as to the underlying causes, and strongly highlights the importance of these areas for global security,” says coauthor Russell A. Mittermeier. He and lead author Thor Hansen argue that protecting nature during war can help recovery, and call for integrating conservation “into military, reconstruction and humanitarian programs in the world’s conflict zones.”
The Bixby Forum, “World in 2050: A Scientific Investigation of the Impact of Global Population Changes on a Divided Planet” included panels on population’s links to war, climate change, and the environment. Malcolm Potts, the chair of the University of California, Berkeley’s Bixby Center for Population Health and Sustainability recently spoke at the Wilson Center about his latest book, Sex and War.
In Troubled Waters: Climate Change, Hydropolitics, and Transboundary Resources from the Henry L. Stimson Center, experts from South Asia, Southeast Asia, and the Middle East “examine the environmental dangers and policy dilemmas confronting the sustainable management of shared water resources in a warming world”—including the potential for conflict. In the concluding chapter, David Micheli finds that climate change is unlikely to lead to full-scale “water wars,” but warns that “rising climatic stresses on common waters will put new and perhaps unprecedented strains on cooperative governance institutions at the local, national, and international levels.”
Rampant logging fueled Cambodia’s decades-long civil war. Now a new report from transparency watchdogs Global Witness, Country for Sale, claims that the country’s emerging oil and mineral sectors may pose a similar threat. Says Gavin Hayman, “The same political elite that pillaged the country’s timber resources has now gained control of its mineral and petroleum wealth. Unless this is changed, there is a real risk that the opportunity to lift a whole generation out of poverty will be squandered.”
Thirty-three countries have been named “highly vulnerable” to the impact of climate change on their fisheries by a new study published in Fish and Fisheries. In these countries, two-thirds of which are in tropical Africa, fish accounts for 27 percent or more of daily protein intake, compared to 13 percent in non-vulnerable nations. InterPress examines the impact of acidification and rising surface temperatures on the fish stocks of coastal South Africa.
Photo: Fish-dependent people of Bangladesh could see their coastal catch reduced as a result of predicted increases in the frequency and intensity of tropical storms. Bangladesh is one of the nations identified as highly dependent on fisheries along with Cambodia, DR Congo, Madagascar, Sierra Leone, Tanzania, and Uganda. Photo credit: Mark Prein, courtesy of WorldFish Center. -
New Director of National Intelligence Assesses Climate, Energy, Food, Water, Health
›February 18, 2009 // By Rachel WeisshaarIn the annual threat assessment he presented last week to the Senate Select Committee on Intelligence, new Director of National Intelligence Dennis Blair named the global economic crisis—not terrorism—the primary near-term threat to U.S. national security, prompting accusations of partisanship from the Washington Times. Yet as the U.S. Naval War College’s Derek Reveron notes, “the economic turmoil of the early 20th century fueled global instability and war,” and today’s economic collapse could strengthen extremists and deprive U.S. allies of the funds they need to deploy troops or increase foreign assistance to vulnerable regions.
Further down the list of potential catastrophes—after terrorism, cybersecurity, and the “arc of instability” that stretches from the Middle East to South Asia—the assessment tackles environmental security threats. The four-page section, which likely draws on sections of the recent National Intelligence Council report Global Trends 2025: A Transformed World, summarizes the interrelated natural-resource and population challenges—including energy, food, water, demography, climate change, and global health—the U.S. intelligence community is tracking.
The world will face mounting resource scarcity, warns Blair. “Access to relatively secure and clean energy sources and management of chronic food and water shortages will assume increasing importance for a growing number of countries. Adding well over a billion people to the world’s population by 2025 will itself put pressure on these vital resources,” he writes.
Drawing on the conclusions of the 2008 National Intelligence Assessment on the impacts of global climate change to 2030, Blair portrays climate change as a variable that could place additional strain on already-stressed agricultural, energy, and water systems: “We assess climate change alone is unlikely to trigger state failure in any state out to 2030, but the impacts will worsen existing problems such as poverty, social tensions, environmental degradation, ineffectual leadership, and weak political institutions.” Direct impacts to the United States include “warming temperatures, changes in precipitation patterns, and possible increases in the severity of storms in the Gulf, increased demand for energy resources, disruptions in US and Arctic infrastructure, and increases in immigration from resource-scarce regions of the world,” writes Blair.
Africa, as usual, is the last of the world’s regions to be analyzed in the assessment. Blair notes that “a shortage of skilled medical personnel, deteriorating health systems, and inadequate budgets to deal with diseases like HIV/AIDS, malaria, and tuberculosis” is threatening stability in sub-Saharan Africa, and explains that agriculture, which he rightly calls “the foundation of most African economies,” is not yet self-sufficient, although some countries have made significant improvements in infrastructure and technology. He highlights ongoing conflicts in the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Nigeria, Sudan, and Somalia as the most serious security challenges in Africa. He fails to note, however, that all four have environmental/natural resource dimensions (see above links for details). -
For Many, Sea-Level Rise Already an Issue
›February 11, 2009 // By Will Rogers Global sea level is projected to rise between 7 and 23 inches by 2100, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Recent melting of the Antarctic ice sheet has prompted geophysicists at the University of Toronto and Oregon State University to warn that global sea level could rise 25 percent beyond the IPCC projections. These catastrophic long-term predictions tend to overshadow the potentially devastating near-term impacts of global sea-level rise that have, in some places, already begun.
Global sea level is projected to rise between 7 and 23 inches by 2100, according to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). Recent melting of the Antarctic ice sheet has prompted geophysicists at the University of Toronto and Oregon State University to warn that global sea level could rise 25 percent beyond the IPCC projections. These catastrophic long-term predictions tend to overshadow the potentially devastating near-term impacts of global sea-level rise that have, in some places, already begun. -
Weekly Reading
›Conflicts among pastoralists over water and land have increased in drought-stricken northeastern Kenya, reports IRIN News.
Country for Sale, a report by Global Witness, alleges that Cambodia’s oil, gas, and mineral industries are highly corrupt.
Foreign Policy features an interview with General William “Kip” Ward, the commander of the new U.S. Africa Command. The New Security Beat covered General Ward’s recent comments on civilian-military cooperation.
Healthy Familes, Healthy Forests: Improving Human Health and Biodiversity Conservation details Conservation International’s integrated population-health-environment projects in Cambodia, Madagascar, and the Philippines.
Double Jeopardy: What the Climate Crisis Means for the Poor, a new report on climate change and poverty alleviation, synthesizes insights from an August 2008 roundtable convened by Richard C. Blum and the Brookings Institution’s Global Economy and Development Program at the Aspen Institute.
“Although the long-term implications of climate change and the retreating ice cap in the Arctic are still unclear, what is very clear is that the High North is going to require even more of the Alliance’s attention in the coming years,” said NATO Secretary General Jaap de Hoop Scheffer at a seminar on security prospects in the High North hosted by the Icelandic government in Reykjavik.
“I think we will work our way towards a position that says that having more than two children is irresponsible. It is the ghost at the table. We have all these big issues that everybody is looking at and then you don’t really hear anyone say the “p” word,” says UK Sustainable Development Commission Chair Jonathon Porrit, speaking about population’s impact on the environment. Porrit has drawn criticism for his remarks.
A local priest has warned that a Norwegian company’s proposed nickel mines will threaten food security on the Philippine island of Mindoro. -
Weekly Reading
›The Feeding of the Nine Billion: Global Food Security for the 21st Century, a report from Chatham House, puts forth 10 proposals designed to make the global food system more resilient, sustainable, and equitable.
Strategic Implications of Global Health, a recent report from the National Intelligence Council, builds on a 2000 National Intelligence Estimate analyzing the links between global health and U.S. national security, but places more emphasis on non-infectious issues like maternal mortality, malnutrition, and chronic diseases.
Bill Gates’ first annual letter about his work at the Gates Foundation includes a chart showing that better overall health is linked to smaller families.
“How Much Would You Pay to Save the Planet? The American Press and the Economics of Climate Change,” a discussion paper from Harvard University’s Joan Shorenstein Center on the Press, Politics, and Public Policy, examines coverage of the economic debate over the Lieberman-Warner Climate Security Act of 2008.
Population Connection’s February 2009 Reporter features stories on Ghana’s slow progress on reproductive health and Thomas Friedman’s book Hot, Flat, and Crowded, among others.
The Economist examines the connections between failed states and conflict, terrorism, poverty, and disease. Failed states were a major concern of the recent U.S. National Defense Strategy.


 Global cereal production – including stable items like wheat, coarse grains, and rice – is
Global cereal production – including stable items like wheat, coarse grains, and rice – is 
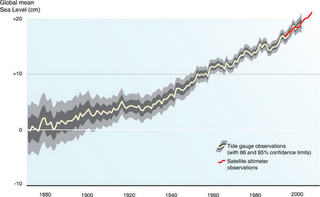 Global sea level is projected to rise between
Global sea level is projected to rise between 

