-
Seven Ways Seven Billion People Affect the Environment and Security (Policy Brief)
›The Wilson Center Policy Briefs are a series of short analyses of critical global issues facing the next administration that will run until inauguration day.
Seven billion people now live on Earth, only a dozen years after the global population hit six billion. But this milestone is not about sheer numbers. Demographic trends will significantly affect the planet’s resources and people’s security.
-
Super Typhoon Bopha Shows Why Developing Countries Are Most Vulnerable to Climate Change
›January 15, 2013 // By Carolyn Lamere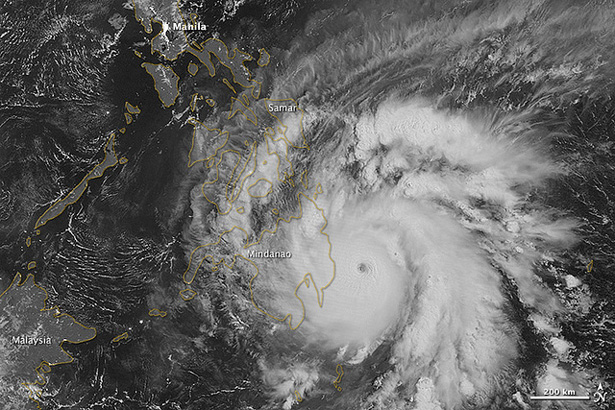
If Hurricane Sandy was a wake-up call for many in the United States to the kind of extreme weather that climate change is expected to bring, Typhoon Bopha, which struck the Philippines a month later, is a reminder of what makes developing regions even more vulnerable to these changes.
-
Afghanistan’s Mineral Potential, Sustainability of Development Efforts Crucial Questions, Says Wilson Center’s Michael Kugelman
›Rich, untapped deposits of gold, iron, copper, lithium, and rare earth minerals have been known in Afghanistan for decades, but recently, extensive reports from the U.S. Department of Defense and U.S. Geological Survey have shed new light on their potential value.
-
National Research Council Produces Climate and Security Analysis at Request of U.S. Intelligence Community
›
The CIA may have shut down its dedicated climate change center earlier this year, but a recently released report sponsored by the intelligence community reaffirms the deep connection between climate change and national security. New threats to U.S. national security – like increased food and water insecurity and more natural disasters requiring humanitarian assistance – have emerged as climate change creates unprecedented changes in the global environment.
-
Autumn Spanne, The Daily Climate
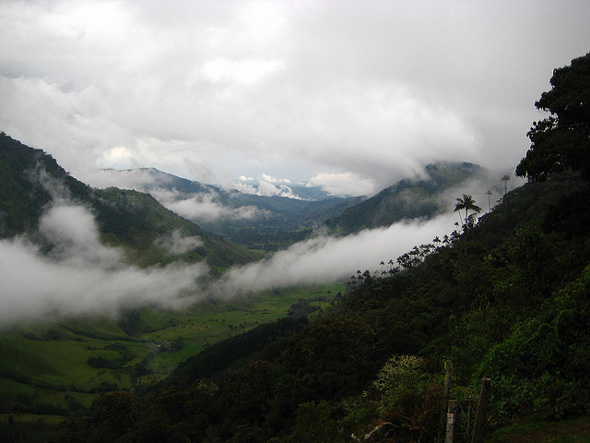
Colombia’s Unexplored Cloud Forests Besieged by Climate Change, Development
›December 13, 2012 // By Wilson Center Staff
The original version of this article, by Autumn Spanne, appeared on The Daily Climate.
Five hours by truck and mule from the nearest town, a rumbling generator cuts through the silent night to power large spotlights as botanists crouch and kneel on large blue tarps spread across a cow pasture. It’s nearly midnight, and the team works urgently to describe every detail of the dozens of colorful orchids, ferns, and other exotic plants they have collected that day in Las Orquídeas National Park, one of the single most biologically diverse places on the planet.
-
World Bank Issues Dire Warning About “Four Degree World”
›December 10, 2012 // By Carolyn Lamere
Without decisive action, global temperatures could rise by at least four degrees Celsius (seven degrees Fahrenheit) by the end of the century. A new World Bank report says that such a world would be “so different from the current one” that it would be difficult to even anticipate the challenges we would face.
-
The Land Matrix Visualizes Ebbs and Flows of Global “Land Grabs”
›Over the past few years, large-scale acquisition of land by foreign or domestic firms, be they public or private, have been making headlines. But although these “land grabs” have received a great deal of attention, their details remain largely unknown. Which countries are the primary investors? Which are the main targets? What is the land used for?
-
Considering “Soft Geoengineering”
›Even as the climate debate has been paralyzed by politics, the concept of geoengineering has been in the news lately, most notably in October when Russ George dumped 120 tons of iron particles into the Pacific Ocean in a scheme to try and score carbon credits. Earlier this month, the Wilson Center’s Science and Technology Innovation Program hosted an event taking a look at “soft geoengineering” – techniques that might have low or minimal environmental side effects but still address or reverse climate change.
Showing posts from category environmental security.








