Showing posts from category development.
-
Book Launch: ‘Human Population: Its Influence on Biological Diversity’
›Measurements of “human population density and growth can be used to identify changes in the viability of native species, and more directly, in changes in ecological systems or habitat quality,” said Richard Cincotta, consultant at the Environmental Change and Security Program and demographer-in-residence at the Stimson Center, speaking at the book launch of Human Population: Its Influence on Biological Diversity.
Cincotta was joined by coeditor L.J. Gorenflo, associate professor of landscape architecture at Penn State University, and contributing author Christopher Small, research professor at the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory and adjunct professor at Columbia University, to discuss the book’s objectives, its diverse and multidisciplinary contributors, and its policy implications. [Video Below]
Establishing a Handbook for the Field
“Human Population: Its Influence on Biological Diversity establishes a handbook for the field,” said Cincotta. While the scientific volume is specifically geared towards researchers and conservation managers rather than policymakers, “there are a few Washington-type policy messages that are useful,” he added.
Human population affects biological diversity in multiple ways. While population density alone can be strongly indicative of the viability of different populations of native species, human activities and their chemical and energetic byproducts can also have a strong impact, even when human population density is low, said Cincotta.
Conserving Biodiversity in Different Settings
“Planned solutions, based on strategic actions, increasingly are essential,” said Gorenflo, a professor at Penn State University. “The days of letting nature take care itself are probably gone.” Gorenflo presented results from the two chapters he worked on: “Human Demography and Conservation in the Apache Highlands Ecoregion, U.S.-Mexico Borderlands” and “Exploring the Association Between People and Deforestation in Madagascar.”
“Population density seems to be a reasonably good indicator of biodiversity loss,” said Gorenflo. Data from the Apache Highland Ecoregion (a 12 million-hectare area located along the U.S.-Mexico border) indicate that biodiversity tends to drop off at population densities of more than 10 people per square kilometer. Conservation efforts in areas within the ecoregion that are at, or close to, this density threshold will likely encounter challenges to maintaining biodiversity, he said.
Human mobility is a major consideration, said Gorenflo: “Whereas high fertility can create population growth over generations, high mobility can create population growth in a matter of months or years.” In the Apache Highlands, for example, the 40 percent increase in population between 1990 and 2000 was largely caused by migration into U.S. cities in the region.
In Madagascar, Gorenflo and colleagues examined whether population growth and poverty were systematically driving deforestation and loss of biodiversity. Using data from the 1990s, they found that higher population density only slightly raises rates of deforestation and large increases in income only modestly decrease deforestation.
Not surprisingly, they found that the likelihood of deforestation decreased dramatically in protected areas. In addition, proximity to roads or footpaths was associated with significantly higher rates of deforestation. “Roads, footpaths, and protected areas are all policy decisions,” Gorenflo pointed out. “So when bilateral or multilateral organizations decide to invest in development in a place like Madagascar, they can look at these sorts of investments as being important.”
While there are some similarities to be drawn between regions’ experience with population and biodiversity, said Gorenflo, “every locality likely has a slightly different story; you need to do context-specific studies to get a real handle on what is going on.”
The Human Habitat
In his chapter, “The Human Habitat,” Christopher Small of the Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory said his goal was “to set the stage for some of the more detailed studies by taking a look at the global distribution of human population.”
Using census data and satellite-derived maps of night lights to serve as a “proxy for development,” Small found that “people are everywhere, but they are not evenly distributed.”
At least half the world’s population lives on less than three percent of the inhabitable land, and most people live at densities between 100 and 1000 people per square kilometer. At both local and global scales, population density and city size are dominated by extremes: There are large numbers of small groups of people, and small numbers of large groups of people, he said.
“The environments where people live are more strongly correlated with features of the landscape than they are with climatic parameters,” said Small. While humans have effectively adapted to a range of climates, the majority of people tend to cluster close to rivers, at low elevations, and close to coastlines. Although it was once thought that three-quarters of the world’s population lived in coastal regions, Small’s results show that the actual number is close to half of these previous assumptions.
Understanding the spatial and environmental distribution of population and managing population growth may therefore help minimize negative impacts on specific habitats and biomes, said Small.
Image Credit: “View from a Madagascar Train,” courtesy of flickr user cr01. -
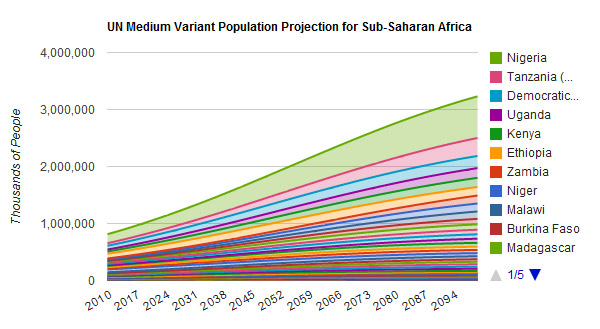
One in Three People Will Live in Sub-Saharan Africa in 2100, Says UN
›June 8, 2011 // By Schuyler NullBetween now and 2100, three out of every four people added to world population will live in sub-Saharan Africa. That’s what the medium variant of the UN’s world population projections estimates.* As we noted in our previous post on the latest UN numbers, Nigeria leads sub-Saharan growth, but other countries will also grow by major multiples: Tanzania and Somalia will be 7 times larger; Malawi more than 8 times; and Niger, to grow to more than 10 times its current population.
-
Michael Kugelman, Dawn
Aquaculture’s Promise for Food-Insecure Pakistan
›June 7, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Michael Kugelman, appeared on Dawn.
“Give a man a fish and you feed him for a day,” the ancient Chinese philosopher Lao Tzu famously said. “Teach a man to fish and you feed him for a lifetime.”
For years, this adage has helped frame debates across a variety of disciplines. However, while globally influential, it is by no means universally applicable – as the sad realities of Sindh make painfully clear. In this parched, food-insecure region flush with fishermen and farmers, people have long known how to fish. The problem is that with water bodies shriveling up, there are increasingly fewer fish to catch. Many impoverished residents would be grateful for a single fish, given their struggles to secure a day’s worth of food.
Pakistan’s natural resource constraints know no provincial borders, yet they are notably severe in Sindh. Water tables are plummeting, with great volumes of Indus River flows diverted upstream to satiate agricultural and urban demand in Punjab.
Sindh’s water security is further threatened by population growth and global warming, and by the water-intensive, large-scale farming envisioned by foreign investors jockeying for agricultural land.
With surface water supplies threatened, users are increasingly tapping groundwater resources – yet according to the Pakistan Council of Research in Water Resources, a staggering 95 percent of the province’s shallow groundwater supplies are bacteriologically contaminated. This is unsurprising, given the technical deficiencies and inefficiency that characterize Sindh’s water treatment facilities.
In a province where so many livelihoods are tied to water availability and food production, water stress aggravates food insecurity and threatens economic well-being. A recent World Bank report concludes that Pakistan’s poorest spend at least 70 percent of their meager incomes on food – and undoubtedly many of them hail from Sindh. According to data from the Pakistan Agricultural Research Council, some of the province’s small farmers spend a whopping 87 percent of their incomes on food.
Continue reading on Dawn.
Michael Kugelman is a program associate for the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson Center.
Photo Credit: A child stands amongst buildings destroyed by the floods in Sindh province, courtesy of flickr user DFID – UK Department for International Development. -
Watch: Younger Generation Will Prioritize Health, Education, Human Rights, Says Frederick Burkle
›June 7, 2011 // By Schuyler Null“Unfortunately, in the last two decades, when globalization became the mantra, it was primarily an economic mantra,” said Frederick Burkle, a senior fellow with the Harvard Humanitarian Initiative, visiting scientist at the Harvard School of Public Health, and senior public policy scholar at the Wilson Center. “The mantra was, ‘if you can improve the economy,” he said, “health, education, everything will follow.’”
“With the financial crisis, that proved not to be true,” Burkle said, and as a result, net expenditures in health and education have declined and the private sector, unfortunately, has not filled the gap.
“We really need to redefine globalization,” Burkle said. “And certainly economics will be there…but health, education, and human rights need to be just as dominant as the economics.”
Burke said he expects a gradual realignment of global priorities to come as younger generations come into decision-making roles. “They don’t have political clout right now,” he said, “but when they do…I think we’re going to see all these aspects that I mentioned – even the humanitarian profession becoming a career – accelerated.” -
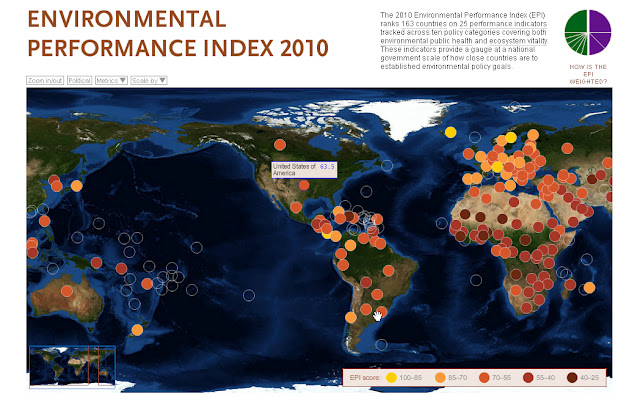
Measuring Ecosystem Vitality and Public Health With the Environmental Performance Index
›The Environmental Performance Index (EPI) is a comparative analytic tool for policymakers created jointly by Yale and Columbia Universities in collaboration with the World Economic Forum and Joint Research Centre of the European Commission. The EPI was created in 2006 and is updated biannually. Data is drawn from 25 performance indicators that fall under 10 well-established policy categories, including the environmental burden of disease, the effects of water on human health, and agriculture. The indicators serve as a “gauge at a national government scale of how close countries are to established environmental [and health] policy goals,” write the authors.
The EPI draws data from a diverse array of sources, such as the World Health Organization, Food and Agriculture Organization, University of New Hampshire, and World Resources Institute. Users can view visualizations of the compiled data via an interactive map and the data is also available in the form of rankings charts, individual country profiles, and country group comparisons. The interactive map also allows users to isolate performance indicators or policy categories in order to compare an individual country’s performance with global trends. Furthermore, indicators may be scaled to visually reflect a country’s performance in relation to drivers of environmental performance, like gross domestic product, level of corruption, and government effectiveness.
This tool is particularly useful because users can effectively leverage points for policy change by identifying linkages between environmental policy and other issue areas, such as public health or sanitation. The EPI enables policymakers to visually conceptualize problematic regions, optimize investments in environmental protection, and identify best practices.
The index’s greatest weakness is its inability to track changes in performance over time. A pilot project was launched last year that tracks whether a country has progressed or deteriorated in an area of environmental performance, but the authors note that the project has “raised more questions than answers,” particularly concerning data availability and interpretation. Additionally, there are gaps in the data. Although these gaps signify a data quality weakness, they also support the continued calls for increased data collection by governments and other organizations to better inform environmental decision-making. -
Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Losing the Battle to Balance Water Supply and Population Growth
›Part three of the “Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions” event, held at the Wilson Center on May 18.
Overlooked in most news coverage of Yemen’s crisis is the country’s struggle to manage its limited natural resources – particularly its rapidly depleting groundwater – in the face of soaring population growth. At the recent Wilson Center event, “Yemen: Beyond the Headlines,” Yemen’s ambassador to Germany, Mohammed Al-Eryani, and Daniel Egel of the RAND Corporation outlined Yemen’s shaky prospects for economic development without more sustainable agricultural practices and more efficient water management. [Video Below]
With a population of more than 24 million and a total fertility rate (TFR) of 5.5 – nearly double the average TFR for the region – Yemen’s population is projected to grow to 36.7 million by 2025 and jump further to 61.6 million by mid-century, according to the latest UN projections. While those figures may not seem large by global standards, given Yemen’s already limited stocks of arable land and groundwater, the country’s rapid rate of growth may quickly outpace its resources.
“Already in a Crisis”: The Groundwater Deficit
Yemen’s per capita water supply is falling fast in the face of booming population growth and agricultural consumption, said Al-Eryani, a water engineer who founded Yemen’s Ministry of Water and the Environment. While the commonly accepted threshold for water scarcity is 1700 cubic meters or less per capita, Yemen’s per capita renewable water availability is now in the neighborhood of 120 cubic meters, he said.
Meanwhile, water scarcity has been exacerbated by erratic precipitation that has hit rainfall-dependent farmers especially hard. In a country with no real rivers or perennial streams, rainfall harvesting has long enabled agricultural production, as evidenced by the country’s many intricately terraced hillsides – “the food baskets of Yemen,” said Al-Eryani.
Yemenis have coped with shifting precipitation patterns by drawing more groundwater for irrigation and other domestic uses. While drilling wells has provided some short-term relief, the practice is unsustainable in the long term, creating a “water deficit,” Al-Eryani said, that continues to grow each year.
In the populous Sanaa basin, home to the Yemeni capital, consumption outweighs the aquifer’s natural rate of recharge by a factor of five to one and groundwater levels have been plummeting at six meters per year, he said. With only minimal government regulation of drilling, the country’s groundwater situation is poised to worsen, one of the reasons Al-Eryani declared his country is “already in a crisis.”
Stalled Economic Development
Yemen’s stalled economic development is particularly pronounced outside of urban areas, “where the resources are,” said Daniel Egel, citing the country’s failure to build modern transportation infrastructure and develop other economic activities besides farming. He called for the international development community to focus on creating jobs in rural areas, particularly by increasing the financing available for non-agricultural businesses and by improving secondary roads. In addition, he warned development actors to be aware of how gender inequality and local social structures, such as tribes, affect development efforts.
Given the country’s dependence on agriculture, water scarcity poses a threat to Yemen’s food security and its economic development. Three out of every four Yemeni villages depend on rainfall for irrigation, Egel said, making them highly vulnerable to unexpected climate change-induced shifts in precipitation patterns. Water scarcity also weakens the financial stability of Yemeni households, with the cost of water “accounting for about 10 percent of income during the dry season,” he said.
Averting a “Domino Effect”
Al-Eryani asserted that water management policies will “have to be designed in piecemeal fashion,” as no one single action will avert a catastrophe. He suggested a number of steps to alleviate the country’s growing water crunch, including:- Focus on the rural population, which makes up 70 percent of the population, has the highest fertility rates, and are the most reliant on agriculture;
- Move development efforts outside of Sanaa to other regions of the country;
- Increase investment in desalination technology for coastal areas;
- Increase water conservation in the agricultural sector; and,
- Exploit fossil groundwater aquifers in Yemen’s sparsely populated eastern reaches.
“The battle to strike a sustainable balance between population growth and sustainable water supplies was lost many years ago,” Al-Eryani said. “But maybe we can still win the war if we can undertake some of these measures.”
See parts one and two of “Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions” for more from this Wilson Center event.
Sources: UN Population Division, World Bank.
Photo Credit: “At the fountain,” courtesy of flickr user Alexbip. -
Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Governance, State Capacity, and the U.S.
›Part two of the “Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions” event, held at the Wilson Center on May 18.
“Moving beyond Ali Abdullah Saleh has proved to be very challenging, not only for the Yemeni people, but for the neighboring countries and for the international community as a whole,” said former U.S. Ambassador to Yemen Edmund Hull, one of a number of speakers on governance and future challenges during the all-day conference, “Yemen Behind the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions,” at the Woodrow Wilson Center. [Video Below]
Don’t Throw Out the Good With the Bad
Yemen’s protest movement is different than those of Egypt or Tunisia because neighboring countries, such as those in the Gulf Cooperation Council, are actively involved. “[They] don’t have the luxury of saying this is a purely Yemeni affair,” said Hull. “They have to identify where their national interests are and then they have to come up with a legitimate and effective way of protecting those interests.” Included in those national interests is dealing with the presence of Al-Qaeda in the Arabian Peninsula.
But, Hull said, “It would be a shame if, as part of this revolution, what was good in Yemen gets tossed out with what was bad.” Among the institutions that should be protected are the Social Fund for Development, a government development initiative designed to reduce poverty , and the Central Security Forces, “still a very necessary institution and one that has to be protected if other challenges in Yemen are to be met,” he said.
“It’s a mistake to over-focus on the end of a regime – yes, it’s important to get a transfer of power, but I would argue [that it is] equally important to institutionalize the forces that have led to this, as a safeguard against the counter revolution and as an impetus to meeting those many, many political challenges that Yemen faces.”
Going forward, Hull said that elections will be key: Yemen had good electoral experiences in 2003 and 2006 but the system has since suffered some “backsliding,” he said. He also emphasized the importance of letting the youth participate, protecting social networking systems and NGOs, instituting legal requirements to promote transparency, and freeing up and protecting the media. “Unless you have a media spotlight, abuses are going to accumulate,” he said.
Not a “Basket-Case”
“Yemen is not a basket case,” said Charles Schmitz, an associate professor at Towson University. “There have been substantial achievements that I think we need to take into account.” Among these achievements, he highlighted Yemen’s growth in life expectancy, literacy rates, and gross domestic product. The country’s population growth rate has also slowed over the past two decades, though its total fertility rate remains one of the highest in the region.
These gains were fuelled by two resource booms, Schmitz explained: mainly, remittances from the construction boom in the 1970s and oil production. However, oil production dropped off dramatically after peaking around 2001, and remittances have not been able to keep up with the growth of the economy.
“Yemen is in a very severe crisis,” Schmitz said. “The oil has stopped… the balance of payments has been going negative for the last couple of years… and the government appears to be dipping into the central bank.” As a result, he said there is a “very real” possibility of the currency – the riyal – collapsing. The currency represents trust in the government, of which there is none right now, he said.
An Opportunity for New Thinking
“The key variable to the future of the Yemeni economy is state capacity, and this is something Yemen has not done well thus far, largely because of the political crisis,” Schmitz said.
“I think we must be attuned to the reality around us,” said Jeremy Sharp, a specialist in Middle Eastern affairs with the Congressional Research Service. “Quite frankly, Yemen needs a lobby in this country. Yes we have a tight budget environment, but it’s also an opportunity for new thinking.”
“The degree and extent of U.S. engagement with Yemen…is based primarily on the perceived terrorist threat there,” said Sharp. “Our policy toward Yemen always seems to be one horrific terrorist attack away from public outcries for deeper U.S. involvement – i.e., military involvement.”
A Cycle of Transitions?
“We may be looking at cycles of transition in Yemen over the coming decades,” said Ginny Hill, an associate fellow with the Middle East and North Africa Programme at Chatham House. “Stable political settlements take time.” The street protestors are not going to get what they want in the short term, “but just two or three of them sitting in government or being involved in the negotiation process… is going to change the dialogue in Yemen,” she said.
The United States has difficult questions to answer, said Sharp: Who will control Yemen’s security forces down the line? How will the next leader deal with the U.S.-Yemen partnership? Will power be fragmented between civilian and military leaders? Will the next leader play the nationalist card and reduce cooperation with the United States to bolster their own public standing?
“In the absence of the degree of engagement that we need, the [U.S. government] aims high rhetorically,” said Sharp. “We speak about these things while pursuing our own national security goals on the ground. Perhaps this path is unsustainable and events will force the U.S. to pay even more attention to Yemen. Or perhaps we will continue to muddle along this path and never quite reach the brink, precipice, or impending crisis that is so routinely predicted in the media.”
See parts one and three of “Yemen Beyond the Headlines: Population, Health, Natural Resources, and Institutions” for more from this Wilson Center event.
Sources: UNICEF, World Bank.
Photo Credit: “Even small children…,” courtesy of flickr user AJTalkEng. -
Health Development: Providing Free Care and Overcoming Gender-Based Violence
›In The Lancet’s “How Did Sierra Leone Provide Free Health Care?,” author John Donnelly of the Ministerial Leadership Initiative attributes the unanticipated success of a free health care program for women and children in Sierra Leone to good organization, transparency, and a high degree of cooperation between the government, donors, and development partners. One distinctive factor that has contributed to the health system’s turnaround is the unusually high level of political will on the part of President Ernest Bai Koroma, writes Donnelly. Similar to Egypt’s health and population initiatives, Sierra Leone’s marked commitment, accountability, and investment as a host country has contributed highly to the success of its program and triggered further investment from donors. In “Systematic Violence: A Barrier to Achieving the Millennium Development Goals for Women,” from the Journal of Women’s Health, authors Joia S. Mukherjee, Donna J. Barry, Hind Satti, Maxi Raymonville, Sarah Marsh, and Mary Kay Smith-Fawzi assert that the elevation of women is integral to the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals, to which structural violence serves as a significant barrier. Murkherjee et al. recommend community-based programs to combat structural violence and prevent disease, such as the Partners in Health (PIH) program in Haiti. PIH trains community health workers, expands health care as a public good, and bolsters social determinants, which include increasing access to family planning and education, providing compensation for medical workers, and improving health infrastructure.
In “Systematic Violence: A Barrier to Achieving the Millennium Development Goals for Women,” from the Journal of Women’s Health, authors Joia S. Mukherjee, Donna J. Barry, Hind Satti, Maxi Raymonville, Sarah Marsh, and Mary Kay Smith-Fawzi assert that the elevation of women is integral to the achievement of the Millennium Development Goals, to which structural violence serves as a significant barrier. Murkherjee et al. recommend community-based programs to combat structural violence and prevent disease, such as the Partners in Health (PIH) program in Haiti. PIH trains community health workers, expands health care as a public good, and bolsters social determinants, which include increasing access to family planning and education, providing compensation for medical workers, and improving health infrastructure.