-
Mapping the Hot Spots of the 2010/11 Food Crisis
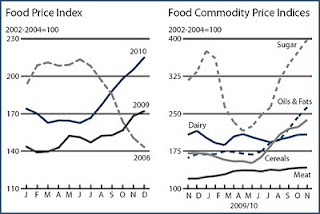
›If you’ve taken a trip to the supermarket lately or scanned the headlines you may have noticed something: Food prices are on the rise. Worldwide, food prices are on track to reach their highest point since their peak in 2008. Using data from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO), the International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), and the World Bank, the Environmental Working Group (EWG) and ActionAid have collaborated to create an interactive world map called, “Hot Spots in the Emerging Global Food Crisis.”
The focus of the map is to highlight the 52 most at-risk countries where increases in staple food prices could tip the scales of stability. There are three variants of the map to choose from: countries at risk which depend on imported cereals, countries where prices are already increasing (featured above), and countries with vulnerable economies and high rates of hunger.
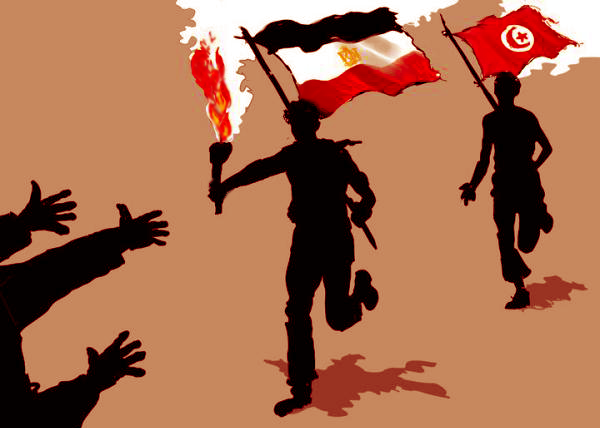
Food prices have become a hot topic of conversation lately for their alleged role in the instability that is rocking the Middle East/North Africa region. But the Middle East is not the only area affected: Besides in Algeria, Tunisia, Morocco, Jordan, and Egypt, food-related riots and protests have also broken out in Mozambique, Bolivia, and India. As the map’s accompanying text puts it, these food riots “feed deeper discontent about economic inequalities and hunger and help give rise to revolutions that can topple governments, as in Tunisia and Egypt.”
Scrolling over a country reveals more information, like, for example, the specific percentage increases in the price of wheat or rice over the past year (wheat prices have risen 15.9 percent in China vs. 54 percent in Kyrgyzstan) or the amounts of corn, soybean, and wheat annually imported and exported (Afghanistan exported 908 million metric tons of wheat in 2010 while Egypt imported 4,978).
Users can also click on vulnerable countries to see how many people are malnourished and their per capita income per day. In the Democratic Republic of the Congo, for example, an estimated 42 million people were undernourished between 2005 and 2007, and the average person lives on $0.28 per day. According to EWG and ActionAid, the total number of people living in extreme poverty rose by 25 million in 2008 during the last global food crisis. Since June 2010, the start of the current upward trend in prices, the World Bank estimates that 44 million people have fallen into extreme poverty.
One recommendation from EWG and ActionAid for developed countries and the United States in particular: Stop looking to biofuels as an energy option. In their view, “spending scarce taxpayer dollars to shift crops from food to biofuels at the expense of hungry people and already stressed resources like soil, water, and air is unsustainable.”
Image Credit: Map courtesy of the Environmental Working Group and ActionAid, and Food Price Index and Food Commodity Indices, extracted from Global Food Price Monitor, January 2011, courtesy of the Food and Agriculture Organization.
Sources: ActionAid International, BBC News, CNN, the Environmental Working Group, The European Union Times, Time, Voice of America, World Bank. -
Celebrating Ordinary Women Doing Extraordinary Things to Improve Gender Equality and Maternal Health Worldwide
›As coordinator of one of the few forums dedicated solely to maternal and reproductive health in Washington, D.C., I am particularly excited about this year’s 100th anniversary of International Women’s Day. This day commemorates ordinary women doing extraordinary things and acknowledges both the progress made and barriers still faced by women worldwide.
“When it comes to the boardroom meetings, government sessions, peace negotiations, and other assemblies where crucial decisions are made in the world, women are too often absent,” said Secretary of State Hillary Clinton during her remarks for International Women’s Day. “It is clear that more work needs to be done to consolidate our gains and to keep momentum moving forward.” [Video Below]
For mothers worldwide, some momentum has indeed been gained: Maternal mortality rates dropped from 526,000 a year in 1980 to 342,900 in 2008, according to a report by the Institute of Health Metrics and Evaluation at the University of Washington. In September of last year, a group of international leaders – including the UN and other multilateral institutions, donors, the business community, and NGOs – launched the “Global Strategy for Women and Children’s Health” and committed $40 billion to save the lives of 16 million women and children in developing countries.
At the sixth meeting of the Wilson Center’s Advancing Policy Dialogue on Maternal Health Series, Mayra Buvinic, sector director of the World Bank’s gender and development group, said: “Investing in women and girls is the right thing to do. It is not only fair for gender equality, but it is smart economics.” She said the World Bank has found that empowering women allows families to better endure economic crises and leads to better futures for their children as well.“When women have better education and health, mothers have greater household decision-making power and prioritize the well-being of their children,” said Buvinic. “In return, children have better educational attainment and are productive adults, building long-term economic growth.”
However, increased investment will only pay off when money is translated into action and stakeholders are held accountable for empowering women.
Since the inauguration of International Women’s Day 100 years ago, the low status of women in many parts of the world has remained relatively unchanged. Many women are still subject to male-dominated values that preclude them from making basic decisions about “who to marry, when to marry, when to have children, and how many children to have,” said Nafis Sadik, special envoy of the UN Secretary-General for HIV/AIDS, in an interview with the Population Reference Bureau. To change this, international development strategies need to prioritize improving gender equality, women’s status, and women’s voice in the political process.
I am grateful to be working in collaboration with extraordinary institutions such as the Maternal Health Task Force (MHTF) and United Nations Population Fund (UNFPA) who take real steps every day to help improve the lives of women and girls. In collaboration with these institutions, the Wilson Center’s Global Health Initiative is please to announce that it will partner with the African Population Health Research Center in Kenya to co-host a three-part dialogue series with local, regional, and national decision-makers on effective maternal health policies and programs. These in-country dialogue meetings will create a platform for field workers, policymakers, program managers, media, and donors to share research, disseminate lessons learned, and address concerns related to policy, institutional, and organizational capacity building for improved maternal health outcomes.
It is our goal that programs like these will continue to highlight neglected maternal health and issues and galvanize the community everyday – and not just on International Women’s Day.
Sources: Population Reference Bureau, UN, UN Population Fund, U.S. State Department.
Photo Credit: Afghan girl, courtesy of flickr user U.S Embassy Kabul Afghanistan, and Secretary Clinton’s video address courtesy of the U.S. State Department. -
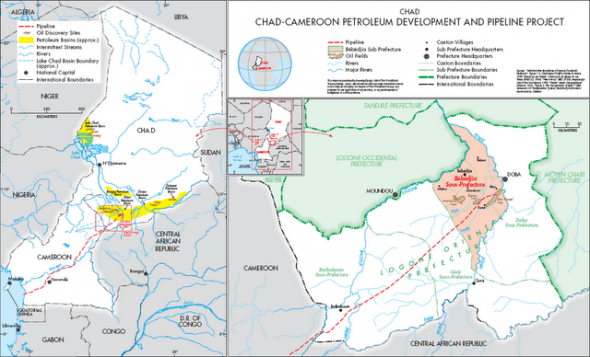
World Bank Pipeline Project in Chad Reveals Development Challenges
›This scholar spotlight was originally featured in the Wilson Center’s Centerpoint, February 2011.
In 2000, the governments of Chad and Cameroon teamed up with a three-company oil consortium, with the help of a World Bank loan, to begin building an oil pipeline. By 2003, oil revenues were flowing. This multi-billion dollar pipeline project, which transports oil from Chad through a 640-mile underground pipeline in neighboring Cameroon, is one of Africa’s largest public-private development projects.“Unfortunately, the project fell short on its social and development-oriented objectives,” said Wilson Center Fellow Lori Leonard.
One of the World Bank’s conditions on granting the loan was compensation for the involuntary resettlement this project would cause. However, Leonard said, the World Bank failed to understand, or take into account, social norms around land use and property relations.
“The compensation plan introduced the idea of private property but there was no institutional or legal framework for it,” she said. “This led to a flood of disputes over land and created breaks in the social safety net and societal fabric in Chad.” Uprooting people led to unprecedented problems, from the loss of land and livelihoods to disputes over compensation payments.
The reality was that in Chad, one of the world’s poorest countries, about a quarter-million people were affected. “People in the oilfield region, like people everywhere, are deeply attached to the place where they live – tied to their land,” Leonard said. Suddenly, their property became monetized. “They were asked to think differently about crops, trees, kitchen gardens, everyday objects,” as everything was given a monetary value.
But all the land was populated so there was nowhere to move to and no other trade or skill to easily adopt. “The pipeline project did not create a local economy, that could absorb people who became land poor,” she said.
The World Bank, which withdrew from the project in 2008 when Chad paid off the loan, accused Chad of misspending oil revenues, but that is just part of the story, said Leonard. The problem is not purely economic. “The economy is not outside of society,” Leonard said. “[This project] put a market value on everyday objects and that reshapes societal relations. And it raises the ethical question: ‘How do I live now?’”
In Chad, a largely agrarian economy, large parcels of land became oil fields, wells, and pumping and collection stations.
“Fields were taken or divided up into small fragments and the people wonder what to do next,” said Leonard. “Fertility rates are high and each successive generation will have to divide up [smaller and smaller amounts of] land. And there is already incredible pressure on the land now. The soil is poor but there is not enough [viable land] to leave land fallow.”
Leonard, who teaches at the Bloomberg School of Public Health at Johns Hopkins University, first came to Chad as a Peace Corps volunteer during the post-civil war reconstruction period in the late 1980s.
“From the time of independence, oil was the promise of the future,” she said. “The lessons the World Bank learned do not inspire confidence that it would be different the next time around. We need a fundamental shift in this development model.”
Dana Steinberg is the editor of the Wilson Center’s Centerpoint.
Photo Credit: “Chad-Cameroon Petroleum Pipeline Development Project,” courtesy of the World Bank. -
Of Revolutions, Regime Change, and State Collapse in the Arab World
›The original version of this article, by David Ottaway and Marina Ottaway, was published by the Wilson Center’s Middle East Program.
With breath-taking speed, massive popular protests across the Arab world have swept away two Arab strongmen and shaken half a dozen monarchies and republics to their core. But the Arab world has yet to witness any fundamental change in ruling elites and even less in the nature of governance.
Libya now seems poised to be the first country to see a true change in governance, thanks to Muammar Qaddafi’s megalomania and his amorphous jamahiriya (state of the masses). But such change may not have a happy ending. The damage Qaddafi has inflicted on his country is likely to extend well past his demise because he leaves behind a weak state without functioning institutions.
The uprisings sweeping across the Middle East have similar causes and share certain conditions: authoritarian and ossified regimes, economic hardship, growing contrast between great wealth and dire poverty, all worsened by the extraordinarily large number of young people who demand a better future. But the consequences will not be the same everywhere.
Tunisia and Egypt: A System Still in Place
Pro-democracy protesters in Tunisia and Egypt have been quick to use the word “revolution” to describe their astounding achievement in forcing Presidents Zine el Abidine Ben Ali and Hosni Mubarak from power after decades of rule. Tunisia’s “Jasmine Revolution” and Egypt’s “January 25 Revolution” have certainly injected the long-silenced voice of the people into the autocratic politics of the region. But they have not brought to the fore a new ruling class, system of governance, or the profound social and economic changes associated with the classical meaning of revolution. And it remains to be seen whether they will succeed in doing so.
Continue reading at the Wilson Center’s Middle East Program.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “Libya-protests_025,” courtesy of flickr user Crethi Plethi. -
Joan Castro on Integrated Population and Coastal Resource Management in the Southern Philippines
› In the southern Philippines, the innovative IPOPCORM program “worked in areas where there is high…marine biodiversity, high population, and high population momentum, which means…about 40 percent of the population are 15 years and below,” Joan Castro told ECSP in this interview. Castro, the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., recently spoke at the Wilson Center on the state of integrated development efforts in her country and elsewhere.
In the southern Philippines, the innovative IPOPCORM program “worked in areas where there is high…marine biodiversity, high population, and high population momentum, which means…about 40 percent of the population are 15 years and below,” Joan Castro told ECSP in this interview. Castro, the executive vice president of PATH Foundation Philippines, Inc., recently spoke at the Wilson Center on the state of integrated development efforts in her country and elsewhere.
From 2000-2006, IPOPCORM (which stands for “integrated population and coastal resource management”) sought to integrate population, health, and environment (PHE) development efforts in Philippine communities. They had four primary objectives, said Castro: 1) improve the reproductive health of the community members; 2) improve management of the coastal resources; 3) increase knowledge of the linkages between population, health, and the environment; and 4) increase the capacity of community leaders to advocate for these links.
“The aspect of livelihoods was very essential,” said Castro, especially for empowering women in the communities. Through family planning services and micro-credit finance initiatives, women were able to better space their pregnancies and contribute to household incomes, she said. In addition, by establishing locally managed, marine protected areas, IPOPCORM increased the protection of high biodiversity zones and improved the likelihood that there will be enough fish to feed future generations.
The “Pop Audio” series is also available as podcasts on iTunes. -
Carrying Capacity: Should We Be Aiming to Survive or Flourish?
›“In the eyes of many governments, population has, as we all know, been a rather uncomfortable topic for a number of years,” said Nobel Laureate Sir John Sulston, FRS, chair of the Institute for Science, Ethics, and Innovation at the University of Manchester and chair of the Royal Society’s People and the Planet working group. At an event at the Wilson Center on February 22, Sulston and his co-panelists, Martha Campbell, president of Venture Strategies for Health and Development, and Professor Parfait Eloundou-Enyegue of Cornell University, encouraged active debate on a range of population dynamics and their connections to economic, environmental, and political futures. [Video Below]
The Nexus of Population and Consumption
The dialogue between population and environmental communities has been pushed aside for many years but has lately been climbing its way back onto national agendas, said Sulston. However, the debate remains polarized. Scientists need to “sort out the facts as best we can” to help bring the communities together, he said. The Royal Society’s People and the Planet study, which will be completed by early 2012, will “provide policy guidance to decision-makers as far as possible” and “play our part in engendering constructive dialogue,” he said.
“What we should be aiming to do is to ensure that every individual on the planet can come to enjoy the same high quality of life whilst living within the Earth’s natural limits,” said Sulston. Instead of talking about the maximum number of people the Earth can hold, we should also focus on “the quality of life of those people,” he said. People are happier, healthier, and wealthier than ever before, according to human development indexes. But, Sulston said, 200 million women worldwide have an unmet need for family planning, ecosystems are degraded, biodiversity has decreased, and there are widespread shortages of food and water.
For centuries humanity has pursued a policy of “competitive growth,” both in population and consumption. But in preparation for the UN “Rio+20” summit on sustainable development in 2012, policymakers should be discussing “pathways to sustainability within the context of population,” said Sulston.
“Humanity needs to learn to act collectively and constructively in the face of these long-term and therefore rather elusive threats, just as we do rather well when we’re faced with immediate and tangible ones,” Sulston said. “So we need the best technology, but we need it in the context of a thoughtful society, and then we can both survive and happily flourish.”
A Demographic Crossroads
“No longer is population growth or population size the only issue of the day,” said Parfait Eloundou-Enyegue. “You have to worry about both population growth and population decline, you have to worry about immigration, you have to worry about aging, you have to worry about HIV and adult mortality, et cetera.”
Some people, Eloundou-Enyegue said, take this diversity of demographic issues as “grounds for complacency” by thinking they do not share in others’ problems. Yet, he said, population and ecology are areas where the risks are shared by all.
These challenges demand a “more comprehensive framework” that details the interactions between population, affluence, environment, technology, and inequality, said Eloundou-Enyegue. Tensions persist between these different areas, and breaking them will require “call[ing] on other qualities of the human spirit,” he said. The world is, Eloundou-Enyegue concluded, at a “demographic crossroads.”
The Timing of Declining Fertility
The key to ending the sensitivity to the issue of population growth is to “understand that this is about options: options for women and options for families,” said Martha Campbell. Strong attention and funding support can meet needs and lead to declining birth rates, as in the case of Kenya before the mid-1990s. But with the broader emphasis on reproductive health and concerns about coercion that followed the 1994 United Nations International Conference on Population and Development (ICPD) in Cairo, funding for family planning declined. As a result, Kenya’s fertility rates leveled off instead of continuing to decline, said Campbell, contributing to an upward revision of global population projections.
Campbell illustrated the impact of delays in achieving replacement-level fertility on the overall population size of individual states. In the case of Pakistan, for example, analysis by Venture Strategies for Health and Development and the African Institute for Development Policy projects that the country will have a total population of 350 million if replacement-level fertility is reached by 2020, and a population of almost 600 million if that same mark is reached by 2060.
Looking ahead to the “Rio+20” summit in 2012, Campbell emphasized the need for continued discussion about population growth and family planning. The silence on these issues after Cairo in 1994 and the subsequent global impact should serve as a warning for future generations, she said: “It is important for this next generation and the current generation to understand what happened so that it will never, ever happen again. The silence on population must not occur.”
Photo Credit: “Rush hour,” courtesy of flickr user Jekkone, and Pakistan fertility chart, courtesy of Martha Campbell and Venture Strategies. -
Sam Rugaba, PHE Champion
Encouraging Childhood Education and Birth Spacing as an Approach to Conservation
›This PHE Champion profile was produced by the BALANCED Project.
Fifty-one-year-old Sam Rugaba is a dedicated teacher who loves his job at the Bujengwe Community Primary School. The school is the result of a community-based project located in the Bujengwe Parish of the Kayonza subcounty in the Kanungu district of Uganda – just 18 kilometers from the Bwindi Impenetrable National Park (BINP). The biodiversity-rich BINP is home to many rare species including the endangered mountain gorilla. Sam is also a Conservation Through Public Health(CTPH) community volunteer and community conservation health worker. -
Top 10 Posts for February 2011
›Continuing turmoil in the Middle East helped keep Richard Cincotta’s political-demographic analysis on Tunisia’s chances of achieving democracy at the top this month, with Bryan McDonald’s piece on food price shocks, comments from demographers on “the age of revolution,” and a look at Pew’s latest iteration of its report on Muslim population growth following close behind:
1. Tunisia’s Shot at Democracy: What Demographics and Recent History Tell Us
2. Guest Contributor Bryan McDonald: Food Price Shocks and Instability Highlight Weaknesses in Governance and Markets
3. The Age of Revolution? Demography Experts Comment on Tunisia’s Shot at Democracy
4. Eye on Environmental Security: Mapping Muslim Population Growth
5. Book Preview: The Future Faces of War: Population and National Security6. Book Preview: Environmental Politics: Scale and Power, Shannon O’Lear, University of Kansas
7. Quantifying the Integration of Population, Health, and Environment in Development: When the Whole Is Greater Than the Sum of its Parts
8. India’s Maoists: South Asia’s “Other” Insurgency
9. Climate-Induced Migration: Catastrophe or Adaptation Strategy?
10. Guest Contributor Richard A. Matthew: Reading the QDDR: Civilian Power in a Complex, Uncertain World
Showing posts from category *Blog Columns.