-
Mapping Population and Climate Change
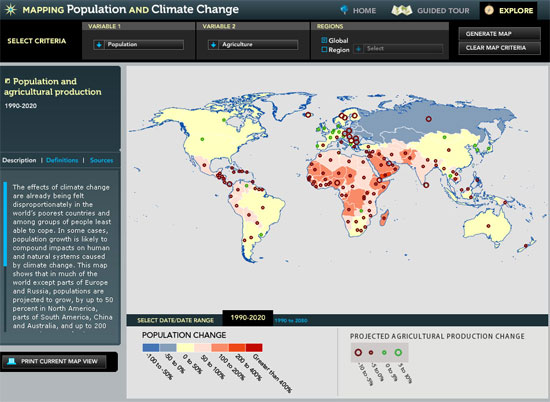
›Climate change, population growth, unmet family planning needs, water scarcity, and changes in agricultural production are among the global challenges confronting governments and ordinary citizens in the 21st century. With the interactive feature “Mapping Population and Climate Change” from Population Action International, users can generate maps using a variety of variables to see how these challenges relate over time.
Users can choose between variables such as water scarcity or stress, temperature change, soil moisture, population, agriculture, need for family planning, and resilience. Global or regional views are available, as well as different data ranges: contemporary, short-term projections (to the year 2035), and long-term projections (2090).
In the example featured above, the variables of population change and agricultural production change were chosen for the time period 1990-2020. Unfortunately, no country-specific data is given, though descriptions in the side-bar offer some helpful explanations of the selected trends.
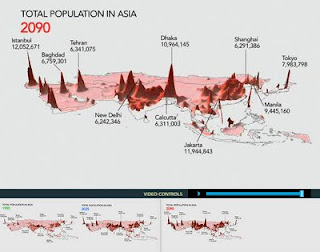
In addition, users can view three-dimensional maps of population growth in Africa and Asia for the years 1990, 2035, and 2090. These maps visually demonstrate the projected dramatic increases in population of these regions by the end of the century. According to the latest UN estimates, most of the world’s population growth will come from Africa and Asia due to persistently high fertility rates.
Image Credit: Population Action International. -
“The Second Front in the War on Terror”
USAID, Muslim Separatists, and Politics in the Southern Philippines
›For some years after the terrorist attacks of 9/11, the existence of violent Muslim separatists on the southern Philippine island of Mindanao gave U.S. officials significant cause for concern. In 2005, for example, the U.S. embassy charge d’affaires to the Philippines, Joseph Mussomeli, told reporters that “certain portions of Mindanao are so lawless, so porous…that you run the risk of it becoming like an Afghanistan situation. Mindanao is almost, forgive the poor religious pun, the new Mecca for terrorism.” During the Bush administration, officials referred to the region as a “second front” in the War on Terror: the region was once seen as a “new Afghanistan” that “threatened to become an epicenter of Al Qaeda.” [Video Below]
Nevertheless, as noted by Wilson Center Fellow Patricio Abinales at an Asia Program event on May 11, U.S. efforts to co-opt and pacify separatist guerrillas have proven remarkably successful in some areas of the islands. Some commentators have highlighted the role of the U.S. military in bringing a relative sense of security to troubled regions, noting that Mindanao presents a “future model for counterinsurgency.” However, Abinales’s research shows the military activities have had little effect, often because troops are stationed far from potential areas of conflict. Instead, it is the civilian side of the American presence that has dampened conflict in the war zones of the southern Philippines.
Abinales specifically explored the factors behind the success of the U.S. Agency for International Development’s (USAID) Growth with Equity in Mindanao (GEM) program in demobilizing and reintegrating 28,000 separatist guerrillas of the Moro National Liberation Front (MNLF), as well as the long-term political consequences of this accomplishment.
“Arms to Farms”
Usually, USAID programs are organized on the basis of grants for specific and limited projects. In contrast, GEM arose as a long-term umbrella organization that oversees the disbursement and management of American funding across a number of long-term projects. Coordinators are trained directly in Mindanao and are encouraged to “go native,” living in the area and becoming part of the community. GEM prioritizes cultural understanding, respect for community leaders, an appreciation of the important role that women play in local societies, and sensitivity to potential divisions within separatist groups and their security concerns vis-à-vis the Philippine government.
There has often been a general tendency for aid organizations to associate the demobilization of warring groups with disarmament. While Philippine officials on Mindanao have sometimes tried this approach, cash-for-guns amnesty schemes have opened up opportunities for corruption and have not been particularly effective. Understanding that one of the major concerns of guerrilla rebels is exploitation by corrupt government officials, GEM established an “Arms to Farms” scheme, whereby Muslim rebels are trained to engage in agriculture, but are not encouraged to put away their weapons. In this way, the program keeps potential guerrillas and Al Qaeda recruits busy with legitimate and peaceful economic activity, while it assuages their concerns about the threat from corrupt government officials, who may otherwise take the fruits of agricultural labor by force.
In fact, Abinales noted that one of the keys to GEM’s success is that the organization has never submitted to the official local authorities, and has largely been allowed a free reign by Manila to conduct its activities on Mindanao. It is precisely because the state has not been successful in delivering welfare regimes which provide stability to the area that GEM is seen as an alternate source of development and security in the region. Moreover, because of GEM’s activities, other American officials are allowed relatively free access, and are even welcomed into areas where the authority of the Philippine government holds no sway. Most of GEM’s activities are conducted with the MNLF, which has maintained its own official treaties and agreements with Manila since the 1970s. However, the American organization is beginning to enter the territory of the Moro Islamic Liberation Front, a splinter group of the MNLF that rejects relations with the national government outright, but one whose leaders are jealous of the development gains the MNLF has made under GEM.
Abinales was quick to point out that although GEM’s activities have been successful, they are tailor-made to specific circumstances. It is therefore difficult to present them as a generalized model that can be applied to other separatist conflicts. Nevertheless, Abinales’s work suggests that government agencies working on counterinsurgency efforts elsewhere might do well to examine the benefits of the flexible civilian approaches to conflict resolution formed with a deep understanding of the concerns of the specific communities involved.
Bryce Wakefield is program associate with the Asia Program at the Woodrow Wilson Center. -
How Does Organic Farming in the U.S. Affect Global Food Security?
›The feature story for last month’s Wilson Center newsletter, Centerpoint, was on the popular full-day conference “Rebuilding the U.S. Economy – One Heirloom Tomato at a Time,” hosted by the Program on America and the Global Economy in March. The conference focused on organic, local farming and the idea of creating “sustainable” food production that was healthier but also better for the economy than relying on imports from afar.
ECSP was asked to provide some international context for the discussion with a brief “Point of View.” I tried to paint a little bit of the big picture 21st century supply and demand story and give a sense of how today, globalization has helped linked everyone in this food security discussion:Dramatic events over the last year have shone a spotlight on the problem of global food security: massive fires in Russia, which reduced wheat supplies; famine and drought in Niger and Chad; and food price riots in the Middle East and elsewhere. These stresses come amid price spikes that echo the food crises of 2008 and reveal the linked nature of food security today and some of the fundamental challenges facing poor countries’ efforts to feed their growing populations.
What do you think: What’s the best way to inject the urgency that people looking at demographics and consumption rates around the world are feeling about global food security into a discussion about organic agriculture in the United States? Is there a tension between quality and quantity of food in the organic vs. agrobusiness debate that needs to be addressed in a global context? And what’s the role of policy in determining that balance?
In most countries, food insecurity is a symptom of poverty, poor governance, and/or poor infrastructure. For example, developed countries can often rebound from natural disasters relatively quickly. However, in drought-prone countries like Niger and Chad or flood victims like Pakistan and North Korea, such structural weaknesses leave them unable to bounce back as quickly from extreme events. This makes development efforts more difficult and can cause vulnerable countries to quickly become a burden on their neighbors or more prone to internal instability.
In the long term, reducing vulnerability in developing countries will be one of the most critical factors to ensuring global food security. But to meet the projected demand from increased consumption and continuing population growth, global yields must also increase.
The Green Revolution of the 1960-70s saved millions of lives by introducing heartier strains of rice and improving other staple crops in South and Southeast Asia, and most agree that a “Second Green Revolution” (whether or not it looks like the first) will likely be necessary. If so, the current tensions in the West over organic or sustainable practices versus agribusiness models will need to be reconciled in a way that can provide the most immediate help for the world’s hungry.
An important requirement, however, is that in a more resource-constrained world, these yields must be increased without destroying our future capacity. How we go about this, whether through traditional industry, organic techniques, or a mixture of both, will be one of the defining challenges of the 21st century. -
Marissa Mommaerts, Aspen Institute
Aspen Institute: The Revolution We Need in Food Security and Population
›April 27, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe first months of this year brought the second global food price crisis in just three years, with soaring food prices against a backdrop of bad weather, poor harvests, and political turmoil in North Africa and the Middle East. This year will see another milestone: the planet’s population is set to surpass seven billion, with most of the population growth occurring in countries least equipped to meet rising demands on agriculture and the environment. As part of its 7 Billion: Conversations that Matter roundtable series, the Aspen Institute’s Global Health and Development Program brought together three experts to discuss “The Revolution We Need in Food Security and Population” on April 12.
-
John Warburton, China Environment Series
UK Helping to Relieve Climate-Related Stress on China’s Agriculture
›The UK and China have been working together since 2001 to better understand how China is going to be impacted by climate change, particularly in the agriculture sector. But understanding must also lead to action, with adaptation needing to be integrated into the development process at both national and local levels. This work, which is ongoing, will increasingly provide a model for how to approach adaptation in other countries.
In my opinion, this work has also contributed to the realization among top-level Chinese officials that it is important to take global action on climate change as part of the international negotiation process; until very recently, most of the international engagement with China has focused on mitigation, with the result that the very real and urgent challenges that China faces in regards to its own adaptation needs have been sidelined.
Another Stressor for Chinese Agriculture
China’s Polices and Actions for Addressing Climate Change, issued in October 2008, state:The impacts of future climate change on agriculture and livestock industry will be mainly adverse. It is likely there will be a drop in the yield of three major crops — wheat, rice and corn; …enlarged scope of crop diseases and insect outbreaks; [and] increased desertification.
Even though assessing the likely impacts of climate change on crop yields is a complicated process, with some evidence showing that in some areas crops may benefit if agricultural technology can keep pace, the overall picture is grim for China.
Potential climate impacts are very worrying for a country which already faces so many other challenges within the agricultural sector, among them the facts that it has to feed nearly one quarter of the world’s population (1.3 billion people) with only seven percent of the world’s arable land; that it has only one-quarter of the world’s average per capita water distribution (one-tenth in large parts of northern China, which are heavily dependent upon agriculture); and that the agricultural land base is fast diminishing due to urbanization, industrialization, and the conversion of arable land to grasslands and forest.
Collaboration on Adaptation
Much of the evidence that supports the understanding of the likely adverse impacts on Chinese agriculture from climate change stems from collaborative work between the UK and China which started in 2001. A joint project, Impacts of Climate Change on Chinese Agriculture (ICCCA), has combined cutting-edge scientific research with practical development policy advice. Although national in scope, the project included pilot work to develop a stakeholder based approach to adaptation in the Ningxia region of northcentral China. ICCCA was successfully completed in December 2008. The UK-China collaboration is now continuing with a major new project which is going beyond agriculture and looking at additional socioeconomic sectors and geographic areas.
Continue reading in the China Environment Forum’s China Environment Series 11, from the Wilson Center. Other articles in the series can be found on CEF’s website.
John Warburton is a DFID senior environment adviser and is currently based in Beijing.
Photo Credit: “Field,” courtesy of flickr user totomaru. -
Biofuels: Food, Fuel, and Future?
›The Wilson Center’s Program on America and the Global Economy (PAGE) together with the Brazil Institute, have held a series of conferences focused on the field of biofuels and its impact both internationally and domestically. As part of the series, PAGE has published the results of a conference held last July on the current “state-of-play” for the biofuels industry in the United States.
In the brief, Biofuels: Food, Fuel, and Future?, C. Ford Runge and Robbin S. Johnson, of the University of Minnesota, and Calestous Juma, of Harvard University, provide context on the various federal mandates, subsidies, and policies that affect the U.S. biofuels market. They also present recommendations to improve what is now a not-so-new market, with the aim of reducing damaging effects on food prices and creating more international competition. The brief was edited by PAGE Director Kent H. Hughes and Elizabeth A. Byers.
Read more from PAGE on their blog, America and the Global Economy, and download the full brief and other PAGE publications from their website at the Wilson Center. -
Michael Kugelman, World Politics Review
The Gathering Global Food Storm
›March 28, 2011 // By Wilson Center StaffThe original version of this article, by Michael Kugelman, appeared on World Politics Review.
In India’s vibrant capital, food seems to be everywhere – from bustling fruit and vegetable markets and greasy kebab stalls, to sumptuous platters in rooftop restaurants and dilli ki chaat, Delhi’s ubiquitous street snacks. Poor street vendors and high-end chefs alike offer a multitude of culinary options to keep the city – and its array of visiting tourists, diplomats and business leaders – well-fed.
Yet behind this apparent culinary prosperity lies rampant food insecurity. Food-related inflation in India soared above 18 percent in December, sparking street protests over high onion prices. Today, food-related inflation remains high, at nearly 12 percent. In a nation where at least 250 million subsist on less than a dollar a day, even modest price rises have a devastating impact on incomes and livelihoods. Yet, when food prices fall, India’s small farmers suffer. Already crippled by debt and encumbered by water shortages, 200,000 of them have committed suicide over the past 13 years.
India is not alone in this story. Just a few years removed from the 2007-2008 global food crisis, the world is once again experiencing the telltale drivers of acute food insecurity: rising prices of both food and oil, low agricultural yields, destructive weather and unquenchable demand. Once again, nations are banning exports in an effort to keep prices down at home – even as such policies drive up food costs in global markets. The consequences can be seen from Bolivia, where top government officials are hoarding food in their homes, to the Middle East, where the rising cost of basic foodstuffs has become a rallying cry for revolution.
Continue reading on World Politics Review.
Michael Kugelman is a program associate for the Asia Program at the Wilson Center and lead editor of Hunger Pains: Pakistan’s Food Insecurity and Land Grab? The Race for the World’s Farmland.
Sources: The Economist, India’s Contemporary Security Challenges, CNN, The Washington Post.
Photo Credit: Adapted from “India’s Food Crisis,” courtesy of flickr user lecercle. -
Integrated Approach Helps “Model Farmers” Increase Productivity in Ethiopia
›March 24, 2011 // By Schuyler Null
To reach the village of Grar Gaber from Addis Ababa, you drive up over the Entoto Mountains overlooking the capital then motor down two hours of new Japanese-built highway to the town of Fiche. From there it’s 20 minutes on a broken dirt road across rocky hills. I was joined there by about 20 others from the PHE Ethiopia Consortium’s general assembly (see day one and day two coverage here) and Population Action International, to visit an integrated population, health, and environment (PHE) development program run by LEM Ethiopia.
Showing posts from category agriculture.